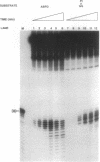
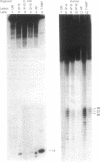
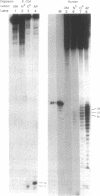
Abstract
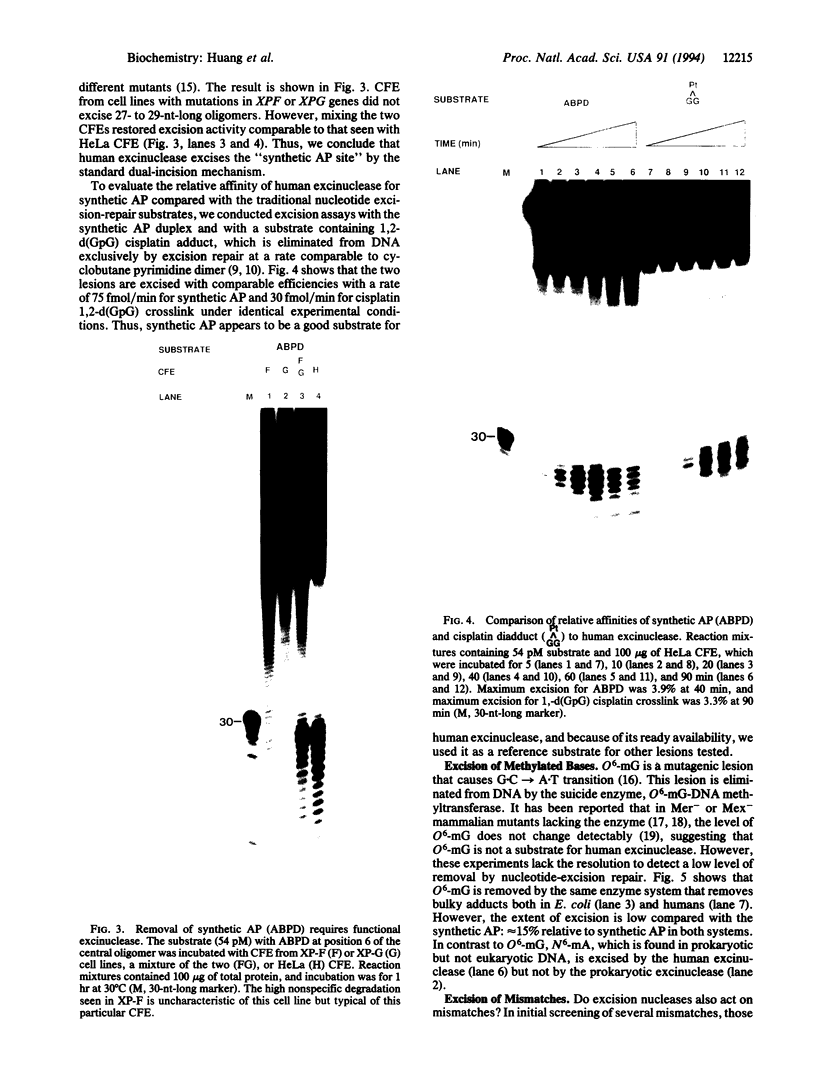
Nucleotide-excision repair is the repair system for removing bulky lesions from DNA. Humans deficient in this repair pathway suffer from xeroderma pigmentosum (XP), a disease characterized by photodermatoses, including skin cancers. At the cellular level, XP patients fail to remove cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers and pyrimidine(6-4)pyrimidone photoproducts induced by UV light, as well as other bulky DNA lesions caused by various genotoxic agents. XP cells are not particularly sensitive to ionizing radiation or to alkylating agents that cause mostly nonbulky DNA lesions. Therefore, it has generally been assumed that the human nucleotide-excision repair enzyme (excinuclease) is specific for bulky adducts. To determine the substrate range of human excinuclease we used the highly sensitive excision assay and tested bulky adducts, synthetic apurinic/apyrimidinic sites, N6-methyladenine, O6-methylguanine, and mismatches as potential substrates. We found that all of these "lesions" were removed by human excinuclease, although with vastly different efficiencies.
