Abstract
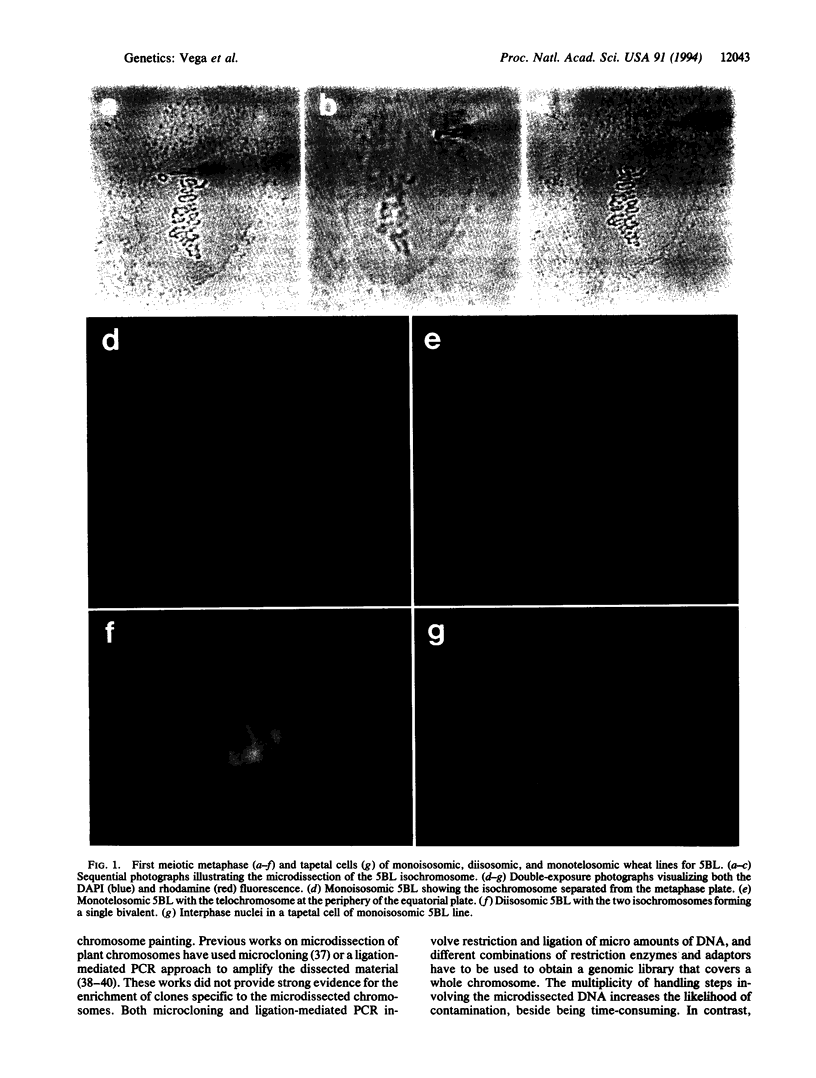
We report here on the successful painting of a specific plant chromosome within its own genome. Isochromosomes for the long arm of chromosome 5 of the wheat B genome (5BL) were microdissected from first meiotic metaphase spreads of a monoisosomic 5BL line of the common wheat Triticum aestivum cv. Chinese Spring. The dissected isochromosomes were amplified by degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR in a single tube reaction. The amplified DNA was used as a complex probe mixture for fluorescent in situ hybridization on first meiotic metaphase spreads of lines carrying 5BL as a distinctive marker. Hybridization signals were observed, specifically, along the entire 5BL. In some of the cells, labeling was also detected in two bivalents, presumably those of the 5B "homoeologues" (partial homologues) found in common wheat (5A and 5D). The probe also revealed discrete domains in tapetal nuclei at interphase, further supporting the probe's high specificity. These data suggest that chromosome and homoeologous group-specific sequences are more abundant in 5BL than genome-specific sequences. Chromosome-painting probes, such as the one described here for 5BL, can facilitate the study of chromosome evolution in polyploid wheat.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbo S., Dunford R. P., Miller T. E., Reader S. M., King I. P. Primer-mediated in situ detection of the B-hordein gene cluster on barley chromosome 1H. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 15;90(24):11821–11824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.24.11821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn S., Anderson J. A., Sorrells M. E., Tanksley S. D. Homoeologous relationships of rice, wheat and maize chromosomes. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Dec;241(5-6):483–490. doi: 10.1007/BF00279889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahn S., Tanksley S. D. Comparative linkage maps of the rice and maize genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 1;90(17):7980–7984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.17.7980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albani D., Côté M. J., Armstrong K. C., Chen Q., Segal A., Robert L. S. PCR amplification of microdissected wheat chromosome arms in a simple 'single tube' reaction. Plant J. 1993 Nov;4(5):899–903. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.04050899.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anamthawat-Jónsson K., Heslop-Harrison J. S. Isolation and characterization of genome-specific DNA sequences in Triticeae species. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Aug;240(2):151–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00277052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arumuganathan K., Martin G. B., Telenius H., Tanksley S. D., Earle E. D. Chromosome 2-specific DNA clones from flow-sorted chromosomes of tomato. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Mar;242(5):551–558. doi: 10.1007/BF00285278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann K. Genome size in mammals. Chromosoma. 1972;37(1):85–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00329560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedbrook J. R., Jones J., O'Dell M., Thompson R. D., Flavell R. B. A molecular description of telometic heterochromatin in secale species. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):545–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90529-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson-Smith M. A. Putting the genetics back into cytogenetics. Am J Hum Genet. 1991 Feb;48(2):179–182. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flavell R. B., O'Dell M., Hutchinson J. Nucleotide sequence organization in plant chromosomes and evidence for sequence translocation during evolution. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1981;45(Pt 2):501–508. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1981.045.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandbastien M. A. Retroelements in higher plants. Trends Genet. 1992 Mar;8(3):103–108. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(92)90198-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson J. P., Butler E., McIntyre C. L. Physical mapping of a low-copy DNA sequence in rye (Secale cereale L.). