Abstract
Congenital depressions of the skull are rare in Western countries. The majority relate to obstetric trauma at delivery. We present a case of a congenital depression of a neonate's skull not relating to obstetric trauma. The child had an ovoid indentation behind the right coronal suture in the temperoparietal region. This skull depression was thought to relate to the position of her right hand in utero. We report her management, neuro-imaging and outcome on follow-up. A literature review is given in brief.
Background
Congenital depressions of the neonatal skull are rare in Western countries occurring in 1 in 10 000 neonates1 and are usually due to trauma on delivery.2 In Africa, this condition is far more common with 1 in 4000 neonates affected. This may be due to the extensive use of obstetric forceps or digital pressure of the obstetrician during manual rotation.3 These acquired depressions are often associated with ‘ping-pong’ fractures.4 The minority of congenital skull depressions are in utero.5 These are explained by prolonged pressure from one of several possible sources. These include bony prominences of the mother such as the sacral promontory or rib cage; uterine leiomyoma of the mother6 and the fetus’ own hand, foot or twin.2 This prolonged pressure can thin and soften the calvarium moulding a skull depression without a true fracture.7
Case presentation
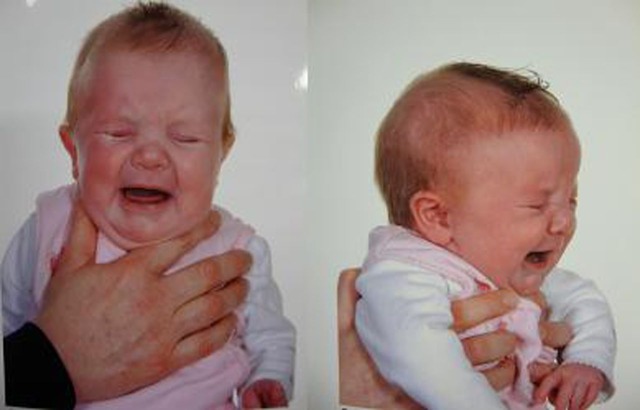
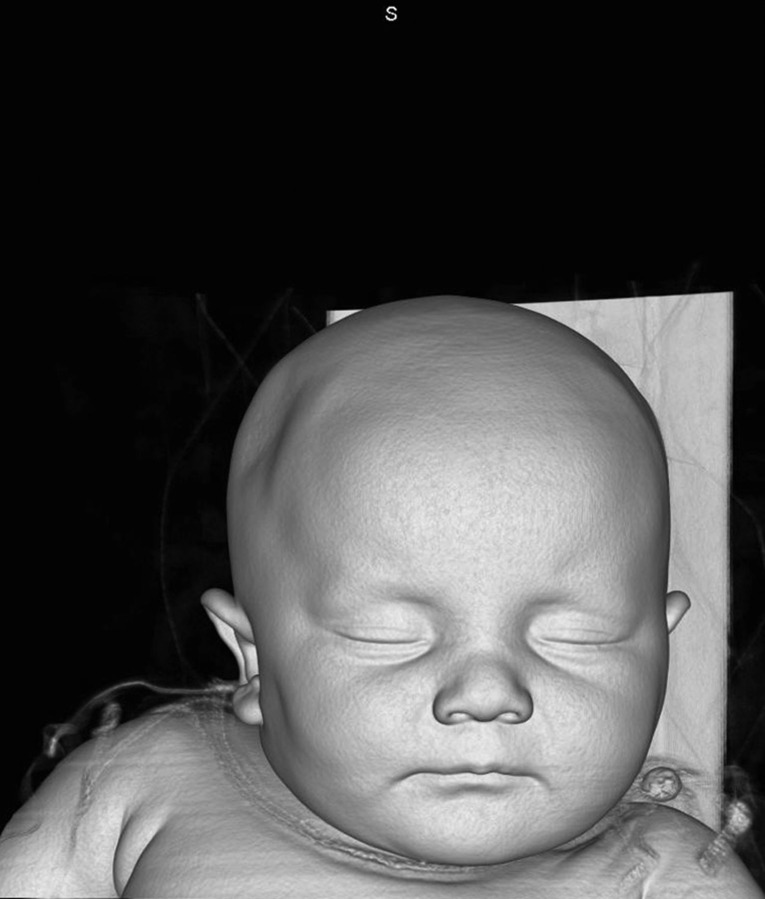
A neonate was reviewed at the age of 8 weeks by the senior author in a multidisciplinary craniofacial clinic. She was born at term by elective caesarean section. There was no history of forceps or any other instrumentation being used. There was no zonal pain during pregnancy and the baby did not have any swelling or bruising in the neonatal period. On examination an ovoid indentation measuring 6 × 8 cm was noted behind the right coronal suture in the temperoparietal region (figure 1). On palpation it felt like solid bone. There was no evidence of mobility, or pulsatility. There was no evidence of coronal ridging. There was an open, soft fontanelle.
