Abstract
Introduction
Early administration of antibiotics for sepsis, and of fluid boluses and vasoactive agents for septic shock, is recommended. Evidence for this in children is limited.
Methods
The Alberta Sepsis Network prospectively enrolled eligible children admitted to the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit (PICU) with sepsis from 04/2012-10/2014. Demographics, severity of illness, and outcomes variables were prospectively entered into the ASN database after deferred consent. Timing of interventions were determined by retrospective chart review using a study manual and case-report-form. We aimed to determine the association of intervention timing and outcome in children with sepsis. Univariate (t-test and Fisher’s Exact) and multiple linear regression statistics evaluated predictors of outcomes of PICU length of stay (LOS) and ventilation days.
Results
Seventy-nine children, age median 60 (IQR 22–133) months, 40 (51 %) female, 39 (49 %) with severe underlying co-morbidity, 44 (56 %) with septic shock, and median PRISM-III 10.5 [IQR 6.0-17.0] were enrolled. Most patients presented in an ED: 36 (46 %) at an outlying hospital ED, and 21 (27 %) at the Children’s Hospital ED. Most infections were pneumonia with/without empyema (42, 53 %), meningitis (11, 14 %), or bacteremia (10, 13 %). The time from presentation to acceptable antibiotic administration was a median of 115.0 [IQR 59.0-323.0] minutes; 20 (25 %) of patients received their antibiotics in the first hour from presentation. Independent predictors of PICU LOS were PRISM-III, and severe underlying co-morbidity, but not time to antibiotics. In the septic shock subgroup, the volume of fluid boluses given in the first 2 hours was independently associated with longer PICU LOS (effect size 0.22 days; 95 % CI 0.5, 0.38; per ml/kg). Independent predictors of ventilator days were PRISM-III score and severe underlying co-morbidity. In the septic shock subgroup, volume of fluid boluses in the first 2 hours was independently associated with more ventilator days (effect size 0.09 days; 95 % CI 0.02, 0.15; per ml/kg).
Conclusion
Higher volume of early fluid boluses in children with sepsis and septic shock was independently associated with longer PICU LOS and ventilator days. More study on the benefits and harms of fluid bolus therapy in children are needed.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13054-015-1010-x) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Introduction
Severe sepsis in children is increasing, associated with significant mortality, and can be followed by significant neurocognitive sequelae [1–5]. The surviving sepsis guidelines aim to improve outcomes in children with severe sepsis, and recommend resuscitation for signs of shock with fluid boluses followed by vasoactive infusions, and appropriate antibiotics, each delivered within the first hour of presentation [6, 7]. Although a ubiquitous intervention, the evidence for dosing of fluid bolus therapy (FBT) in septic shock is of very low quality [8]. The evidence for FBT in children is predominantly based on two observational studies finding improved outcomes with aggressive FBT in children with septic shock [9, 10]. Other observational studies in children have concluded that bundles for recognition and early resuscitation of septic shock that include aggressive FBT may reduce mortality and hospital length of stay (LOS) [11–16]. However, the role of FBT resuscitation is unclear in most of these studies [11, 12, 14, 15], and others have limitations including having unusually high mortality [15, 16], an unclear definition of “early fluid resuscitation” [16], and retrospective patient identification [12–14, 16].
There is also evidence that each hour of delayed antibiotic therapy in adults with septic shock is associated with increasing mortality [17, 18]. Although this is theoretically compelling, there is only limited evidence for this early antibiotic administration in children with sepsis [19, 20]. Finally, the evidence for timing of vasoactive infusions is even more limited; in adults, there are data to suggest that starting at 1–6 h after onset of septic shock, or by 14 h after onset of septic shock, is associated with lower mortality [21, 22].
The Alberta Sepsis Network (ASN) prospectively enrolled a cohort of children with sepsis admitted to the only two pediatric intensive care units (PICUs) in Alberta, Canada. In this study we retrospectively reviewed the charts of children enrolled at the Stollery Children’s Hospital PICU to determine timing of antibiotic administration, and in the septic shock subgroup, timing of fluid boluses and vasoactive infusions. The objective of this study was to determine whether there is an association between timing of these interventions and outcomes in children with sepsis. We hypothesized that early antibiotics, volume, and vasoactive infusions would be associated with fewer days of ventilation and shorter LOS in the PICU.
Methods
Ethics
This study was approved by the Health Research Ethics Board of the University of Alberta (Pro00008797), and all enrolled patients gave deferred signed informed consent for participation. Deferred consent allowed enrolment as early as possible in PICU, followed by informed consent to use blood work and continue in the study within 3 days of inclusion.