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1899–1902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulbert S. H., Richter T. E., Axtell J. D., Bennetzen J. L. Genetic mapping and characterization of sorghum and related crops by means of maize DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4251–4255. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung C., Claussen U., Horsthemke B., Fischer F., Herrmann R. G. A DNA library from an individual Beta patellaris chromosome conferring nematode resistance obtained by microdissection of meiotic metaphase chromosomes. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Nov;20(3):503–511. doi: 10.1007/BF00040609. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson J. Stomatal size in fossil plants: evidence for polyploidy in majority of angiosperms. Science. 1994 Apr 15;264(5157):421–424. doi: 10.1126/science.264.5157.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre C. L., Pereira S., Moran L. B., Appels R. New Secale cereale (rye) DNA derivatives for the detection of rye chromosome segments in wheat. Genome. 1990 Oct;33(5):635–640. doi: 10.1139/g90-094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meltzer P. S., Guan X. Y., Burgess A., Trent J. M. Rapid generation of region specific probes by chromosome microdissection and their application. Nat Genet. 1992 Apr;1(1):24–28. doi: 10.1038/ng0492-24. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G., Cheung W., Schwarzacher T., Flavell R. BIS 1, a major component of the cereal genome and a tool for studying genomic organization. Genomics. 1991 Jun;10(2):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(91)90334-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Graves J. A. Report of the committee on comparative gene mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1990;55(1-4):406–433. doi: 10.1159/000133025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Womack J. E., Lyons L. A., Moore K. J., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. Anchored reference loci for comparative genome mapping in mammals. Nat Genet. 1993 Feb;3(2):103–112. doi: 10.1038/ng0293-103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pich U., Houben A., Fuchs J., Meister A., Schubert I. Utility of DNA amplified by degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR (DOP-PCR) from the total genome and defined chromosomal regions of field bean. Mol Gen Genet. 1994 Apr;243(2):173–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00280314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Landegent J., Collins C., Fuscoe J., Segraves R., Lucas J., Gray J. Fluorescence in situ hybridization with human chromosome-specific libraries: detection of trisomy 21 and translocations of chromosome 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):9138–9142. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.9138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherthan H., Cremer T., Arnason U., Weier H. U., Lima-de-Faria A., Frönicke L. Comparative chromosome painting discloses homologous segments in distantly related mammals. Nat Genet. 1994 Apr;6(4):342–347. doi: 10.1038/ng0494-342. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanksley S. D., Bernatzky R., Lapitan N. L., Prince J. P. Conservation of gene repertoire but not gene order in pepper and tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6419–6423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenius H., Carter N. P., Bebb C. E., Nordenskjöld M., Ponder B. A., Tunnacliffe A. Degenerate oligonucleotide-primed PCR: general amplification of target DNA by a single degenerate primer. Genomics. 1992 Jul;13(3):718–725. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(92)90147-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telenius H., Pelmear A. H., Tunnacliffe A., Carter N. P., Behmel A., Ferguson-Smith M. A., Nordenskjöld M., Pfragner R., Ponder B. A. Cytogenetic analysis by chromosome painting using DOP-PCR amplified flow-sorted chromosomes. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Apr;4(3):257–263. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. L., Leitch A. R., Schwarzacher T., Heslop-Harrison J. S., Moore G. Construction of a chromosome-enriched HpaII library from flow-sorted wheat chromosomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 25;20(8):1897–1901. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.8.1897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]