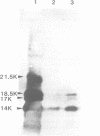
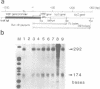
Abstract
A hereditary dysmyelinating mutation, named myelin deficient (shi(mld)), is characterized by reduced expression of myelin basic protein (MBP). In shi(mld), the MBP gene is duplicated and its reduced expression is mainly determined by the level of mRNA. We have characterized the structure and function of the promoter regions of the duplicated MBP genes in shi(mld). Among the lambda clones containing promoter regions of the duplicated MBP genes in shi(mld), one (gene 1) had the same restriction enzyme pattern as that in control mice, but another (gene 2) had a rearrangement on a distal part of the promoter. A 712-bp nucleotide sequence upstream of the first exons of both of the duplicated MBP genes of shi(mld) was completely consistent with that of the control. Promoter activities of 1.3-kb 5'-flanking regions from respective genes of shi(mld) measured by in vitro run-off assay using HeLa whole-cell extracts were indistinguishable from that of the control MPB gene. Chromosomal mapping by in situ hybridization suggested that the duplicated MBP genes were located closely to each other at the distal part of chromosome 18. A recombinational event including the inversion seemed to have occurred within gene 1 and its possible relationship to the reduced expression of MBP is discussed.
Full text
PDF

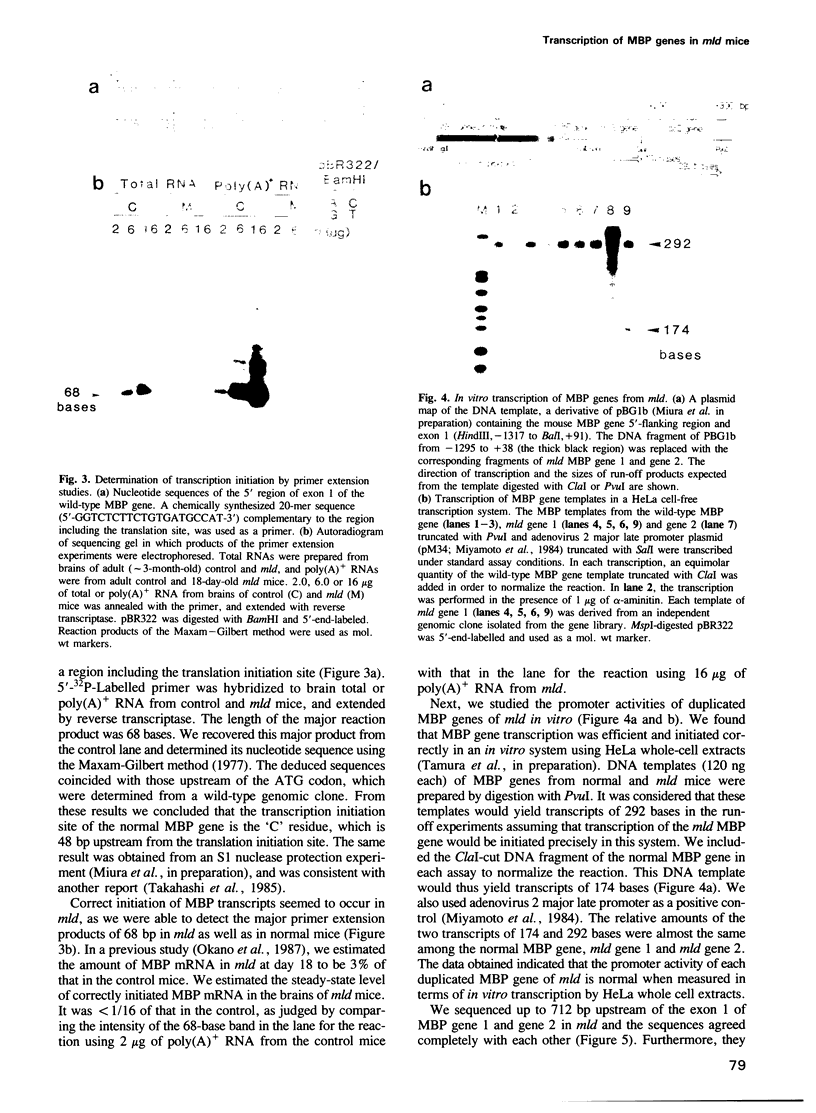
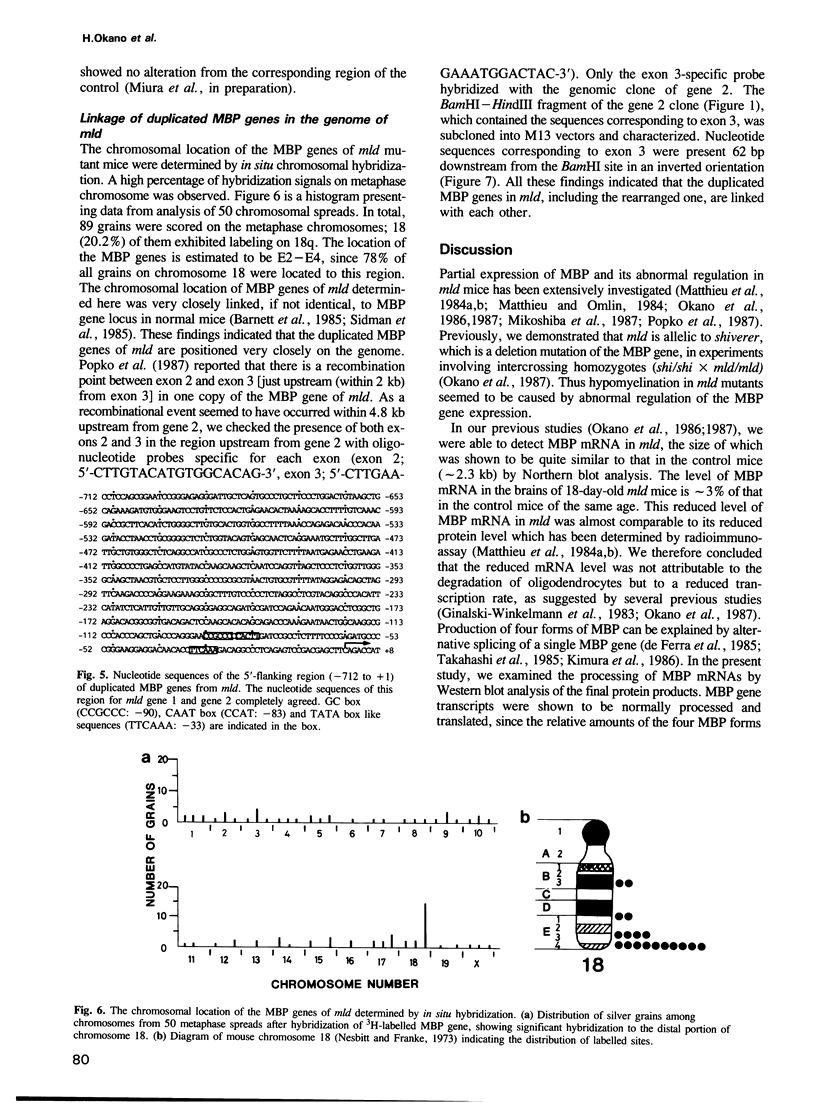



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amano T., Hamprecht B., Kemper W. High activity of choline acetyltransferase induced in neuroblastoma x glia hybrid cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Apr;85(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90142-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbarese E., Carson J. H., Braun P. E. Accumulation of the four myelin basic proteins in mouse brain during development. J Neurochem. 1978 Oct;31(4):779–782. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1978.tb00110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourre J. M., Jacque C., Delassalle A., Nguyen-Legros J., Dumont O., Lachapelle F., Raoul M., Alvarez C., Baumann N. Density profile and basic protein measurements in the myelin range of particulate material from normal developing mouse brain and from neurological mutants (Jimpy; quaking; Trembler; shiverer and its mld allele) obtained by zonal centrifugation. J Neurochem. 1980 Aug;35(2):458–464. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06287.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dupouey P., Jacque C., Bourre J. M., Cesselin F., Privat A., Baumann N. Immunochemical studies of myelin basic protein in shiverer mouse devoid of major dense line of myelin. Neurosci Lett. 1979 Apr;12(1):113–118. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)91490-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman M., Temin H. M. Genes with promoters in retrovirus vectors can be independently suppressed by an epigenetic mechanism. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):449–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner I., Minty A. J., Alonso S., Barton P. J., Buckingham M. E. A 5' duplication of the alpha-cardiac actin gene in BALB/c mice is associated with abnormal levels of alpha-cardiac and alpha-skeletal actin mRNAs in adult cardiac tissue. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2559–2567. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04535.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginalski-Winkelmann H., Almazan G., Matthieu J. M. In vitro myelin basic protein synthesis in the PNS and CNS of myelin deficient (mld) mutant mice. Brain Res. 1983 Oct 31;277(2):386–388. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90952-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall C. V., Jacob P. E., Ringold G. M., Lee F. Expression and regulation of Escherichia coli lacZ gene fusions in mammalian cells. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(1):101–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Saunders G. F. Localization of single copy DNA sequences of G-banded human chromosomes by in situ hybridization. Chromosoma. 1981;83(3):431–439. doi: 10.1007/BF00327364. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson L. D., Berndt J. A., Puckett C., Kozak C. A., Lazzarini R. A. Aberrant splicing of proteolipid protein mRNA in the dysmyelinating jimpy mutant mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1454–1458. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue Y., Nakamura R., Mikoshiba K., Tsukada Y. Fine structure of the central myelin sheath in the myelin deficient mutant Shiverer mouse, with special reference to the pattern of myelin formation by oligodendroglia. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 24;219(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura M., Inoko H., Katsuki M., Ando A., Sato T., Hirose T., Takashima H., Inayama S., Okano H., Takamatsu K. Molecular genetic analysis of myelin-deficient mice: shiverer mutant mice show deletion in gene(s) coding for myelin basic protein. J Neurochem. 1985 Mar;44(3):692–696. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb12870.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthieu J. M., Eggenberger P., Almazan G., Ginalski-Winkelmann H. Anticonvulsive treatment of myelin-deficient (mld) mice improves survival and confirms the delayed increase of myelin basic protein. Neurochem Pathol. 1984 Summer;2(2):115–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02834250. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthieu J. M., Omlin F. X. Murine leukodystrophies as tools to study myelinogenesis in normal and pathological conditions. Neuropediatrics. 1984 Sep;15 (Suppl):37–52. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikoshiba K., Nagaike K., Tsukada Y. Subcellular distribution and developmental change of 2',3'-cyclic nucleotide 3'-phosphohydrolase in the central nervous system of the myelin-deficient shiverer mutant mice. J Neurochem. 1980 Aug;35(2):465–470. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1980.tb06288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikoshiba K., Okano H., Inoue Y., Fujishiro M., Takamatsu K., Lachapelle F., Baumann N., Tsukada Y. Immunohistochemical, biochemical and electron microscopic analysis of myelin formation in the central nervous system of myelin deficient (mld) mutant mice. Brain Res. 1987 Sep;432(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(87)90013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto N. G., Moncollin V., Wintzerith M., Hen R., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Stimulation of in vitro transcription by the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter involves a specific factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 11;12(23):8779–8799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.23.8779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morello D., Dautigny A., Pham-Dinh D., Jollès P. Myelin proteolipid protein (PLP and DM-20) transcripts are deleted in jimpy mutant mice. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3489–3493. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04674.