The Alberta sepsis network
The ASN prospectively enrolled all eligible children up to age 17 y who were admitted to the two PICUs in Alberta with a diagnosis of sepsis, between April 2010 and March 2014. Sepsis was defined as systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) caused by a suspected or proven bacterial or fungal infection, with antibiotics prescribed, and an arterial and/or central venous line in place [23]. The requirement for an arterial and/or central venous line was to facilitate study blood work and justify deferred consent. Patients were excluded if they were not expected to survive ≥24 h, were refusing intubation or vasoactive infusions (i.e., palliative care), or if they had already had severe sepsis for ≥48 h (defined as sepsis with cardiovascular dysfunction, acute respiratory distress syndrome, or two other organ dysfunctions). Demographic, infection, and severity of illness variables (including pediatric logistic organ dysfunction (PELOD), and pediatric risk of mortality (PRISM)-III scores) were recorded prospectively [24, 25]. Site of infection was defined as that diagnosed by the attending medical team. Septic shock was defined as having an infusion of an inotrope or vasopressor (dopamine, dobutamine, epinephrine, norepinephrine, or milrinone) started (i.e., a new vasoactive agents started, or a dose change of a vasoactive agent) on the first calendar day of sepsis. This was a pragmatic definition, meant to identify children who almost certainly required FBT according to current guidelines. Severe underlying co-morbidity was defined as having a cardiac, neurological, or at least two other organ systems involved in a chronic disease prior to onset of sepsis.
Retrospective data collection
The Stollery Children’s Hospital has the only PICU serving Northern Alberta, much of Northern British Columbia, Yukon, the North West Territories and Nunavut, and is the largest referral center for cardiac surgery, extracorporeal life support, and solid organ transplantation for Western Canada. The charts of all enrolled patients in our PICU were reviewed to determine the following information: 1) time of presentation with sepsis: the admission time to the emergency department (ED), or if onset was on the hospital ward or PICU, the time when there was both new fever with a temperature >38.2 °C and a blood culture had been sent. Both fever and blood culture were required in the hospitalized PICU or ward patients because those patients can have recurrent fever, and performing a blood culture was thought to signify that a new episode of sepsis was suspected; and 2) antibiotic administration time: the antibiotic(s) administered fulfill the predefined criteria for the type of infection. This time is at the start of the infusion of intravenous antibiotic (or time when given enterally, for ciprofloxacin, metronidazole, or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole). If more than one antibiotic is required by the predefined criteria, the time is the start of the second antibiotic. In patients with septic shock, the following was also recorded: 1) fluid bolus time: time from presentation with sepsis to the first fluid bolus of at least 20 ml/kg (the usually suggested individual FBT volume) of isotonic intravenous fluid, including crystalloids (normal saline, Ringer’s lactate, plasmalyte), and/or colloids (5 % albumin, plasma); 2) volume of fluid boluses in first 2 h after presentation (to reflect a pragmatic definition of early FBT in resuscitating septic shock); 3) volume of fluid boluses given from presentation until first vasoactive infusion was started; and 4) vasoactive infusion time: time from presentation with sepsis to start of the first intravenous vasoactive infusion.
A case report form and study manual were created for data collection, definitions, and a predefined list of acceptable antibiotic(s) for each site of infection (Additional file 1). This list was based on the published Bugs & Drugs handbook [26], and expanded to include antibiotic choices that were not the local first choice, but that could be expected to be acceptable (i.e., antibiotics that are broader spectrum than required for that infection) [20]. The expanded list was prepared by one of the authors (ARJ) who is a pediatric infectious diseases specialist.
Statistics
Descriptive results are presented as proportions (percentages), mean (standard deviation), or median (IQR). The primary outcome was the association between timing of antibiotic administration and PICU LOS. In the septic shock subgroup, the main outcomes of interest were the association between timing of antibiotic administration and the amount of early fluid boluses, and PICU LOS. Predefined potential predictors of outcome were: 1) demographic variables: age (in months), and severe underlying co-morbidity; 2) severity of illness measures: admission day PRISM-III and PELOD scores; 3) timing variables in the entire cohort: time to appropriate antibiotic(s); appropriate antibiotic(s) given within 1 h; and 4) timing variables in the septic shock subgroup: time to vasoactive infusion; vasoactive infusion within 3 h; time to volume bolus of 20 ml/kg; volume of boluses given in first 2 h; volume boluses of ≤20 ml/kg in first 2 h; and volume of boluses given prior to the start of the first vasoactive infusion. Predefined outcomes were: 1) ventilator days; 2) PICU LOS in days; 3) delta-PELOD: the drop in PELOD from day 1 to 3 of PICU admission, as an indicator of improvement in organ dysfunction(s); and 4) mortality by 1 y after the index sepsis admission. Univariate comparisons were performed using the t test for independent samples and Fisher’s exact test. Multiple linear regression analysis was used to determine adjusted effect sizes for predictor variables of continuous outcomes. Multiple logistic regression was used to determine association between potential predictors with mortality by 1 y after the index sepsis admission. Age, PRISM-III score, and severe underlying co-morbidity were entered into all regression analyses, and we planned to enter time to antibiotic(s), volume boluses given in the first 2 h, and volume boluses given prior to vasoactive infusion into the regressions, unless univariate analysis suggested other timing variables were statistically significant and should replace these variables. For all analyses, a two-sided p value ≤0.05 was considered significant.