Figure 1.
Photos of the neonate.
Investigations
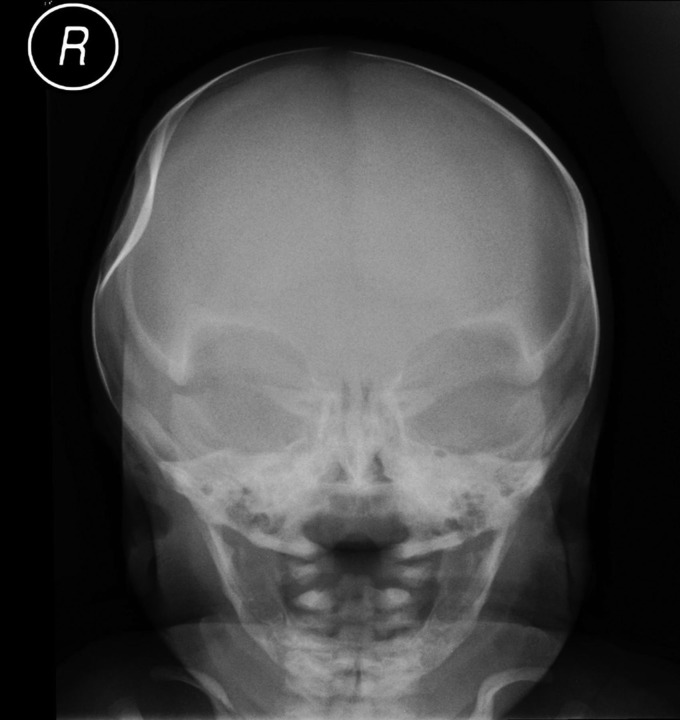
The antero-posterior radiograph showed a significant indentation but with no evidence of a fracture line (figure 2). The sutures appeared to be patent.
Figure 2.
Skull x-ray: antero-posterior view.
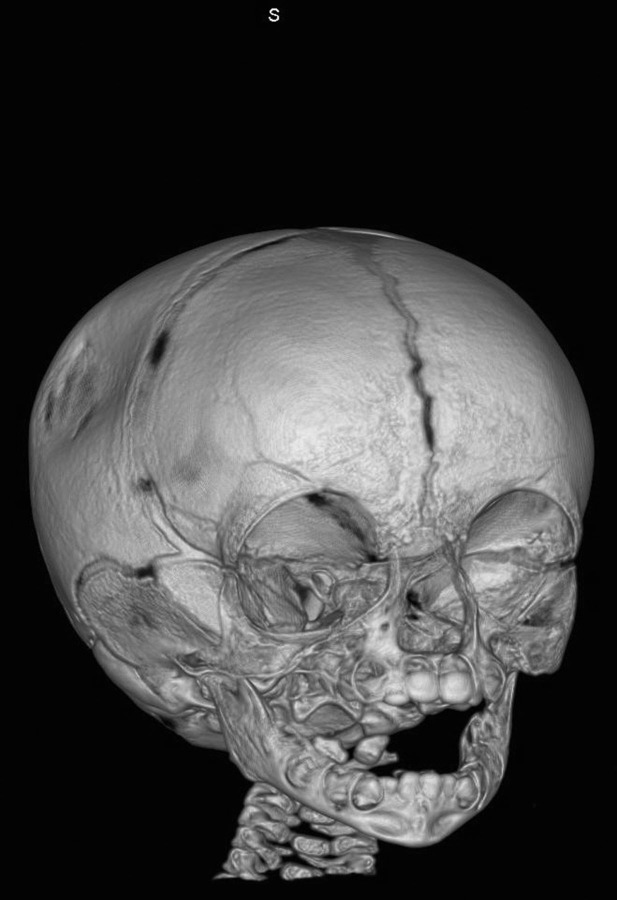
A three-dimensional CT scan confirmed that there was an oval depression posterior to the right coronal suture (figures 3 and 4). There was no definite fracture. All the major sutures were patent and the metopic suture remained open. There was some asymmetry to the calvaria with a small right temporo-parietal bulge inferior to the depression. The CT scan showed no neurological damage.