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriguchi A., Ikenaka K., Furuichi T., Okano H., Iwasaki Y., Mikoshiba K. The fifth exon of the myelin proteolipid protein-coding gene is not utilized in the brain of jimpy mutant mice. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):333–337. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Hogness D. S. Isolation, sequence analysis, and intron-exon arrangement of the gene encoding bovine rhodopsin. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):807–814. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90537-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave K. A., Lai C., Bloom F. E., Milner R. J. Jimpy mutant mouse: a 74-base deletion in the mRNA for myelin proteolipid protein and evidence for a primary defect in RNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9264–9268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbitt M. N., Francke U. A system of nomenclature for band patterns of mouse chromosomes. Chromosoma. 1973;41(2):145–158. doi: 10.1007/BF00319691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano H., Miura M., Moriguchi A., Ikenaka K., Tsukada Y., Mikoshiba K. Inefficient transcription of the myelin basic protein gene possibly causes hypomyelination in myelin-deficient mutant mice. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):470–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson A., Marler J. P1 deficiency in shiverer myelin is expressed by Schwann cells in shiverer dystrophic normal mouse chimaera nerves. Neurosci Lett. 1983 Jul 29;38(2):163–168. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(83)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popko B., Puckett C., Lai E., Shine H. D., Readhead C., Takahashi N., Hunt S. W., 3rd, Sidman R. L., Hood L. Myelin deficient mice: expression of myelin basic protein and generation of mice with varying levels of myelin. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):713–721. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90249-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privat A., Jacque C., Bourre J. M., Dupouey P., Baumann N. Absence of the major dense line in myelin of the mutant mouse "shiverer". Neurosci Lett. 1979 Apr;12(1):107–112. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(79)91489-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roch J. M., Brown-Luedi M., Cooper B. J., Matthieu J. M. Mice heterozygous for the mld mutation have intermediate levels of myelin basic protein mRNA and its translation products. Brain Res. 1986 Nov;387(2):137–144. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R., Barrell B. G., Smith A. J., Roe B. A. Cloning in single-stranded bacteriophage as an aid to rapid DNA sequencing. J Mol Biol. 1980 Oct 25;143(2):161–178. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90196-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman R. L., Conover C. S., Carson J. H. Shiverer gene maps near the distal end of chromosome 18 in the house mouse. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1985;39(4):241–245. doi: 10.1159/000132151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Roach A., Teplow D. B., Prusiner S. B., Hood L. Cloning and characterization of the myelin basic protein gene from mouse: one gene can encode both 14 kd and 18.5 kd MBPs by alternate use of exons. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ferra F., Engh H., Hudson L., Kamholz J., Puckett C., Molineaux S., Lazzarini R. A. Alternative splicing accounts for the four forms of myelin basic protein. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]