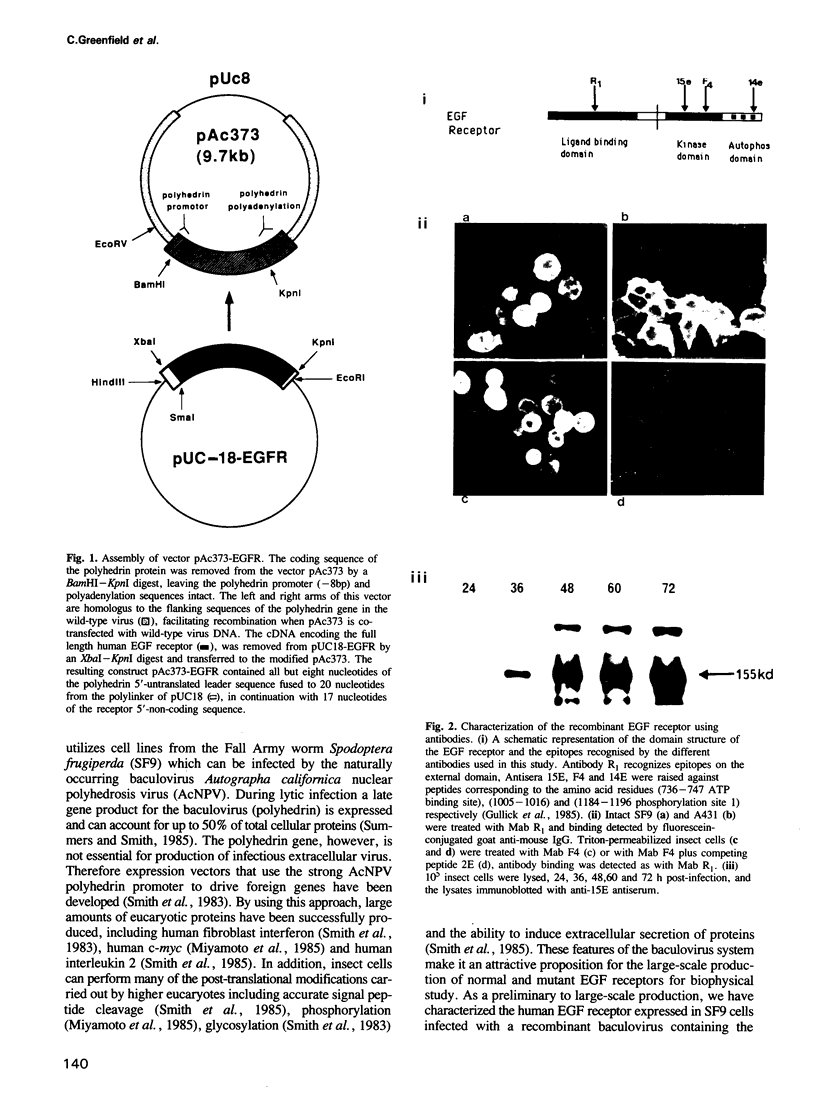
Abstract
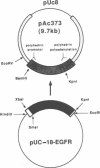
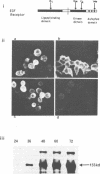
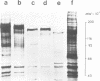
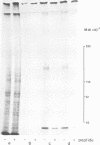
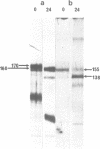
The mechanism by which the binding of epidermal growth factor (EGF) to specific cell surface receptors induces a range of biological responses remains poorly understood. An important part of the study of signal transduction in this system involves the production of sufficient native and mutant EGF receptor species for X-ray crystallographic and spectroscopic analysis. Baculovirus vectors containing the cDNA encoding the human EGF receptor protein have here been utilized to infect insect cells. This results in expression of a 155-kb transmembrane protein which is recognized by four antibodies against different regions of the human EGF receptor. Studies with tunicamycin, monensen and endoglycosidase H show the difference in size between the recombinant and the native receptor is due to alterations in glycocsylation. Studies of [125I] EGF binding shows a Kd of 2 X 10(-9) M in intact infected insect cells which falls to 2 X 10(-7) M upon detergent solubilization. The recombinant protein exhibits an EGF-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity and an analysis of tryptic peptides shows that the phosphate acceptor sites are similar to those of the EGF receptor isolated from A431 cells. These observations indicate that functional EGF receptor can be expressed in insect cells, and furthermore, this system can be used for large-scale production.