Results
Description of the cohort
Of 83 patients enrolled in the ASN database, 4 were excluded due to lost charts, with no way to determine timing of interventions. Of 79 children included, the median age was 60 (IQR 22–133) months, 40 (51 %) were female, 39 (49 %) had severe underlying co-morbidity, and the median PRISM III score on the day of sepsis was 10.5 (6.0–17.0). Mortalities by 1 y after the sepsis admission numbered 5/79 (6.3 %); only one of these occurred during the hospitalization, the others at 5, 6, 11, and 12 months after the admission. Most patients presented in an ED: 36 (46 %) at an outlying hospital ED, and 21 (27 %) at the our Children’s Hospital ED. Only 2 (3 %) had developed sepsis while on our Children’s Hospital wards, and 20 (25 %) while in the PICU. Most infections were pneumonia with/without empyema (n = 42, 53 %), meningitis (n = 11, 14 %), or bacteremia (n = 10, 13 %); other sites included intra-abdominal (n = 4, 5 %), urinary tract (n = 3, 4 %), cellulitis (n = 2, 3 %), and other (n = 7, 9 %). Median time from presentation to acceptable antibiotic administration was 115.0 (IQR 59.0–323.0) minutes; 20 patients (25 %) received their antibiotics during the first hour after presentation (Fig. 1). There were 44 patients (56 %) with septic shock, of whom 3 (6.8 %) died by 1 y after the sepsis admission.
Fig. 1.
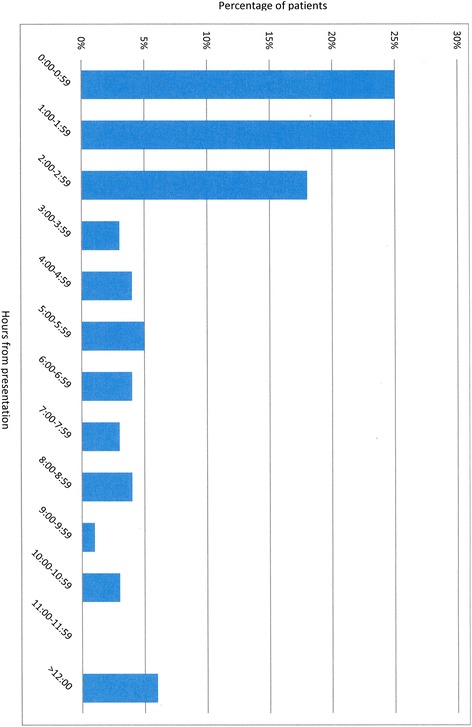
Time to administration of appropriate antibiotics after presentation with sepsis
Univariate analyses
The association between antibiotic administration within 1 h of presentation and demographics and outcomes is shown in Table 1. Early administration of antibiotics was associated with higher PRISM-III score, and longer PICU LOS. Among the patients with septic shock, the association between volume ≤20 ml/kg given in the first 2 h and demographics and outcomes is shown in Table 1. Administration of higher-volume boluses was associated with older age and higher PRISM-III score, with no difference in outcomes.
Table 1.
Univariate associations with early (within 1 h) appropriate antibiotic therapy and with early therapy with bolus volume over 20 ml/kg in children with sepsis and septic shock, respectively
| Variable | Abx 0–1 h | Abx >1 h | P value | ≤20 ml/kg in 2 h | >20 ml/kg in 2 h | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 20 | 59 | 26 | 18 | ||
| Age | 69 (60) | 79 (66) | 0.56 | 56 (52) | 120 (62) | 0.001 |
| PRISM | 15 (7) | 11 (7) | 0.03 | 11 (7) | 17 (8) | 0.006 |
| PELOD | 15 (8) | 17 (10) | 0.44 | 16 (9) | 21 (12) | 0.090 |
| Severe underlying disease | 11/20 (55 %) | 28/59 (47 %) | 0.61 | 15/26 (58 %) | 9/18 (50 %) | 0.76 |
| ΔPELOD | 3.4 (8.4) | 6.0 (11.6) | 0.35 | 3.2 (12.7) | 10.0 (9.9) | 0.067 |
| Ventilator days | 10.4 (9.2) | 7.1 (8.9) | 0.17 | 6.5 (4.8) | 9.1 (7.8) | 0.18 |
| PICU days | 19.5 (21.2) | 10.2 (10.1) | 0.01 | 10.7 (7.4) | 17.2 (22.4) | 0.17 |
Comparisons were performed using the t test for independent samples, and Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. Values are presented as mean (standard deviation) or proportion (percent). Abx appropriate antibiotic therapy, PRISM pediatric risk of mortality score, PELOD pediatric logistic organ dysfunction score, PICU pediatric ICU
The association between the potential predictors and dichotomous outcomes of ventilator days >7, PICU LOS >7 days, and delta-PELOD > median are shown in Table 2. FBT in those ventilated for at least 7 days was mean 36.7 (SD 34.9 ml/kg) compared to FBT in those ventilated for <7 days of mean 20.2 (SD 17.6), p = 0.05 (Table 2). The association between potential predictors and mortality by 1 y after admission are shown in Table 3. The FBT volume given in the first 2 h was similar according to outcomes of number of PICU days, delta PELOD from day 1 to 3, and mortality by 1 y (Tables 2 and 3).
Table 2.
