Abstract
We report the 4.9-Mb genome sequence of Citrobacter freundii strain GTC 09479, isolated from urine sample collected during the year 1983 at Gifu University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan. This draft genome consist of 4,899,578 bp with 51.62% G + C, 4,574 predicted CDSs, 72 tRNAs and 10 rRNAs.
Keywords: Citrobacter freundii strain GTC 09479, Illumina-HiSeq, NGS QC toolkit, Rapid annotations using subsystems technology (RAST)
| Specifications | |
|---|---|
| Organism/cell line/tissue | Citrobacter freundii |
| Strain(s) | GTC 09479 |
| Sequencer or array type | Sequencer; the Illumina-HiSeq 1000 |
| Data format | Processed |
| Experimental factors | Microbial strain |
| Experimental features | Draft genome sequence of Citrobacter freundii strain GTC 09479, assembly and annotation |
| Consent | n/a |
The Genus Citrobacter was first proposed by Werkman and Gillen [1]. At present, the genus Citrobacter consists of ten recognized species. The organism in this study is Citrobacter freundii strain GTC 09479, a Gram-negative, aerobic, short rods bacterium isolated from urine sample. Genomic DNA was extracted from a 48 hour old culture using ZR Fungal/Bacterial DNA MiniPrep™ as per the manufacturer's instructions. The genome of C. freundii strain GTC 09479 was sequenced using the Illumina-HiSeq 1000 paired-end technology produced a total of 17,547,712 paired-end reads (insert size of 350 bp) of 101 bp. We have used NGS QC toolkit v2.3 [2] to filter the data for high quality (Cut off read length for HQ = 70%, Cut off quality score = 20), vector/adaptor free reads for genome assembly. A total of 17,080,322 high quality, vector filtered reads (~ 345 × coverage) were used for assembly with Velvet 1.2.08 (at hash length of 53) [3]. The final assembly contains 31 contigs of total size 4,899,578 bp with an N50 contig length of 370.8 kb; the largest contig assembled measured 773.9 kb. The draft genome (31 contigs) comprising 4,899,578 nt was annotated with the help of RAST (rapid annotation using subsystem technology) server [4]. A total of 4574 predicted coding regions (CDSs), 10 rRNAs and 72 tRNAs were predicted.
Whole genome annotation available at the RAST server shows that strain GTC 09479 contains genes of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, TCA cycle, pentose phosphate pathway and lactose and galactose uptake and utilization. Some important genes like alkaline phosphatase (EC 3.1.3.1), galactosidase (alpha and beta both) [EC 3.2.1.22], alpha-xylosidase (EC 3.2.1.−), xylanase, xylulose kinase (EC 2.7.1.17), xyloside transporter XynT, catalase (EC 1.11.1.6) and ferroxidase (EC 1.16.3.1). Genes involved in decomposition of urea i.e. urea ABC transporter (ATPase protein UrtB, UrtC, UrtD and UrtE), urease accessory protein (UreD, UreE, UreF and UreG) and urease (alpha, beta and gamma subunit) [EC 3.5.1.5] are also present in the genome annotation. Polysaccharide export lipoprotein Wza gene is also found in the annotation.
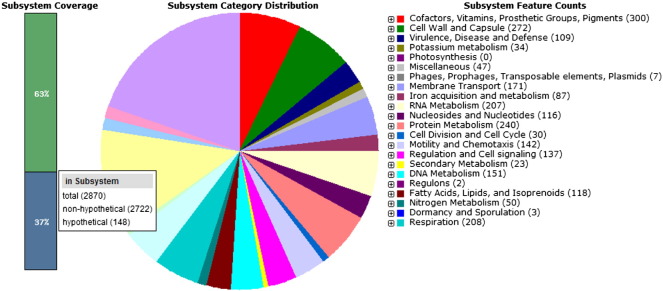
Sub-system distribution of C. freundii strain GTC 09479 (based on RAST annotation server).
Nucleotide sequence accession number
The C. freundii strain GTC 09479 whole genome shot gun (WGS) project has been deposited at DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank under the project accession AOMS00000000 of the project (01) has the accession number AOMS01000000 and consists of sequences AOMS01000001-AOMS01000031AOMS01000001AOMS01000031.
Direct link: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/AOMS01000000.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest on any work published in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by The Regional Innovation Strategy Support Programme (2012-Ministry of Education, Cultures, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan and the JSPS invitation fellowship(Fellow's ID No: L-12546) for research in Japan granted to Dr. Shanmugam Mayilraj). KK is supported by Hyogo Analysis Center Co., Ltd., Himeji, Japan and SK is supported by a research fellowship from Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR-INDIA). We thank C-CAMP (http://www.ccamp.res.in/) next generation genomics facility for help in obtaining the genome sequence. Genome assembly and annotation data can be downloaded from http://crdd.osdd.net/raghava/genomesrs/. This is IMTECH communication number 55/2013.
Contributor Information
Masahiro Takeo, Email: takeo@eng.u-hyogo.ac.jp.
Shanmugam Mayilraj, Email: mayil@imtech.res.in.
References
- 1.Werkman C.H., Gillen G.F. Bacteria producing trimethylene glycol. J. Bacteriol. 1932;23:167. doi: 10.1128/jb.23.2.167-182.1932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Patel R.K., Jain M. NGS QC Toolkit: a toolkit for quality control of next generation sequencing data. PLoS One. 2012;7:e30619. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0030619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zerbino D.R., Birney E. Velvet: algorithms for de novo short read assembly using de Bruijn graphs. Genome Res. 2008;18:821–829. doi: 10.1101/gr.074492.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Aziz R.K., Bartels D., Best A.A., DeJongh M., Disz T., Edwards R.A., Formsma K., Gerdes S., Glass E.M., Kubal M., Meyer F., Olsen G.J., Olson R., Osterman A.L., Overbeek R.A., McNeil L.K., Paarmann D., Paczian T., Parrello B., Pusch G.D., Reich C., Stevens R., Vassieva O., Vonstein V., Wilke A., Zagnitko O. The RAST Server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics. 2008;9:75. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-9-75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


