Abstract
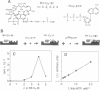
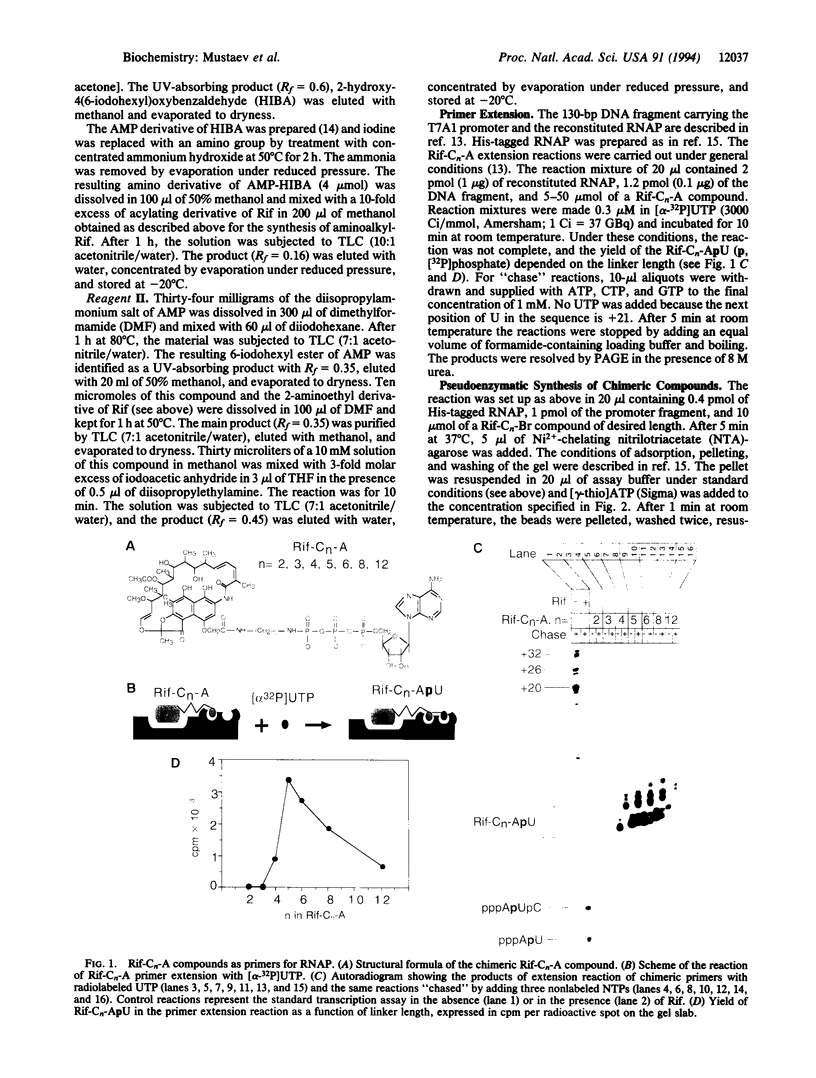
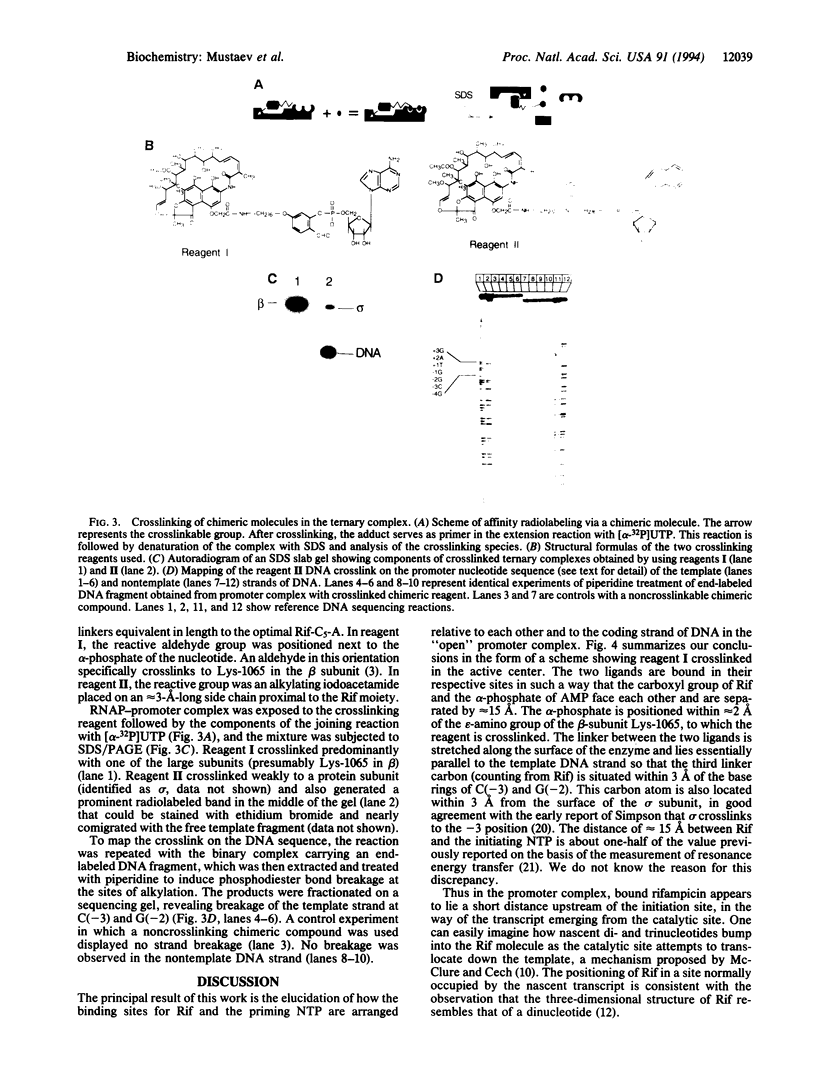
Spatial organization of the binding sites for the priming substrate, the template DNA, and the transcription inhibitor rifampicin (Rif) in Escherichia coli RNA polymerase (EC 2.7.7.6) was probed with chimeric compounds in which Rif is covalently attached to a ribonucleotide. The compounds bind to RNA polymerase in bifunctional manner and serve as substrates for RNA chain extension, yielding chains up to 8 nucleotides in length, with Rif linked to their 5' termini. These products act as potent inhibitors of normal transcription. Using the linker between the two ligands as ruler, we determined the distance between the sites for Rif and the priming nucleotide to be approximately 15 A. A reactive side group placed in the linker next to Rif crosslinks to the template strand of DNA at the -2 or -3 position of the promoter. Thus, bound Rif is juxtaposed to DNA immediately upstream of the start site, suggesting that Rif plugs the channel leading RNA out of the active center.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altmann C. R., Solow-Cordero D. E., Chamberlin M. J. RNA cleavage and chain elongation by Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase in a binary enzyme.RNA complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Apr 26;91(9):3784–3788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.9.3784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthony D. D., Goldthwait D. A., Wu C. W. Studies with the ribonucleic acid polymerase. II. Kinetic aspects of initiation and polymerization. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):246–256. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Lee J., Goldfarb A. Mapping of a contact for the RNA 3' terminus in the largest subunit of RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23932–23935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Sagitov V., Goldfarb A. Transcript cleavage factors from E. coli. Cell. 1993 Feb 12;72(3):459–466. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90121-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borukhov S., Sagitov V., Josaitis C. A., Gourse R. L., Goldfarb A. Two modes of transcription initiation in vitro at the rrnB P1 promoter of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1993 Nov 5;268(31):23477–23482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlin M. J. New models for the mechanism of transcription elongation and its regulation. Harvey Lect. 1992 1993;88:1–21. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chertov O. Iu, Obukhov A. N., Lipkin V. M. RNK-polimeraza-rifamitsin. Molekuliarnaia model' ingibirovaniia. Bioorg Khim. 1983 May;9(5):633–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grachev M. A., Kolocheva T. I., Lukhtanov E. A., Mustaev A. A. Studies on the functional topography of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Highly selective affinity labelling by analogues of initiating substrates. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Feb 16;163(1):113–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb10743.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grachev M. A., Lukhtanov E. A., Mustaev A. A., Zaychikov E. F., Abdukayumov M. N., Rabinov I. V., Richter V. I., Skoblov Y. S., Chistyakov P. G. Studies of the functional topography of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. A method for localization of the sites of affinity labelling. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Apr 1;180(3):577–585. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jin D. J., Gross C. A. Mapping and sequencing of mutations in the Escherichia coli rpoB gene that lead to rifampicin resistance. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 5;202(1):45–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90517-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashlev M., Martin E., Polyakov A., Severinov K., Nikiforov V., Goldfarb A. Histidine-tagged RNA polymerase: dissection of the transcription cycle using immobilized enzyme. Gene. 1993 Aug 16;130(1):9–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar K. P., Chatterji D. Resonance energy transfer study on the proximity relationship between the GTP binding site and the rifampicin binding site of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 16;29(2):317–322. doi: 10.1021/bi00454a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisitsyn N. A., Sverdlov E. D., Moiseyeva E. P., Danilevskaya O. N., Nikiforov V. G. Mutation to rifampicin resistance at the beginning of the RNA polymerase beta subunit gene in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;196(1):173–174. doi: 10.1007/BF00334112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. R., Cech C. L. On the mechanism of rifampicin inhibition of RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1978 Dec 25;253(24):8949–8956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustaev A., Kashlev M., Lee J. Y., Polyakov A., Lebedev A., Zalenskaya K., Grachev M., Goldfarb A., Nikiforov V. Mapping of the priming substrate contacts in the active center of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):23927–23931. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustaev A., Kashlev M., Zaychikov E., Grachev M., Goldfarb A. Active center rearrangement in RNA polymerase initiation complex. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 15;268(26):19185–19187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudler E., Goldfarb A., Kashlev M. Discontinuous mechanism of transcription elongation. Science. 1994 Aug 5;265(5173):793–796. doi: 10.1126/science.8047884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz W., Zillig W. Rifampicin inhibition of RNA synthesis by destabilisation of DNA-RNA polymerase-oligonucleotide-complexes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6889–6906. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinov K., Soushko M., Goldfarb A., Nikiforov V. RifR mutations in the beginning of the Escherichia coli rpoB gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Jul 25;244(2):120–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00283512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severinov K., Soushko M., Goldfarb A., Nikiforov V. Rifampicin region revisited. New rifampicin-resistant and streptolydigin-resistant mutants in the beta subunit of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 15;268(20):14820–14825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson R. B. The molecular topography of RNA polymerase-promoter interaction. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):277–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90047-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wehrli W., Staehelin M. The rifamycins--relation of chemical structure and action on RNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 May 20;182(1):24–29. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90516-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]