Univariate analysis for predictors of prolonged ventilation and PICU length of stay, and for drop in PELOD score between days 1 to 3 of sepsis
| Variable | Ventilated 1–7 d | Ventilated >7 d | P value | PICU 0–7 d | PICU >7 d | P value | Δ PELOD ≤ median | Δ PELOD > median | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 45 | 19 | 33 | 46 | 40 | 35 | |||
| Age, months | 82 (62) | 62 (66) | 0.17 | 90 (64) | 67 (63) | 0.12 | 60 (65) | 94 (59) | 0.022 |
| PRISM | 10.4 (6.1) | 14.5 (8.6) | 0.02 | 10.3 (5.5) | 13.0 (8.3) | 0.11 | 11.5 (6.6) | 12.7 (7.5) | 0.45 |
| PELOD | 14.4 (8) | 20.7 (11) | 0.007 | 14.4 (8.6) | 17.8 (10.4) | 0.13 | - | - | |
| Severe underlying disease | 18/45 (40 %) | 19/29 (66 %) | 0.056 | 11/33 (33 %) | 28/46 (61 %) | 0.022 | 22/40 (55 %) | 14/35 (40 %) | 0.25 |
| Delta PELOD | 6.9 (8.4) | 2.7 (14.0) | 0.12 | 8.1 (8.4) | 3.4 (11.9) | 0.06 | - | - | |
| Time to Abx | 243 (306) | 235 (359) | 0.92 | 223 (296) | 243 (336) | 0.79 | 234 (329) | 239 (325) | 0.95 |
| Abx in first hour | 10/45 (22 %) | 9/29 (31 %) | 0.43 | 5/33 (15 %) | 15/46 (33 %) | 0.12 | 13/40 (33 %) | 7/35 (20 %) | 0.30 |
| Time to inotropes | 546 (395) | 428 (342) | 0.32 | 654 (368) | 428 (359) | 0.056 | 533 (421) | 493 (344) | 0.74 |
| Inotropes within 3 h | 6/24 (25 %) | 5/18 (28 %) | 0.66 | 2/15 (13 %) | 9/29 (31 %) | 0.27 | 6/20 (30 %) | 4/22 (18 %) | 0.34 |
| Time to 20 ml/kg volume | 225 (247) | 132 (179) | 0.22 | 212 (220) | 185 (252) | 0.75 | 233 (306) | 152 (167) | 0.32 |
| Volume in 2 h | 20.2 (17.6) | 36.7 (34.9) | 0.05 | 23 (18.9) | 29 (30.2) | 0.48 | 23 (23) | 33 (30) | 0.27 |
| Volume ≤20 ml/kg in 2 h | 16/24 (67 %) | 9/18 (50 %) | 0.35 | 10/15 (67 %) | 16/29 (55 %) | 0.53 | 14/20 (70 %) | 10/22 (45 %) | 0.098 |
| Volume to inotropes | 35.2 (32.1) | 46.7 (34.4) | 0.27 | 41 (35) | 39 (32) | 0.88 | 37 (28) | 46 (36) | 0.35 |
| Ventilator days | - | - | - | - | 10.3 (11.2) | 5.8 (5.1) | 0.036 | ||
| PICU days | - | - | - | - | 15.8 (17.8) | 9.7 (8.1) | 0.071 |
Comparisons were performed using the t test for independent samples, and Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. Values are given as mean (standard deviation) or proportion (percent); times are given in minutes. PICU pediatric ICU, PELOD pediatric logistic organ dysfunction score, Abx antibiotic therapy
Table 3.
Univariate associations with mortality by one year after the index sepsis admission
| Variable | Alive (n = 74) | Dead (n = 5) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to appropriate antibiotics, minutes | 247 (325) | 45 (30) | 0.17 |
| Time to inotrope, minutes | 495 (350) | 652 (711) | 0.74 |
| Volume in 2 h, ml/kg | 29 (27) | 7 (12) | 0.18 |
| Volume to inotrope, ml/kg | 42 (32) | 17 (29) | 0.20 |
| Age, months | 80 (65) | 25 (26) | 0.004 |
| PRISM | 11.8 (7.4) | 12.0 (5.9) | 0.96 |
| PELOD day 1 | 16.5 (9.7) | 15.2 (12.0) | 0.78 |
| Severe underlying co-morbidity | 35/74 (47 %) | 4/5 (80 %) | 0.20 |
Data were analyzed using the t test for independent samples and Fisher’s exact test as appropriate. Values are given as mean (standard deviation) or proportion (percent). PRISM pediatric risk of mortality score; PELOD pediatric logistic organ dysfunction score
Multiple regression analyses
Using multiple logistic regression analysis the independent predictors of ventilator days, PICU LOS, and delta-PELOD from day 1 to 3 are shown in Table 4, for both the overall cohort, and for the septic shock subgroup. Independent predictors of PICU LOS were PRISM-III score, and severe underlying co-morbidity, but not time to antibiotics. In the septic shock subgroup, the volume of fluid boluses given in the first 2 h was independently associated with longer PICU LOS (effect size 0.22 days; 95 % CI 0.5, 0.38, per ml/kg; p = 0.01). Independent predictors of ventilator days were PRISM-III score and severe underlying co-morbidity. In the septic shock subgroup, volume of fluid boluses in the first 2 h was also independently associated with more ventilator days (effect size 0.09 days; 95 % CI 0.02, 0.15, per ml/kg; p = 0.009). The only independent predictor of the delta-PELOD was age (effect size 0.042; 95 % CI 0.004, 0.080; p = 0.032), and in the septic shock subgroup there were no independent predictors. Using multiple logistic regression, there were no independent predictors for mortality by 1 y after admission in the entire cohort, or the septic shock subgroup.
