Abstract
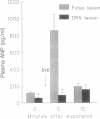
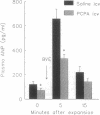
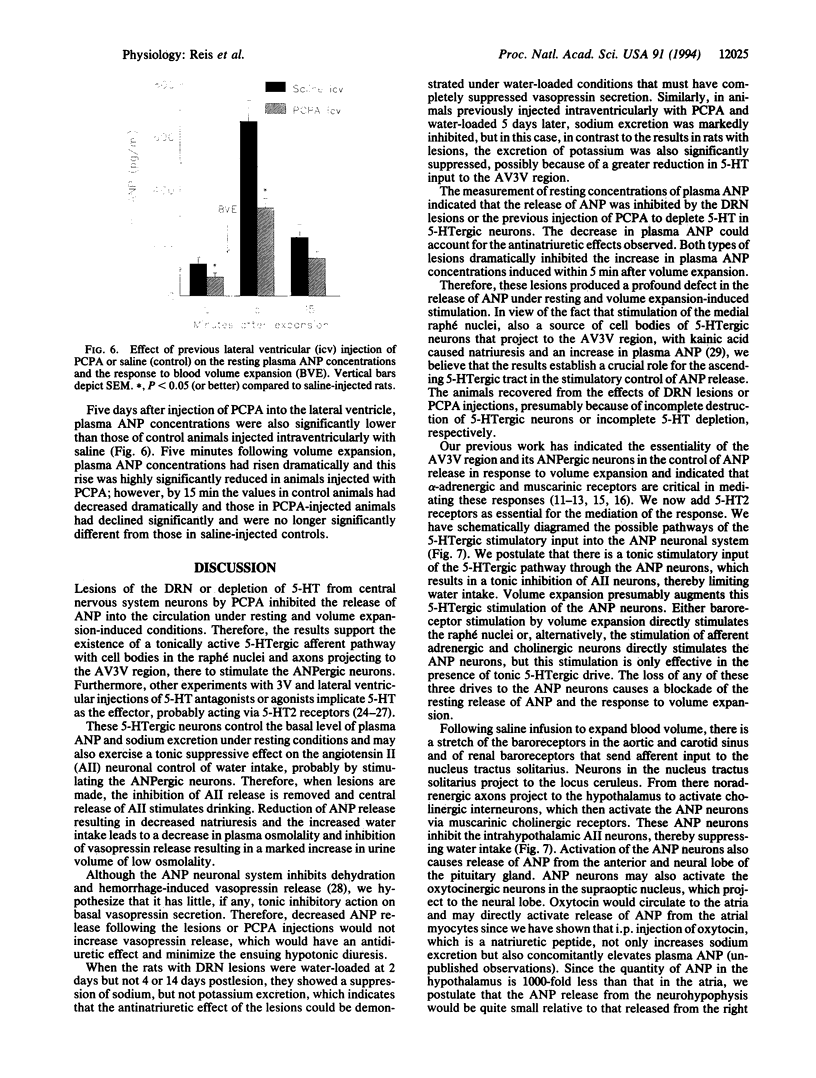
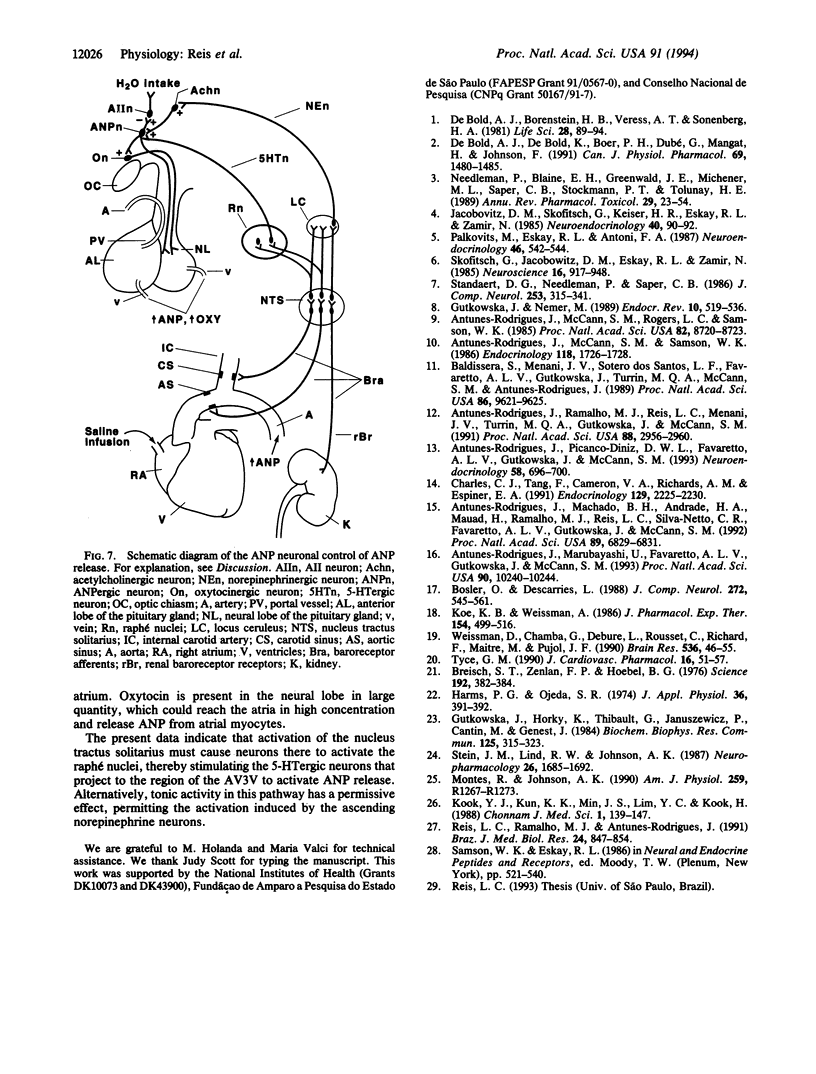
Results obtained in our laboratories have provided evidence for the participation of the hypothalamic atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) neuronal system in the regulation of water and electrolyte homeostasis. The anterior ventral third ventricular (AV3V) region, a site of the perikarya of the ANP neurons, receives important afferent input from ascending serotoninergic axons. We hypothesized that the ascending serotoninergic tract might be involved in control of the liberation of ANP. Therefore, electrolytic lesions were produced in the mesencephalic dorsal raphé nucleus (DRN), the site of perikarya of serotonin (5-HT) neurons whose axons project to the AV3V region. Rats with sham lesions constituted the control group. In a second group of animals, the serotoninergic system was depleted of 5-HT by lateral ventricular administration of p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA), an amino acid that causes depletion of 5-HT from the serotoninergic neurons. Control animals were injected with an equal amount of isotonic saline. The DRN lesions induced an increase of water intake and urine output beginning on the first day that lasted for 1 week after lesions were produced. There was a concomitant sodium retention that lasted for the same period of time. When water-loaded, DRN-lesioned and PCPA-injected animals showed diminished excretion of sodium, accompanied by a decrease in basal plasma ANP concentrations, and blockade of the increase in plasma ANP, which followed blood volume expansion by intraatrial injection of hypertonic saline. The results are interpreted to mean that ascending stimulatory serotoninergic input into the ANP neuronal system in the AV3V region produces a tonic stimulation of ANP release, which augments sodium excretion and inhibits water intake. Therefore, in the absence of this serotoninergic input following destruction of the serotoninergic neurons by DRN lesions or intraventricular injection of PCPA, an antinatriuretic effect is obtained that is associated with increased drinking, either because of sodium retention per se or removal of ANP-induced inhibition of release of the dipsogenic peptide, angiotensin II. The serotoninergic afferents also play an essential, stimulatory role in volume expansion-induced release of ANP and the ensuing natriuresis.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antunes-Rodrigues J., Machado B. H., Andrade H. A., Mauad H., Ramalho M. J., Reis L. C., Silva-Netto C. R., Favaretto A. L., Gutkowska J., McCann S. M. Carotid-aortic and renal baroreceptors mediate the atrial natriuretic peptide release induced by blood volume expansion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 1;89(15):6828–6831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.15.6828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antunes-Rodrigues J., Marubayashi U., Favaretto A. L., Gutkowska J., McCann S. M. Essential role of hypothalamic muscarinic and alpha-adrenergic receptors in atrial natriuretic peptide release induced by blood volume expansion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Nov 1;90(21):10240–10244. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.21.10240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antunes-Rodrigues J., McCann S. M., Rogers L. C., Samson W. K. Atrial natriuretic factor inhibits dehydration- and angiotensin II-induced water intake in the conscious, unrestrained rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8720–8723. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antunes-Rodrigues J., McCann S. M., Samson W. K. Central administration of atrial natriuretic factor inhibits saline preference in the rat. Endocrinology. 1986 Apr;118(4):1726–1728. doi: 10.1210/endo-118-4-1726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antunes-Rodrigues J., Picanco-Diniz D. W., Favaretto A. L., Gutkowska J., McCann S. M. Brain atrial natriuretic peptide neurons play an essential role in volume expansion-induced release of atrial natriuretic peptide and natriuresis. Neuroendocrinology. 1993 Dec;58(6):696–700. doi: 10.1159/000126611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antunes-Rodrigues J., Ramalho M. J., Reis L. C., Menani J. V., Turrin M. Q., Gutkowska J., McCann S. M. Lesions of the hypothalamus and pituitary inhibit volume-expansion-induced release of atrial natriuretic peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2956–2960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldissera S., Menani J. W., dos Santos L. F., Favaretto A. L., Gutkowska J., Turrin M. Q., McCann S. M., Antunes-Rodrigues J. Role of the hypothalamus in the control of atrial natriuretic peptide release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9621–9625. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosler O., Descarries L. Monoamine innervation of the organum vasculosum laminae terminalis (OVLT): a high resolution radioautographic study in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Jun 22;272(4):545–561. doi: 10.1002/cne.902720408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breisch S. T., Zemlan F. P., Hoebel B. G. Hyperphagia and obesity following serotonin depletion by intraventricular p-chlorophenylalanine. Science. 1976 Apr 23;192(4237):382–385. doi: 10.1126/science.130678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charles C. J., Tang F., Cameron V. A., Richards A. M., Espiner E. A. Intracerebroventricular atrial natriuretic factor (ANF) antiserum inhibits volume-induced ANF in sheep: evidence for the brain's regulation of ANF secretion. Endocrinology. 1991 Oct;129(4):2225–2230. doi: 10.1210/endo-129-4-2225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkowska J., Horký K., Thibault G., Januszewicz P., Cantin M., Genest J. Atrial natriuretic factor is a circulating hormone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):315–323. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutkowska J., Nemer M. Structure, expression, and function of atrial natriuretic factor in extraatrial tissues. Endocr Rev. 1989 Nov;10(4):519–536. doi: 10.1210/edrv-10-4-519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms P. G., Ojeda S. R. A rapid and simple procedure for chronic cannulation of the rat jugular vein. J Appl Physiol. 1974 Mar;36(3):391–392. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1974.36.3.391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobowitz D. M., Skofitsch G., Keiser H. R., Eskay R. L., Zamir N. Evidence for the existence of atrial natriuretic factor-containing neurons in the rat brain. Neuroendocrinology. 