Abstract
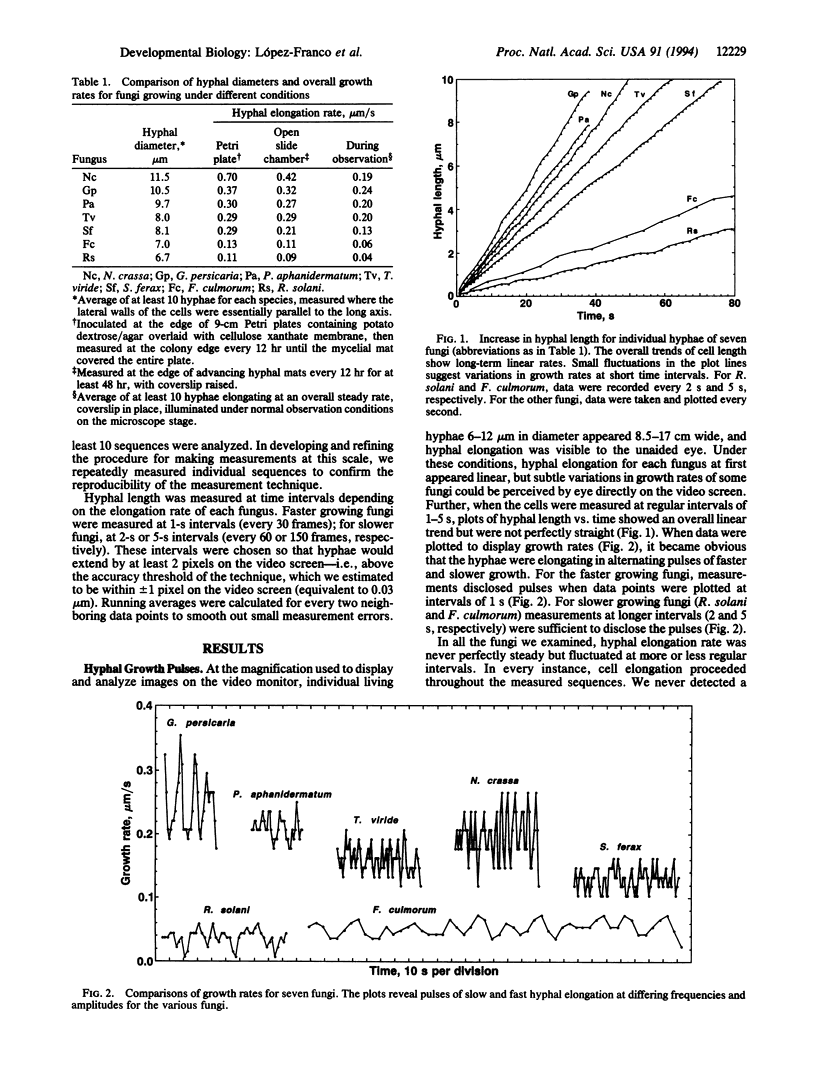
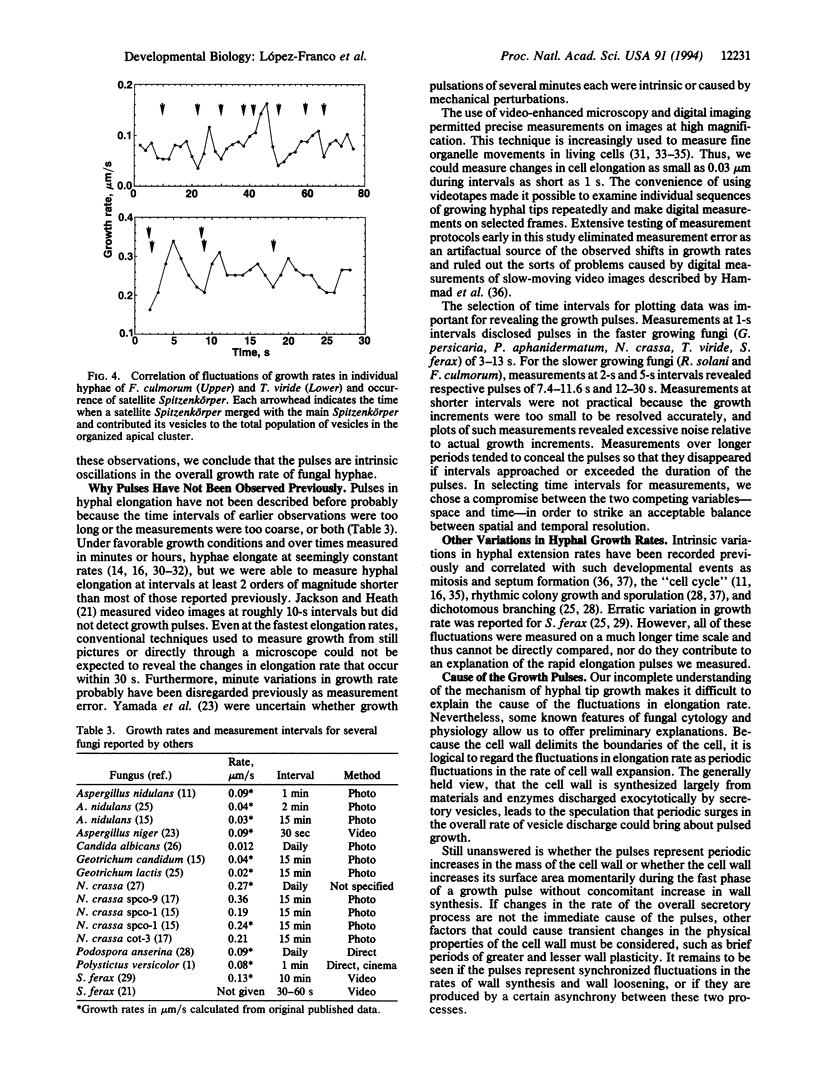
Somatic fungal hyphae are generally assumed to elongate at steady linear rates when grown under constant environmental conditions with ample nutrients. However, patterns of pulsed hyphal elongation were detected during apparent steady growth of hyphal tips in fungi from several major taxonomic groups (Oomycetes, Pythium aphanidermatum and Saprolegnia ferax; Zygomycetes, Gilbertella persicaria; Deuteromycetes, Trichoderma viride; Ascomycetes, Neurospora crassa and Fusarium culmorum; Basidiomycetes, Rhizoctonia solani). Growing hyphal tips were recorded with video-enhanced phase-contrast microscopy at high magnification, and digital images were measured at very short time intervals (1-5 s). In all fungi tested, the hyphal elongation rate was never perfectly steady but fluctuated continuously with alternating periods of fast and slow growth at more or less regular intervals. Pulsed growth was observed in fungi differing in cell diameter, overall growth rate, taxonomic position, and presence and pattern of Spitzenkörper organization, suggesting that this is a general phenomenon. Frequency and amplitude of the pulses varied among the test organisms. T. viride and N. crassa showed the most frequent pulses (average of 13-14 per min), and F. culmorum the least frequent (2.7 per min). Average pulse amplitude varied from 0.012 microns/s for F. culmorum to 0.068 microns/s for G. persicaria. In F. culmorum and T. viride, the fast phase of the growth pulses was correlated with the merger of satellite Spitzenkörper with the main Spitzenkörper. These findings are consistent with a causal relationship between fluctuations in the overall rate of secretory vesicle delivery/discharge at the hyphal apex and the fluctuations in hyphal elongation rate.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartnicki-Garcia S., Lippman E. Fungal morphogenesis: cell wall construction in Mucor rouxii. Science. 1969 Jul 18;165(3890):302–304. doi: 10.1126/science.165.3890.302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calakos N., Bennett M. K., Peterson K. E., Scheller R. H. Protein-protein interactions contributing to the specificity of intracellular vesicular trafficking. Science. 