Table 4.
Multiple linear regression analysis of independent predictors of outcomes in children with sepsis, and with septic shock
| Variable | PICU days | Ventilator days | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect size | 95 % CI | P value | Effect size | 95 % CI | P value | |
| PRISM | 0.64 | 0.23, 1.04 | 0.003 | 0.30 | 0.01, 0.59 | 0.04 |
| Age | 0.015 | - | 0.89 | −0.02 | - | 0.22 |
| Severe underlying disease | 7.27 | 1.34, 13.2 | 0.017 | 4.1 | - | 0.05 |
| Time to antibiotics, minutes | −0.010 | - | 0.92 | 0.002 | - | 0.45 |
| Model R2 | 15.2 % | 7.4 % | ||||
| Subgroup: septic shock | ||||||
| PRISM | 0.71 | 0.16, 1.25 | 0.012 | 0.24 | 0.03, 0.45 | 0.024 |
| Age | 0.05 | - | 0.30 | −0.22 | - | 0.12 |
| Severe underlying disease | 0.29 | - | 0.06 | 3.82 | 0.57, 1.07 | 0.023 |
| Time to antibiotics, minutes | -.067 | - | 0.63 | 0.049 | - | 0.72 |
| Volume in 2 h | 0.22 | 0.05, 0.38 | 0.010 | 0.09 | 0.02, 0.15 | 0.009 |
| Volume prior to inotropes | −0.19 | - | 0.38 | −0.13 | - | 0.54 |
| Model R2 | 23.4 % | 32.1 % | ||||
Analyses were performed using stepwise multiple linear regression, except for ventilator days in the entire cohort, where the variables were forced into the model. For the drop in pediatric logistic organ dysfunction score (PELOD) from day 1 to 3 of sepsis, the only independent predictor in the entire cohort was age (effect size 0.042; 95 % CI 0.004, 0.080; p = 0.032); for the septic shock subgroup, there were no independent predictors. PRISM pediatric risk of mortality score
Discussion
We retrospectively reviewed the timing of antibiotics, fluid, and vasoactive agents in children who were prospectively enrolled in the ASN database from the PICU for Northern Alberta. The main findings are the following. First, early timing of appropriate antibiotics was associated with longer PICU LOS on univariate analysis; however, it was not independently associated with PICU LOS, ventilator days, or change in PELOD score from day 1 to 3 in all included children (n = 79) or those with septic shock (n = 44). This is despite fairly wide variability in time to administration of appropriate antibiotics in the patients (median 115.0; IQR 59.0 − 323.0 minutes). Second, higher volume of fluid boluses in the first 2 h of presentation with sepsis was independently associated with longer PICU LOS and more ventilator days in children with septic shock. Of note, time to starting vasoactive agents was not associated with outcomes. Third, severity of illness (PRISM-III score) and severe underlying co-morbidity were independently associated with longer PICU LOS and more ventilator days. Fourth we did not identify independent predictors of mortality by 1 y after the index sepsis admission. These results are contrary to our initial hypotheses, which were that early appropriate antibiotics, and more volume bolus resuscitation, would be associated with improved outcomes.
The evidence for aggressive FBT has been questioned; two systematic reviews found that FBT may be harmful in children [27, 28]. These results are largely driven by the randomized controlled FEAST trial performed in the developing world in which FBT led to increased mortality from cardiovascular collapse, regardless of presentation syndrome or initial response to fluid therapy [29–32]. Two single-center retrospective observational studies suggest improved outcome in 9 and 24 children receiving more FBT for septic shock; however, these studies involved only 34 and 91 children with septic shock who had survived to PICU admission, were inotrope-dependent, and had a pulmonary artery catheter in situ [9, 10]. In the larger study, children who had signs of shock that resolved quickly were included in the appropriate fluid therapy group; the median fluid volumes given to children who died (32.9 ml/kg) were higher than those given to survivors (20 ml/kg) [10, 30]. Theoretically, FBT could cause harm by several mechanisms: rapid reduction in sympathetically mediated compensatory mechanisms; treatment-induced hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis; ischemia-reperfusion injury; fluid overload; and endothelial glycocalyx degradation [8, 31–33]. The endothelial glycocalyx has important functions in regulating vasomotor tone, oncotic gradient, endothelial porosity, microvascular thrombosis, oxidative stress, and endothelial adhesion of platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells [34]. It is surprising that no evidence exists for the effect of fluid boluses on outcomes more than a few hours after the bolus [8]. Contrary to the initial study by Rivers et al. [35], three large well-conducted randomized controlled trials of early goal-directed therapy (EGDT) in septic shock in adults suggest that the EGDT group received more fluid, inotrope, and blood transfusion than the standard care group, yet had either equivalent or worse outcomes [36–39]. Our finding that FBT was independently associated with longer PICU LOS and ventilator days, without improving the change in PELOD score between days 1 and 3 of septic shock, is compatible with these findings.