Full text
PDF
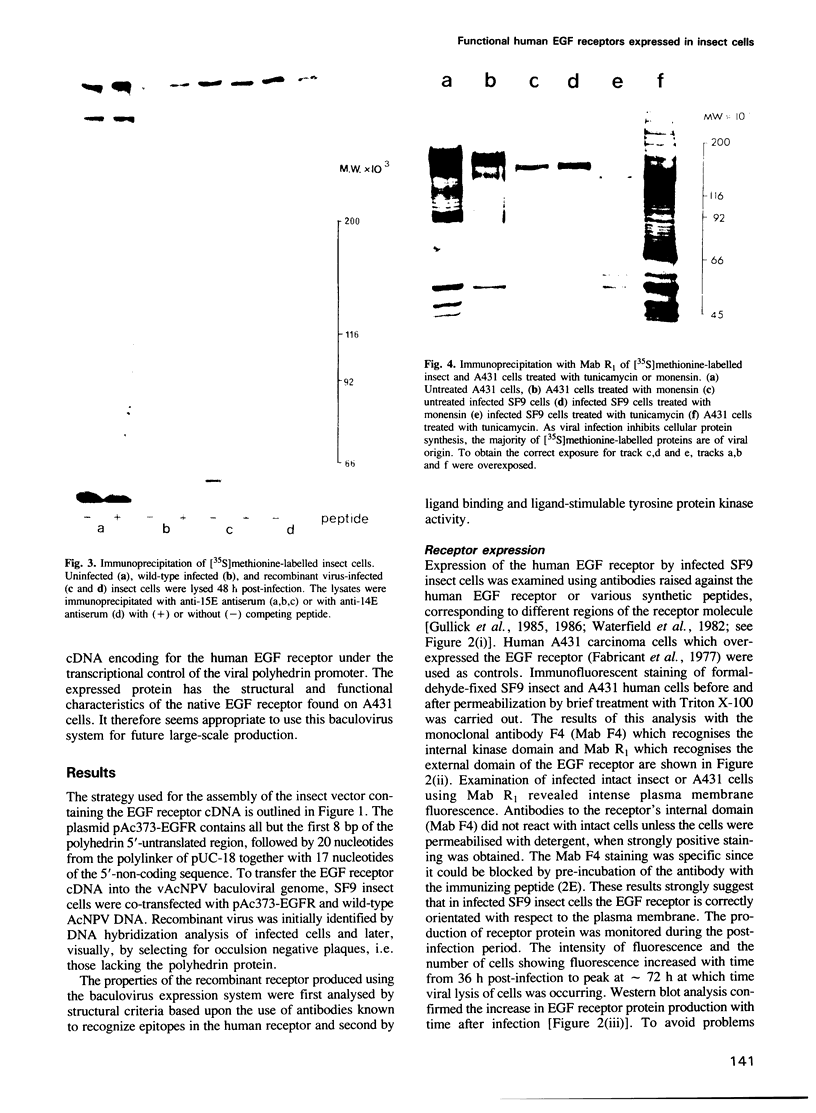
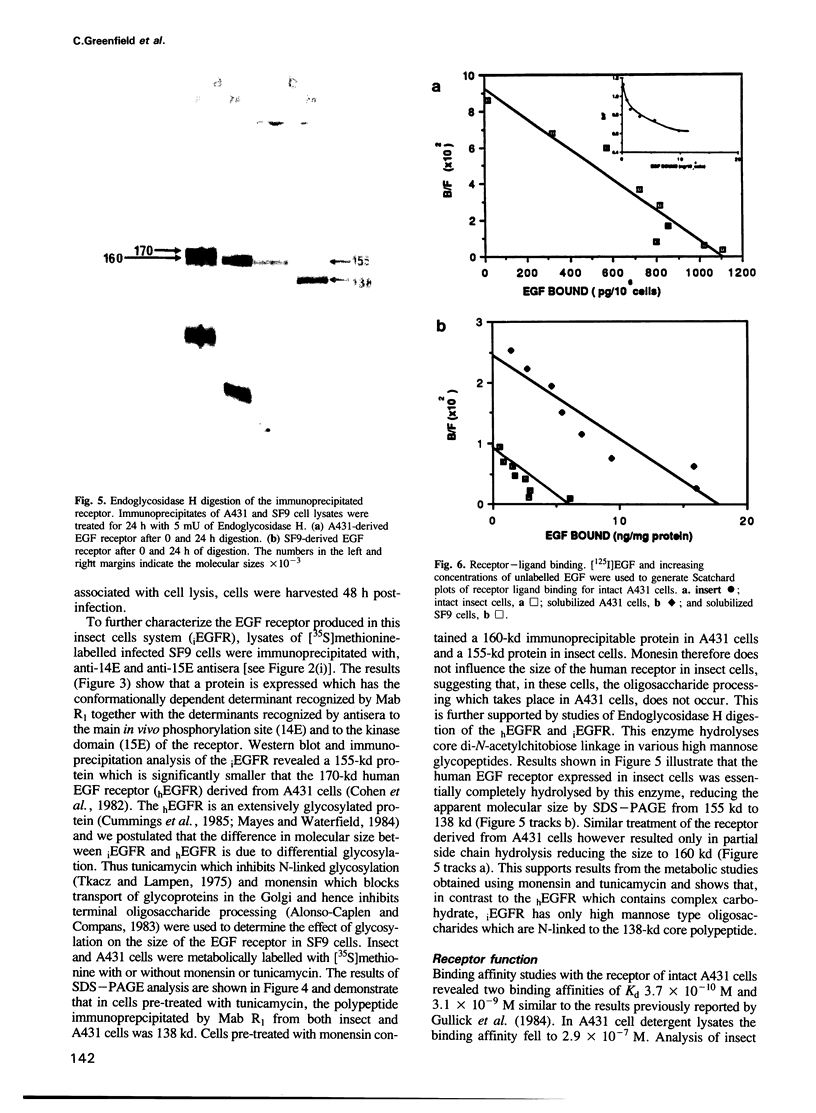
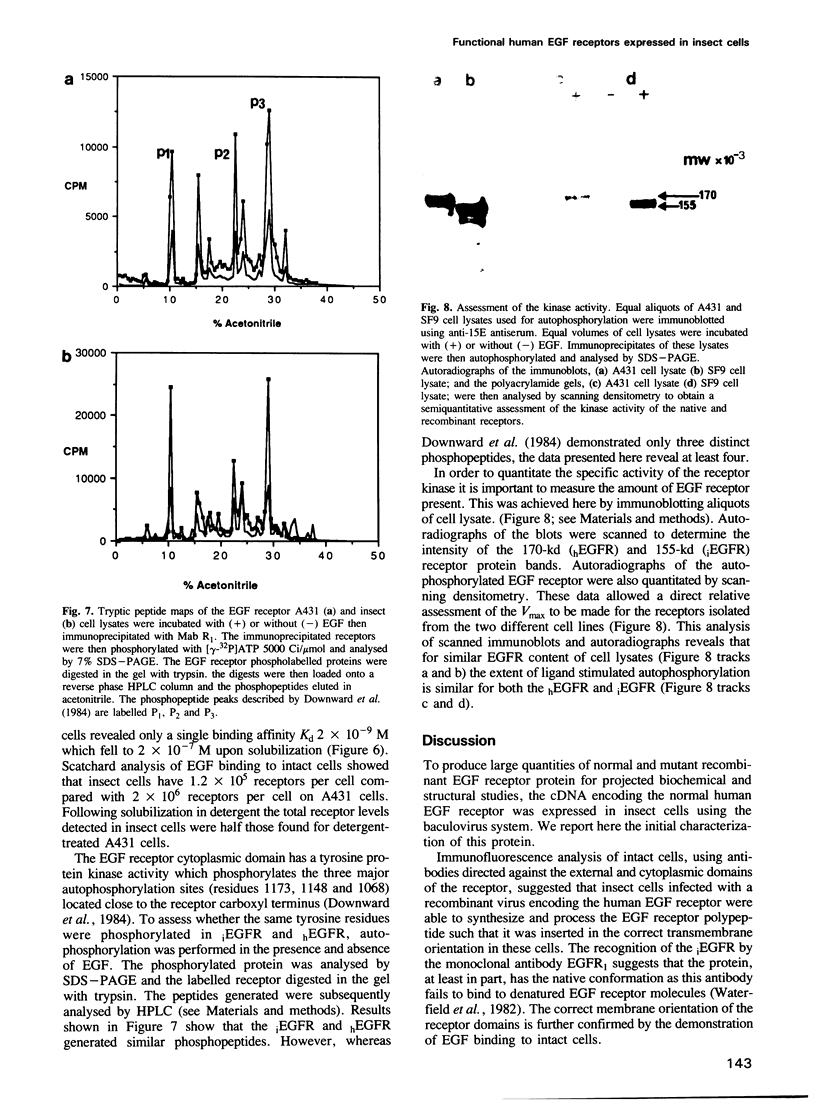



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alonso-Caplen F. V., Compans R. W. Modulation of glycosylation and transport of viral membrane glycoproteins by a sodium ionophore. J Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;97(3):659–668. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G. Receptors for epidermal growth factor and other polypeptide mitogens. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:881–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., McKanna J. A., Cohen S. Rapid induction of morphological changes in human carcinoma cells A-431 by epidermal growth factors. J Cell Biol. 1979 Oct;83(1):260–265. doi: 10.1083/jcb.83.1.260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., McKanna J. A., Cohen S. Rapid rounding of human epidermoid carcinoma cells A-431 induced by epidermal growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;88(2):422–429. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cummings R. D., Soderquist A. M., Carpenter G. The oligosaccharide moieties of the epidermal growth factor receptor in A-431 cells. Presence of complex-type N-linked chains that contain terminal N-acetylgalactosamine residues. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):11944–11952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J. Effects of epidermal growth factor and 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate on metabolism of the epidermal growth factor receptor in normal human fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1718–1724. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Parker P., Waterfield M. D. Autophosphorylation sites on the epidermal growth factor receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):483–485. doi: 10.1038/311483a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., Waterfield M. D., Parker P. J. Autophosphorylation and protein kinase C phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Effect on tyrosine kinase activity and ligand binding affinity. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 25;260(27):14538–14546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabricant R. N., De Larco J. E., Todaro G. J. Nerve growth factor receptors on human melanoma cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):565–569. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Downward D. J., Marsden J. J., Waterfield M. D. A radioimmunoassay for human epidermal growth factor receptor. Anal Biochem. 