Abstract
The in vitro phosphorylation of chicken desmin by the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase was analysed. Phosphorylated desmin loses the ability to form intermediate filaments (IFs). Fragmentation at the sole cysteine and mild chymotryptic treatment show a differential phosphorylation of the three structural domains. Only the amino-terminal head domain is the target of the kinase. Peptide analysis shows that serine 29 is fully phosphorylated, while serine 35 and 50 are phosphorylated at least at 22 and 50% respectively. All three sites show the sequence arginine-X-serine with X being a small residue. These results strengthen the view that the nonhelical head domain has a strong influence on filament integrity most likely via a direct influence of some of its arginine residues. Taken together with previous results (Inagaki et al., 1987) on the phosphorylation of vimentin by kinase A, a new view on IFs emerges. Phosphorylation could allow for regulatory processes in assembly and turnover.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burke B., Gerace L. A cell free system to study reassembly of the nuclear envelope at the end of mitosis. Cell. 1986 Feb 28;44(4):639–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90273-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral F., Gottesman M. M. Phosphorylation of the 10-nm filament protein from Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 25;254(14):6203–6206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celis J. E., Larsen P. M., Fey S. J., Celis A. Phosphorylation of keratin and vimentin polypeptides in normal and transformed mitotic human epithelial amnion cells: behavior of keratin and vimentin filaments during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1429–1434. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Fink L. M. An alteration in the phosphorylation of vimentin-type intermediate filaments is associated with mitosis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):43–52. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. Peptide mapping of phosphorylated vimentin. Evidence for a site-specific alteration in mitotic cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5372–5375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer S., Vandekerckhove J., Ampe C., Traub P., Weber K. Protein-chemical identification of the major cleavage sites of the Ca2+ proteinase on murine vimentin, the mesenchymal intermediate filament protein. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1986 Nov;367(11):1147–1152. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1986.367.2.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher D. Z., Chaudhary N., Blobel G. cDNA sequencing of nuclear lamins A and C reveals primary and secondary structural homology to intermediate filament proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6450–6454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Grund C., Kuhn C., Lehto V. P., Virtanen I. Transient change of organization of vimentin filaments during mitosis as demonstrated by a monoclonal antibody. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Oct;154(2):567–580. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Grund C., Geiger B. Intermediate filament proteins in nonfilamentous structures: transient disintegration and inclusion of subunit proteins in granular aggregates. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):103–113. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser R. D., MacRae T. P., Parry D. A., Suzuki E. Intermediate filaments in alpha-keratins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1179–1183. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Bell P. B., Lazarides E. Coexistence of desmin and the fibroblastic intermediate filament subunit in muscle and nonmuscle cells: identification and comparative peptide analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3894–3898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Cyclic AMP-modulated phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins in cultured avian myogenic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Fischer S., Vandekerckhove J., Plessmann U., Weber K. Hybrid character of a large neurofilament protein (NF-M): intermediate filament type sequence followed by a long and acidic carboxy-terminal extension. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2701–2706. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02196.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Antiparallel orientation of the two double-stranded coiled-coils in the tetrameric protofilament unit of intermediate filaments. J Mol Biol. 1985 Mar 5;182(1):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Kaufmann E., Weber K. Proteinchemical characterization of three structurally distinct domains along the protofilament unit of desmin 10 nm filaments. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):277–286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90033-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Vandekerckhove J., Weber K. Location and sequence characterization of the major phosphorylation sites of the high molecular mass neurofilament proteins M and H. FEBS Lett. 1987 Sep 14;221(2):403–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80964-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Comparison of the proteins of two immunologically distinct intermediate-sized filaments by amino acid sequence analysis: desmin and vimentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4120–4123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. Purification of smooth-muscle desmin and a protein-chemical comparison of desmins from chicken gizzard and hog stomach. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Oct;111(2):425–433. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04957.