1985 Jan;40(1):92–94. doi: 10.1159/000124058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koe B. K., Weissman A. p-Chlorophenylalanine: a specific depletor of brain serotonin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1966 Dec;154(3):499–516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montes R., Johnson A. K. Efferent mechanisms mediating renal sodium and water excretion induced by centrally administered serotonin. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):R1267–R1273. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.1990.259.6.R1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Blaine E. H., Greenwald J. E., Michener M. L., Saper C. B., Stockmann P. T., Tolunay H. E. The biochemical pharmacology of atrial peptides. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:23–54. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.000323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits M., Eskay R. L., Antoni F. A. Atrial natriuretic peptide in the median eminence is of paraventricular nucleus origin. Neuroendocrinology. 1987 Dec;46(6):542–544. doi: 10.1159/000124878. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis L. C., Ramalho M. J., Antunes-Rodrigues J. Participation of the median raphe nucleus and central serotoninergic pathways in the control of water electrolyte excretion. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1991;24(8):847–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skofitsch G., Jacobowitz D. M., Eskay R. L., Zamir N. Distribution of atrial natriuretic factor-like immunoreactive neurons in the rat brain. Neuroscience. 1985 Dec;16(4):917–948. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(85)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standaert D. G., Needleman P., Saper C. B. Organization of atriopeptin-like immunoreactive neurons in the central nervous system of the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1986 Nov 15;253(3):315–341. doi: 10.1002/cne.902530304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. M., Lind R. W., Johnson A. K. Central serotonergic influences on renal electrolyte and water excretion. Neuropharmacology. 1987 Dec;26(12):1685–1692. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(87)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weissmann D., Chamba G., Debure L., Rousset C., Richard F., Maître M., Pujol J. F. Variation of tryptophan-5-hydroxylase concentration in the rat raphe dorsalis nucleus after p-chlorophenylalanine administration. II. Anatomical distribution of the tryptophan-5-hydroxylase protein and regional variation of its turnover rate. Brain Res. 1990 Dec 17;536(1-2):46–55. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J., Borenstein H. B., Veress A. T., Sonnenberg H. A rapid and potent natriuretic response to intravenous injection of atrial myocardial extract in rats. Life Sci. 1981 Jan 5;28(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90370-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bold A. J., Kuroski-de Bold M. L., Boer P. H., Dubé G., Mangat H., Johnson F. A decade of atrial natriuretic factor research. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Oct;69(10):1480–1485. doi: 10.1139/y91-222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]