1984 Aug 15;141(1):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90454-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Downward J., Parker P. J., Whittle N., Kris R., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A., Waterfield M. D. The structure and function of the epidermal growth factor receptor studied by using antisynthetic peptide antibodies. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1985 Oct 22;226(1242):127–134. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1985.0087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gullick W. J., Marsden J. J., Whittle N., Ward B., Bobrow L., Waterfield M. D. Expression of epidermal growth factor receptors on human cervical, ovarian, and vulval carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1986 Jan;46(1):285–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh P., Robbins P. W. Regulation of asparagine-linked oligosaccharide processing. Oligosaccharide processing in Aedes albopictus mosquito cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2375–2382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard S. C., Ivatt R. J. Synthesis and processing of asparagine-linked oligosaccharides. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:555–583. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.003011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. The epidermal growth factor receptor gene and its product. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):414–416. doi: 10.1038/311414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. C., Cuatrecasas P. Resolution of high and low affinity epidermal growth factor receptors. Inhibition of high affinity component by low temperature, cycloheximide, and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3053–3060. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda K., Hauser C., Rott R., Klenk H. D., Doerfler W. Expression of the influenza virus haemagglutinin in insect cells by a baculovirus vector. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1359–1365. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04367.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura Y., Possee R. D., Overton H. A., Bishop D. H. Baculovirus expression vectors: the requirements for high level expression of proteins, including glycoproteins. J Gen Virol. 1987 May;68(Pt 5):1233–1250. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-68-5-1233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayes E. L., Waterfield M. D. Biosynthesis of the epidermal growth factor receptor in A431 cells. EMBO J. 1984 Mar;3(3):531–537. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01842.