Alternatives to FBT may include slower infusion of volume, or earlier use of vasoactive infusions. The evidence for timing of vasoactive agents in children is weak. In adults, recent observational studies have found an improved survival if vasoactive agents were started in hours 1–6, or by hour 14 after onset of septic shock [21, 22]. The effect may be confounded by the level of blood pressure that is aimed for, and the evidence for how low a level of blood pressure is too low is being questioned [40]. Nevertheless, in our study, we found no association between timing of vasoactive agents and outcomes in children with septic shock. There are limitations to this finding, however. First, we did not determine the time of onset of hypotension, and that is likely a better indicator of when to start vasoactive agents than time from presentation with sepsis. Second, we had a small cohort of children with septic shock (n = 44). Third, because of the small cohort, we did not analyze outcomes according to individual agents; it is possible that one agent may be better than another in determining outcome, although this has not been shown in adult studies [41, 42].
Early administration of antibiotics has been associated with better outcome in septic shock and ICU patients with infection in many adult observational studies [17, 43–45]. Each hour of delayed antibiotic administration from onset of hypotension has been associated with increased mortality, although a recent study suggested this may only start after 4 h [17, 22]. This suggests a paradigm of septic shock where the bacterial load must be reduced early and quickly in order to prevent the sequelae of uncontrolled infection [18]. Recent data in children suggest early antibiotics are independently associated with improved outcomes in septic shock, particularly after a cutoff of 3 h [18, 19]. We did not find this effect in our cohort. Nevertheless, we do not suggest that antibiotics can be safely delayed in children with sepsis, due to limitations of our study.
This study has limitations. This is a single-center cohort of children admitted to PICU with sepsis and an arterial and/or central venous line who consented to enrollment in the ASN database in which extra blood work was performed for research purposes; thus, not all children with sepsis were included. It is possible that the inclusion criteria may have missed children who responded quickly to FBT, and thus, did not require PICU admission or an arterial/central line. The number of children included is modest (n = 79), particularly in the septic shock subgroup (n = 44). The septic shock subgroup included only children who went on vasoactive infusions, and may have missed children who had aggressive FBT alone. The onset of hypotension was not recorded, and therefore, we cannot determine timing of interventions from that event. Not all patients had microbiologically confirmed infection, and thus, it is possible that some of the patients may have had non-infection causes of severe systemic inflammatory response syndrome. The mortality in hospital (1/79, 1.3 %) and 1 y after the sepsis hospitalization (5/79, 6.3 %) was low, suggesting this may have been a less sick cohort of PICU sepsis patients. Finally, the timing of interventions was recorded retrospectively from chart review. Nevertheless, this is a cohort of PICU patients with clinically diagnosed sepsis and reflects the real-world situation in managing these patients. We pre-specified primary and secondary outcomes, and the analysis plan. In addition, the PRISM and PELOD scores of enrolled patients were comparable to published pediatric trials with higher mortality (Additional file 2: Table E1), suggesting the cohort comprised patients with high severity of illness.
Conclusions
Administration of a higher volume of early fluid boluses in children with sepsis and septic shock was independently associated with longer PICU LOS and ventilator days. There was no adverse effect on outcomes with administration of early appropriate antibiotics and early vasoactive infusions. This small single-center observational study cannot prove cause and effect, and is hypothesis-generating only. Our results are not sufficient to suggest a change in clinical practice. Nevertheless, we believe that the results suggest that more study on the benefits and harms of FBT in children with sepsis are needed to better inform management.
Key messages
Early timing of appropriate antibiotics was not independently associated with PICU LOS, ventilator days, or change in PELOD score from days 1 to 3 in all included children (n = 79) or those with septic shock (n = 44)
Higher volume of fluid boluses in the first 2 h of presentation with sepsis was independently associated with longer PICU LOS and more ventilator days in children with septic shock
More study on the benefits and harms of fluid bolus therapy in children is needed, as there are multiple theoretical reasons why fluid boluses may be harmful
Acknowledgements
The Alberta Sepsis Network was funded by Alberta Innovates-Health Solutions. The sponsors had no role in any of the design and conduct of the study; collection, management, analysis, and interpretation of the data; and preparation, review, or approval of the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- ASN
Alberta Sepsis Network
- ED
emergency department
- EGDT
early goal-directed therapy
- FBT
fluid bolus therapy
- IQR
interquartile range
- LOS
length of stay
- PELOD
pediatric logistic organ dysfunction score
- PICU
pediatric intensive care unit
- PRISM
pediatric risk of mortality score
- SIRS
systemic inflammatory response syndrome
Additional files
The case report form and study manual for the chart review. This file provides the definitions used, and the acceptable antibiotics for the different types of infection. (PDF 2280 kb)
Comparison of patient severity to recent studies of children in intensive care. This file describes the severity of illness in the Alberta Sepsis Network (ASN) cohort and its comparability to several recent studies of critically ill children. (PDF 1529 kb)
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
ARJ contributed to conception and design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, drafted the article, and had final approval of the version to be published. BMvP contributed to design, acquisition of data, analysis and interpretation of data, revising the article critically for important intellectual content, and had final approval of the version to be published. CS contributed to acquisition of data, interpretation of data, revising the article critically for important intellectual content, and had final approval of the version to be published. GG contributed to design, analysis and interpretation of data, revising the article critically for important intellectual content, and had final approval of the version to be published. ARJ had full access to all of the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis. ARJ conducted and is responsible for the data analysis. All authors have read and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Contributor Information
Bregje M. van Paridon, Email: bmvanparidon@gmail.com
Cathy Sheppard, Email: cathy.sheppard@albertahealthservices.ca.