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geisler N., Weber K. The amino acid sequence of chicken muscle desmin provides a common structural model for intermediate filament proteins. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1649–1656. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01368.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Blobel G. Lamin B constitutes an intermediate filament attachment site at the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):117–125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Blobel G. Two distinct attachment sites for vimentin along the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope in avian erythrocytes: a basis for a vectorial assembly of intermediate filaments. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):105–115. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Marchesi V. T. The binding of vimentin to human erythrocyte membranes: a model system for the study of intermediate filament-membrane interactions. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1955–1961. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgatos S. D., Weber K., Geisler N., Blobel G. Binding of two desmin derivatives to the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope of avian erythrocytes: evidence for a conserved site-specificity in intermediate filament-membrane interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6780–6784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georges E., Lefebvre S., Mushynski W. E. Dephosphorylation of neurofilaments by exogenous phosphatases has no effect on reassembly of subunits. J Neurochem. 1986 Aug;47(2):477–483. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1986.tb04526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
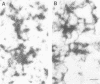
- Inagaki M., Nishi Y., Nishizawa K., Matsuyama M., Sato C. Site-specific phosphorylation induces disassembly of vimentin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 13;328(6131):649–652. doi: 10.1038/328649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip W., Hartzer M. K., Pang Y. Y., Robson R. M. Assembly of vimentin in vitro and its implications concerning the structure of intermediate filaments. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90007-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julien J. P., Mushynski W. E. The distribution of phosphorylation sites among identified proteolytic fragments of mammalian neurofilaments. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):4019–4025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann E., Weber K., Geisler N. Intermediate filament forming ability of desmin derivatives lacking either the amino-terminal 67 or the carboxy-terminal 27 residues. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 20;185(4):733–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krohne G., Wolin S. L., McKeon F. D., Franke W. W., Kirschner M. W. Nuclear lamin LI of Xenopus laevis: cDNA cloning, amino acid sequence and binding specificity of a member of the lamin B subfamily. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3801–3808. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02716.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane E. B., Goodman S. L., Trejdosiewicz L. K. Disruption of the keratin filament network during epithelial cell division. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1365–1372. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKeon F. D., Kirschner M. W., Caput D. Homologies in both primary and secondary structure between nuclear envelope and intermediate filament proteins. Nature. 1986 Feb 6;319(6053):463–468. doi: 10.1038/319463a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer H. E., Hoffmann-Posorske E., Korte H., Heilmeyer L. M., Jr Sequence analysis of phosphoserine-containing peptides. Modification for picomolar sensitivity. FEBS Lett. 1986 Aug 11;204(1):61–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81388-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson W. J., Traub P. Proteolysis of vimentin and desmin by the Ca2+-activated proteinase specific for these intermediate filament proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jun;3(6):1146–1156. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.6.1146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor C. M., Gard D. L., Lazarides E. Phosphorylation of intermediate filament proteins by cAMP-dependent protein kinases. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90278-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quax W., Egberts W. V., Hendriks W., Quax-Jeuken Y., Bloemendal H. The structure of the vimentin gene. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90224-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soellner P., Quinlan R. A., Franke W. W. Identification of a distinct soluble subunit of an intermediate filament protein: tetrameric vimentin from living cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7929–7933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Rice R. H., Roop D. R., Trus B. L., Steven A. C. Complete amino acid sequence of a mouse epidermal keratin subunit and implications for the structure of intermediate filaments. Nature. 1983 Apr 28;302(5911):794–800. doi: 10.1038/302794a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinert P. M., Steven A. C., Roop D. R. The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90098-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub P., Vorgias C. E. Involvement of the N-terminal polypeptide of vimentin in the formation of intermediate filaments. J Cell Sci. 1983 Sep;63:43–67. doi: 10.1242/jcs.63.1.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tölle H. G., Weber K., Osborn M. Keratin filament disruption in interphase and mitotic cells--how is it induced? Eur J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;43(1):35–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]