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. K., Adang M. J., Browne D. Protein Kinase Activity Associated with the Extracellular and Occluded Forms of the Baculovirus Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):275–278. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.275-278.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C., Smith G. E., Farrell-Towt J., Chizzonite R., Summers M. D., Ju G. Production of human c-myc protein in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2860–2865. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Yarden Y., de Laat S. W., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces electrically silent Na+ influx in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8502–8506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann G. F. Polyhedrin structure. J Gen Virol. 1986 Aug;67(Pt 8):1499–1513. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-8-1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shechter Y., Hernaez L., Cuatrecasas P. Epidermal growth factor: biological activity requires persistent occupation of high-affinity cell surface receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5788–5791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Ju G., Ericson B. L., Moschera J., Lahm H. W., Chizzonite R., Summers M. D. Modification and secretion of human interleukin 2 produced in insect cells by a baculovirus expression vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8404–8408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D., Fraser M. J. Production of human beta interferon in insect cells infected with a baculovirus expression vector. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2156–2165. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkacz J. S., Lampen O. Tunicamycin inhibition of polyisoprenyl N-acetylglucosaminyl pyrophosphate formation in calf-liver microsomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):248–257. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trimble R. B., Maley F. Optimizing hydrolysis of N-linked high-mannose oligosaccharides by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. Anal Biochem. 1984 Sep;141(2):515–522. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfield M. D., Mayes E. L., Stroobant P., Bennet P. L., Young S., Goodfellow P. N., Banting G. S., Ozanne B. A monoclonal antibody to the human epidermal growth factor receptor. J Cell Biochem. 1982;20(2):149–161. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240200207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Self-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: evidence for a model of intermolecular allosteric activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1434–1442. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]