Full text
PDF
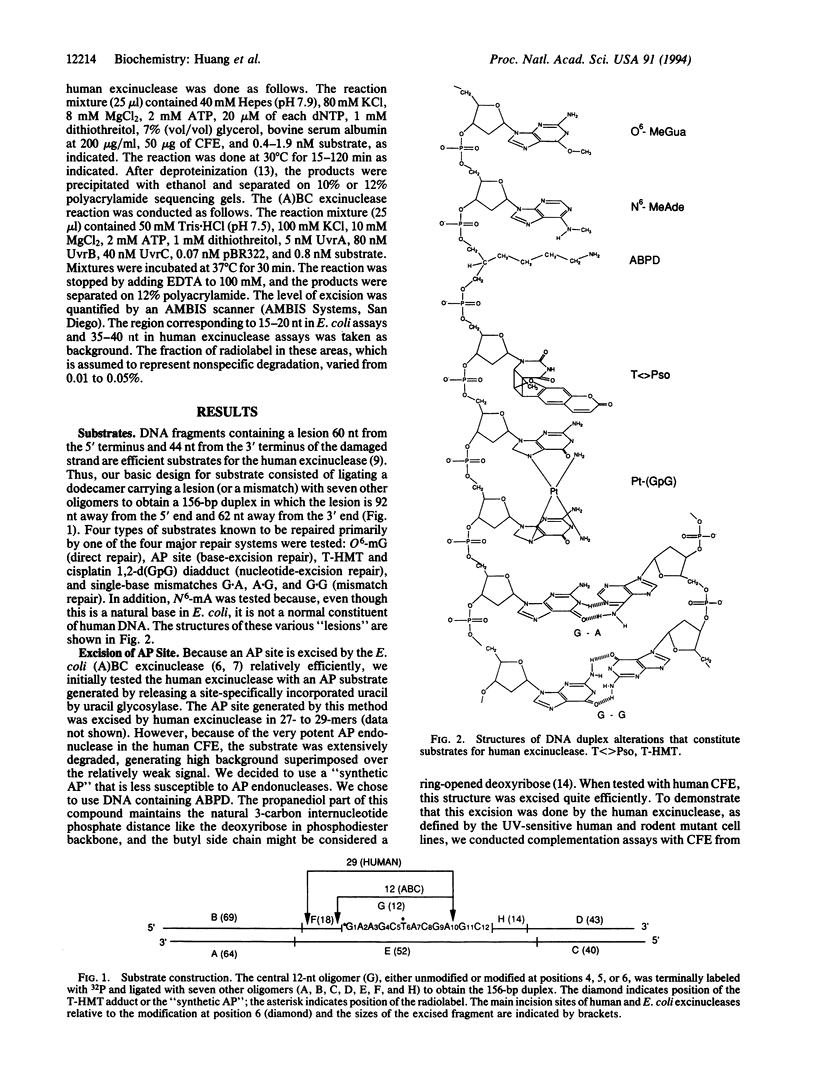


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Caron P. R., Grossman L. Potential role of proteolysis in the control of UvrABC incision. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10903–10912. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czeczot H., Tudek B., Lambert B., Laval J., Boiteux S. Escherichia coli Fpg protein and UvrABC endonuclease repair DNA damage induced by methylene blue plus visible light in vivo and in vitro. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3419–3424. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3419-3424.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. S., 3rd, Ziolkowski C. H., Scudiero D. A., Meyer S. A., Lubiniecki A. S., Girardi A. J., Galloway S. M., Bynum G. D. Defective repair of alkylated DNA by human tumour and SV40-transformed human cell strains. Nature. 1980 Dec 25;288(5792):724–727. doi: 10.1038/288724a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demple B., Harrison L. Repair of oxidative damage to DNA: enzymology and biology. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:915–948. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.63.070194.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra M. F., Malone R. E. Excision repair functions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae recognize and repair methylation of adenine by the Escherichia coli dam gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3555–3558. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes J., Jr, Clark S., Modrich P. Strand-specific mismatch correction in nuclear extracts of human and Drosophila melanogaster cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5837–5841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Sancar A. Determination of minimum substrate size for human excinuclease. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 22;269(29):19034–19040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Svoboda D. L., Reardon J. T., Sancar A. Human nucleotide excision nuclease removes thymine dimers from DNA by incising the 22nd phosphodiester bond 5' and the 6th phosphodiester bond 3' to the photodimer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3664–3668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang J. C., Zamble D. B., Reardon J. T., Lippard S. J., Sancar A. HMG-domain proteins specifically inhibit the repair of the major DNA adduct of the anticancer drug cisplatin by human excision nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10394–10398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karran P., Macpherson P., Ceccotti S., Dogliotti E., Griffin S., Bignami M. O6-methylguanine residues elicit DNA repair synthesis by human cell extracts. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 25;268(21):15878–15886. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. J., Sancar A. A new mechanism for repairing oxidative damage to DNA: (A)BC excinuclease removes AP sites and thymine glycols from DNA. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):7979–7984. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Sedgwick B., Sekiguchi M., Nakabeppu Y. Regulation and expression of the adaptive response to alkylating agents. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:133–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modrich P. Mechanisms and biological effects of mismatch repair. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:229–253. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.001305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. S., Kent M., Muthini S. Oligonucleotide labeling methods. 