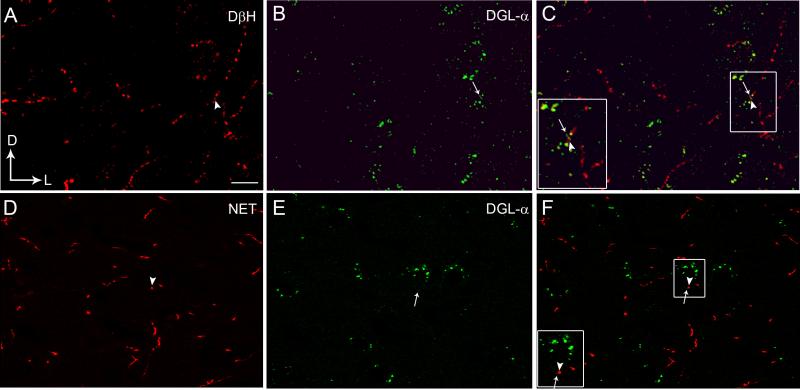
Figure 1.
Confocal fluorescence photomicrographs showing immunolabeling of diacylglycerol lipase-α (DGL-α) in the frontal cortex with respect to noradrenergic afferents as visualized by the presence of dopamine-β-hydroxylase (DβH) or the norepinephrine transporter (NET) (Panels A-F). A. DβH was detected using a rhodamine isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody (TRITC donkey anti-mouse; red). B. DGL-α was detected using a fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated secondary antibody (FITC donkey anti-rabbit; green). C. Merged image of panels A and B. The inset shows a higher magnification view of the area outlined by the boxed region showing close associations between DβH (arrowhead) and DGL-α (arrow). D. NET (red) was detected using a TRITC donkey anti-mouse secondary antibody. E. DGL-α (green) was detected using a FITC donkey anti-rabbit secondary antibody. F. Merged image of panels D and E. The inset shows a higher magnification view of the area outlined by the boxed region showing close associations of NET (arrowhead) with DGL-α (arrow). Scale bars = 100 μm.