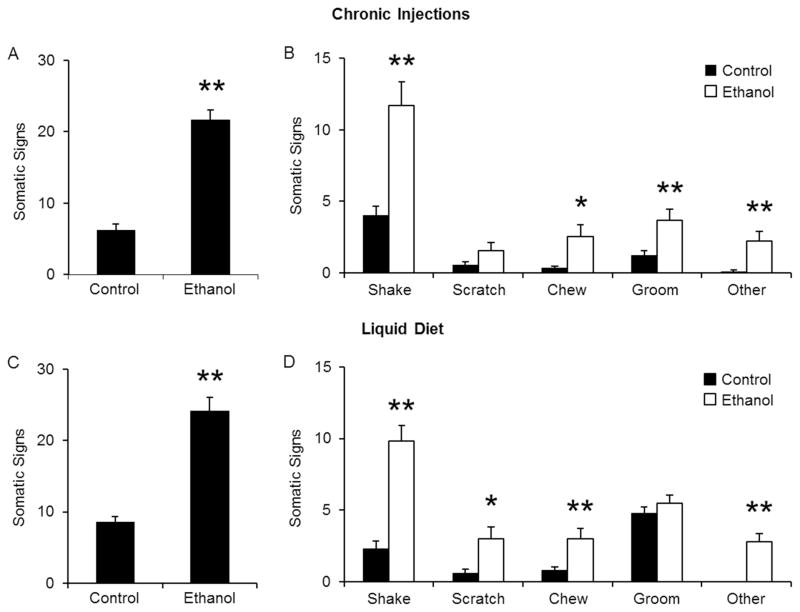
Figure 5. Ethanol withdrawal increases somatic signs.
Mice were observed for 20 min for the following signs: shaking, scratching, chewing, grooming, tail rattling, vocalizations, writhing, and cage scratching. Ethanol withdrawal produced a significant increase in the total number of somatic signs in both injection-treated (A) and liquid diet-treated mice (C). Changes were also observed when individual signs were examined (B, D). *p<0.05, **p<0.01 compared to control treated mice as measured by student t-test. N’s are 13, 12 for injections and 13, 13 for liquid diet.