3. Direct labeling of oligonucleotides employing a novel, non-nucleosidic, 2-aminobutyl-1,3-propanediol backbone. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6253–6259. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S., Sung P., Prakash L. DNA repair genes and proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Annu Rev Genet. 1993;27:33–70. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.27.120193.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reardon J. T., Thompson L. H., Sancar A. Excision repair in man and the molecular basis of xeroderma pigmentosum syndrome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1993;58:605–617. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1993.058.01.067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samson L., Thomale J., Rajewsky M. F. Alternative pathways for the in vivo repair of O6-alkylguanine and O4-alkylthymine in Escherichia coli: the adaptive response and nucleotide excision repair. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2261–2267. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03066.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Tang M. S. Nucleotide excision repair. Photochem Photobiol. 1993 May;57(5):905–921. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1993.tb09233.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi Y. B., Gamper H., Hearst J. E. The effects of covalent additions of a psoralen on transcription by E. coli RNA polymerase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6843–6854. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6843. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sklar R., Strauss B. Removal of O6-methylguanine from DNA of normal and xeroderma pigmentosum-derived lymphoblastoid lines. Nature. 1981 Jan 29;289(5796):417–420. doi: 10.1038/289417a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snowden A., Kow Y. W., Van Houten B. Damage repertoire of the Escherichia coli UvrABC nuclease complex includes abasic sites, base-damage analogues, and lesions containing adjacent 5' or 3' nicks. Biochemistry. 1990 Aug 7;29(31):7251–7259. doi: 10.1021/bi00483a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Wood R. D. Xeroderma pigmentosum and nucleotide excision repair of DNA. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):83–86. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90040-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Kunkel T. A., Casna N. J., Ford J. P., Sancar A. Activities and incision patterns of ABC excinuclease on modified DNA containing single-base mismatches and extrahelical bases. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14496–14505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Levy M., Sancar A. Amplification and purification of UvrA, UvrB, and UvrC proteins of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 15;260(17):9875–9883. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Roberts J. D., Kunkel T. A. Heteroduplex repair in extracts of human HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3744–3751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Busch D. B., Brookman K., Mooney C. L., Glaser D. A. Genetic diversity of UV-sensitive DNA repair mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten B., Sancar A. Repair of N-methyl-N'-nitro-N-nitrosoguanidine-induced DNA damage by ABC excinuclease. J Bacteriol. 1987 Feb;169(2):540–545. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.2.540-545.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voigt J. M., Van Houten B., Sancar A., Topal M. D. Repair of O6-methylguanine by ABC excinuclease of Escherichia coli in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):5172–5176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]