Garcia Guerra G, Email: gonzalo.guerra@albertahealthservices.ca.
Ari R. Joffe, Phone: 780 2485435, Email: ari.joffe@albertahealthservices.ca
References
- 1.Watson RS, Carcillo JA, Linde-Zwirble WT, Clermont G, Lidicker J, Angus DC. The epidemiology of severe sepsis in children in the United States. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2003;167:695–701. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200207-682OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hartman ME, Linde-Zwirble W, Angus DC, Watson RS. Trends in the epidemiology of pediatric severe sepsis. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013;14:686–93. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3182917fad. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Dombrovskiy VY, Martin AA, Sunderram J, Paz HL. Rapid increase in hospitalization and mortality rates for severe sepsis in the United States: A trend analysis from 1993 to 2003. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1244–50. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000261890.41311.E9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Als LC, Nadel S, Cooper M, Pierce CM, Sahakian BJ, Garralda ME. Neuropsychologic function three to six months following admission to the PICU with meningoencephalitis, sepsis, and other disorders: a prospective study of school-aged children. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:1094–103. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e318275d032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Farris RWD, Weiss NS, Zimmerman JJ. Functional outcomes in pediatric severe sepsis: further analysis of the researching severe sepsis and organ dysfunction in children: A Global Perspective Trial. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2013;14:835–42. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0b013e3182a551c8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Rhodes A, Annane D, Gerlach H, Opal SM, et al. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2013;41:580–637. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31827e83af. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brierley J, Carcillo JA, Choong K, Cornell T, DeCaen A, Deymann A, et al. Clinical practice parameters for hemodynamic support of pediatric and neonatal septic shock: 2007 update from the American College of Critical Care Medicine. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:666–88. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31819323c6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Glassford NJ, Eastwood GM, Bellomo R. Physiological changes after fluid bolus therapy in sepsis: a systematic review of contemporary data. Crit Care. 2014;18:696. doi: 10.1186/s13054-014-0696-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Carcillo JA, Davis AL, Zaritsky A. Role of early fluid resuscitation in pediatric septic shock. JAMA. 1991;266:1242–5. doi: 10.1001/jama.1991.03470090076035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Han YY, Carcillo JA, Dragotta MA, Bills DM, Watson RS, Westerman ME, et al. Early reversal of pediatric-neonatal septic shock by community physicians is associated with improved outcome. Pediatrics. 2003;112:793–9. doi: 10.1542/peds.112.4.793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Inwald DP, Tasker RC, Peters MJ, Nadel S. Emergency management of children with severe sepsis in the United Kingdom: the results of the Paediatric Intensive Care Society sepsis audit. Arch Dis Child. 2009;94:348–53. doi: 10.1136/adc.2008.153064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Larsen GY, Mecham N, Greenberg R. An emergency department septic shock protocol and care guideline for children initiated at triage. Pediatrics. 2011;127:e1585–92. doi: 10.1542/peds.2010-3513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Paul R, Neuman MI, Monuteaux MC, Melendez E. Adherence to PALS sepsis guidelines and hospital length of stay. Pediatrics. 2012;130:e273–80. doi: 10.1542/peds.2012-0094. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Paul R, Melendez E, Stack A, Capraro A, Monuteaux M, Neuman MI. Improving adherence to PALS septic shock guidelines. Pediatrics. 2014;133:e1358–66. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-3871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sankar J, Sankar MJ, Suresh CP, Dubey NK, Singh A. Early goal-directed therapy in pediatric septic shock: comparison of outcomes “with” and “without” intermittent superior venacaval oxygen saturation monitoring: a prospective cohort study. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2014;15:e157–67. doi: 10.1097/PCC.0000000000000073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Oliveira CF, de Nogueira Sa FR, Oliveira DSF, Gottschald AFC, Moura JDG, Shibata ARO, et al. Time- and fluid-sensitive resuscitation for hemodynamic support of children in septic shock. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2008;24:810–5. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e31818e9f3a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kumar A, Roberts D, Wood KE, Light B, Parrillo JE, Sharma S, et al. Duration of hypotension before initiation of effective antimicrobial therapy is the critical determinant of survival in human septic shock. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:1589–96. doi: 10.1097/01.CCM.0000217961.75225.E9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kumar A. An alternate pathophysiologic paradigm of sepsis and septic shock: implications for optimizing antimicrobial therapy. Virulence. 2014;5:80–97. doi: 10.4161/viru.26913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fletcher M, Hodgkiss H, Zhang S, Browning R, Hadden C, Hoffman T, et al. Prompt administration of antibiotics is associated with improved outcomes in febrile neutropenia in children with cancer. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2013;60:1299–306. doi: 10.1002/pbc.24485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Weiss SL, Fitzgerald JC, Balamuth F, Alpern ER, Lavelle J, Chilutti M, et al. Delayed antimicrobial therapy increases mortality and organ dysfunction duration in pediatric sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:2409–17. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Beck V, Chateau D, Bryson GL, Pisipati A, Zanotti S, Parrillo JE, et al. Timing of vasopressor initiation and mortality in septic shock: a cohort study. Crit Care. 2014;18:R97. doi: 10.1186/cc13868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Waechter J, Kumar A, Lapinsky SE, Marshall J, Dodek P, Arabi Y, et al. Interaction between fluids and vasoactive agents on mortality in septic shock: a multicenter, observational study. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:2158–68. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Goldstein B, Giroir B, Randolph A, and the members of the International Consensus Conference on Pediatric Sepsis International pediatric sepsis consensus conference: definitions for sepsis and organ dysfunction in pediatrics. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2005;6:2–8. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000149131.72248.E6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Leteurtre S, Martinot A, Duhamel A, Proulx F, Grandbastien B, Cotting J, et al. Validation of the paediatric logistic organ dysfunction (PELOD) score: prospective, observational, multicentre study. Lancet. 2003;362:192–7. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13908-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pollack MM, Patel KM, Ruttimann UE. PRISM III: an updated pediatric risk of mortality score. Crit Care Med. 1996;24:743–52. doi: 10.1097/00003246-199605000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Blondel-Hill E, Fryters S. Bugs and Drugs: An Antimicrobial/Infectious Diseases Reference. 5. Edmonton, Alberta, Canada: Alberta Health Services; 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ford N, Hargreaves S, Shanks L. Mortality after fluid bolus in children with shock due to sepsis or severe infection: a SR and MA. PLoS One. 2012;7:e43953. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Opiyo N, Molyneux E, Sinclair D, Garner P, English M. Immediate fluid management of children with severe febrile illness and signs of impaired circulation in low-income settings: a contextualized SR. BMJ Open. 2014;4:e004934. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-004934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Maitland K, Kiguli S, Opoka RO, Engoru C, Olupot-Olupot P, Akech SO, et al. Mortality after fluid bolus in African children with severe infection. NEJM. 2011;364:2483–95. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1101549. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Maitland K, George EC, Evans JA, Kiguli S, Olupot-Olupot P, Akech SO, et al. Exploring mechanisms of excess mortality with early fluid resuscitation: insights from the FEAST trial. BMC Med. 2013;11:68. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Myburgh J, Finfer S. Causes of death after fluid bolus resuscitation: new insights from FEAST. BMC Med. 2013;11:67. doi: 10.1186/1741-7015-11-67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Brown SGA. Fluid resuscitation for people with sepsis: it’s time to challenge our basic assumptions. BMJ. 2014;349:g4611. doi: 10.1136/bmj.g4611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Inwald DP, Butt W, Tasker RC. Fluid resuscitation of shock in children: what, whence and whither? Intensive Care Med. 2015;41:1457–9. doi: 10.1007/s00134-015-3905-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Chelazzi C, Billa G, Mancinelli P, De Gaudio AR, Adembri C. Glycocalyx and sepsis-induced alterations in vascular permeability. Crit Care. 2015;19:26. doi: 10.1186/s13054-015-0741-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Rivers E, Nguyen B, Haystad S, Ressler J, Muzzin A, Knoblich B, et al. Early goal-directed therapy in the treatment of severe sepsis and septic shock. NEJM. 2001;345:1368–77. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa010307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Perner A, Myburgh J. Ten ‘short-lived’ beliefs in intensive care medicine. Intensive Care Med. 2015. Epub 2015 Mar 13. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 37.Mouncey PR, Osborn TM, Power S, Harrison DA, Sadique MZ, Grieve RD, et al. Trial of early goal-directed resuscitation for septic shock. NEJM. 2015;372:1301–11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1500896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.The ProCESS Investigators A randomized trial of protocol-based care for early septic shock. NEJM. 2014;370:1683–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1401602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.The ARISE Investigators and the ANZICS Clinical Trials Group Goal-directed resuscitation for patients with early septic shock. NEJM. 2014;371:1496–506. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1404380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Asfar P, Meziani F, Hamel J-F, Grelon F, Megarbane B, Anguel N, et al. High versus low blood-pressure target in patients with septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1583–93. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1312173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.De Backer D, Biston P, Devriendt J, Madl C, Chochrad D, Aldecoa C, et al. Comparison of dopamine and norepinephrine in the treatment of shock. NEJM. 2010;362:779–89. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0907118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Annane D, Vignon P, Renault A, Bollaert P-E, Charpentier C, Martin C, et al. Norepinephrine plus dobutamine versus epinephrine alone for management of septic shock: a randomized trial. Lancet. 2007;370:676–84. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61344-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Puskarich M, Trzeciak S, Shapiro NI, Arnold RC, Horton JM, Studnek JR, et al. Association between timing of antibiotic administration and mortality from septic shock in patients treated with a quantitative resuscitation protocol. Crit Care Med. 2011;39:2066–71. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e31821e87ab. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gaieski DF, Mikkelsen ME, Band RA, Pines JM, Massone R, Furia FF, et al. Impact of time to antibiotics on survival in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock in whom early goal-directed therapy was initiated in the emergency department. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:1045–53. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181cc4824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ferrer R, Martin-Loeches I, Phillips G, Osborn TM, Townsend S, Dellinger RP, et al. Empiric antibiotic treatment reduces mortality in severe sepsis and septic shock from the first hour: results from a guideline-based performance improvement program. Crit Care Med. 2014;42:1749–55. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