1994 Feb 25;263(5150):1146–1149. doi: 10.1126/science.8108733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiddy C., Trinci A. P. Mitosis, septation, branching and the duplication cycle in Aspergillus nidulans. J Gen Microbiol. 1976 Dec;97(2):169–184. doi: 10.1099/00221287-97-2-169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girbardt M. Ultrastructure and dynamics of the moving nucleus. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1968;22:249–259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow N. A. Circulating ionic currents in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1989;30:89–123. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gow N. A., Gooday G. W. Growth kinetics and morphology of colonies of the filamentous form of Candida albicans. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2187–2194. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove S. N., Bracker C. E. Protoplasmic organization of hyphal tips among fungi: vesicles and Spitzenkörper. J Bacteriol. 1970 Nov;104(2):989–1009. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.2.989-1009.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lysek G. Rhythmic mycelial growth in Podospora anserina. VI. An attempt to elucidate the growth pattern of a clock mutant. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;87(2):129–137. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBINOW C. F. Observations on cell growth, mitosis, and division in the fungus Basidiobolus ranarum. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:123–152. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steele G. C., Trinci A. P. Morphology and growth kinetics of hyphae of differentiated and undifferentiated mycelia of Neurospora crassa. J Gen Microbiol. 1975 Dec;91(2):362–368. doi: 10.1099/00221287-91-2-362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinci A. P. A study of the kinetics of hyphal extension and branch initiation of fungal mycelia. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Mar;81(1):225–236. doi: 10.1099/00221287-81-1-225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Cao J., Sumita O., Kurasawa K., Kurata H., Oh K., Matsuoka H. Automatic antifungal activity analyzing system on the basis of dynamic growth process of a single hypha. Mycopathologia. 1992 May;118(2):65–69. doi: 10.1007/BF00442533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]