Figure 3.
Three-dimensional CT scan.
Figure 4.
Three-dimensional reconstruction.
Differential diagnosis
The main differential diagnosis is an obstetric-related fracture or intrauterine moulding. The former seemed unlikely in view of the lack of bruising and swelling, or instrumentation at birth. There was no evidence of craniosynostosis or any other alternative aetiology. Intrauterine moulding by the fetus’ own hand has previously been described.1
Treatment
The child was managed conservatively with observation.
Outcome and follow-up
The child was reviewed at 6 months of age and the indentation was found to be improving, though still present. This indentation is thought to be due to the intrauterine position of the fetus’ right fist on the right side of her head.
Discussion
Rarely congenital depressions of the neonatal skull can have severe neurological sequelae if associated with the underlying brain injury.8 For this reason, a CT scan is performed to rule this out.9 Without neurological complications, which require surgery, these patients should be treated conservatively. Suction procedures have been described to reverse the skull depression.4 However, the majority of the skull depressions spontaneously resolve within 4 months.10 In the absence of neurological symptoms, it is advised that the neonate is observed for 6 months. If resolution does not occur in this time then surgical intervention may be indicated.
Learning points.
The majority of congenital skull depressions relate to obstetric trauma.
A CT scan is indicated to look for underlying brain injury.
The majority resolve spontaneously within 4 months.
We advocate conservative management for the majority of clinical patients.
Footnotes
Competing interests: None.
Patient consent: Obtained.
References
- 1.Ben-Ari Y, Merlob P, Hirsch M, et al. Congenital depression of the neonatal skull. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 1986;22:249–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Eisenberg D, Kirchner SG, Perrin EC. Neonatal skull depression unassociated with birth trauma. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1984;143:1063–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Guha-Ray DK. Intrauterine spontaneous depression of fetal skull: a case report and review of literature. J Reprod Med 1976;16:321–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mastrapa TL, Fernandez LA, Alvarez MD, et al. Depressed skull fracture in Ping Pong: elevation with Medeva extractor. Childs Nerv Syst 2007;23:787–90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Axton JH, Levy LF. Congenital moulding depressions of the skull. Br Med J 1965;1:1644–7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Alexander E, Jr, Davis CH., Jr Intra-uterine fracture of the infant's skull. J Neurosurg 1969;30:446–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Strong TH, Jr, Feldman DB, Cooke JK, et al. Congenital depression of the fetal skull. Obstet Gynecol Surv 1990;45:284–9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Batton DG, DiCarmine F, Boal DK. Intrauterine skull depression and intracranial hemorrhage in a premature infant. Pediatr Radiol 1988;18:181–2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Captier G, Lebarazer M, Bigorre M, et al. Congenital skull depression. Ann Chir Plast Esthet 1999;44:266–71. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hanlon L, Hogan B, Corcoran D, et al. Congenital depression of the neonatal skull: a self limiting condition. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed 2006;91:F272. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]