Abstract
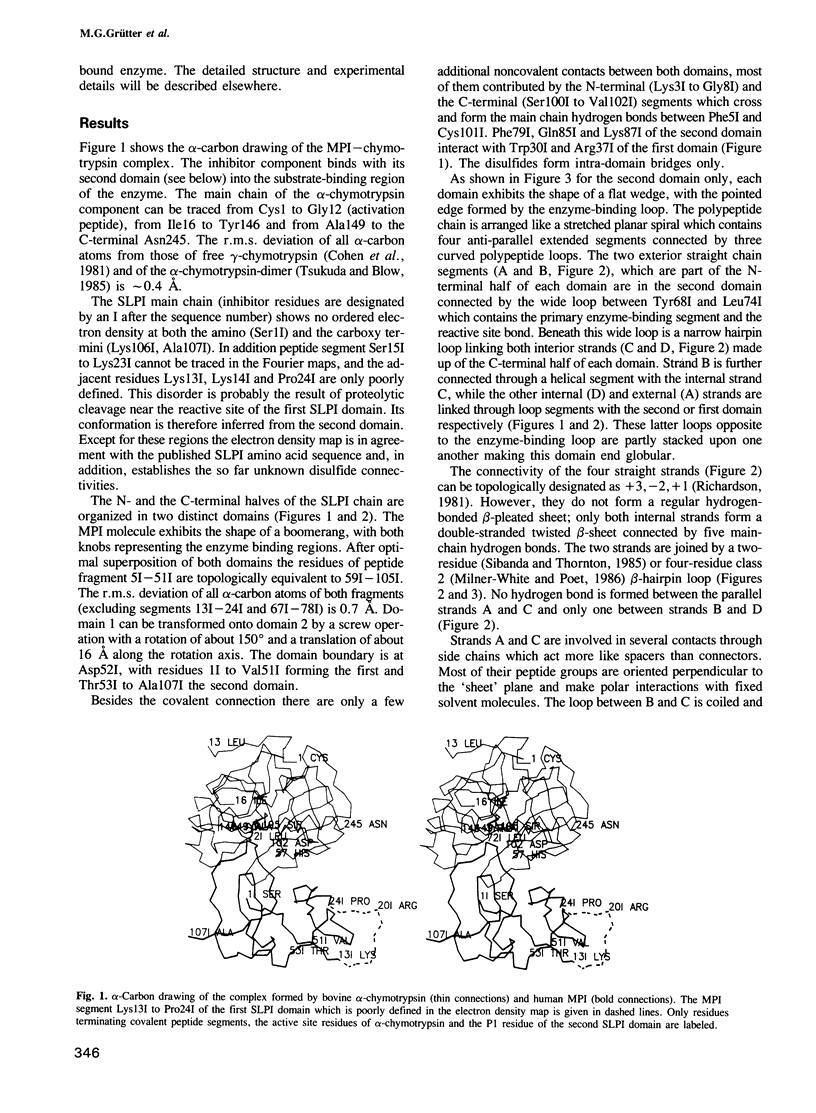
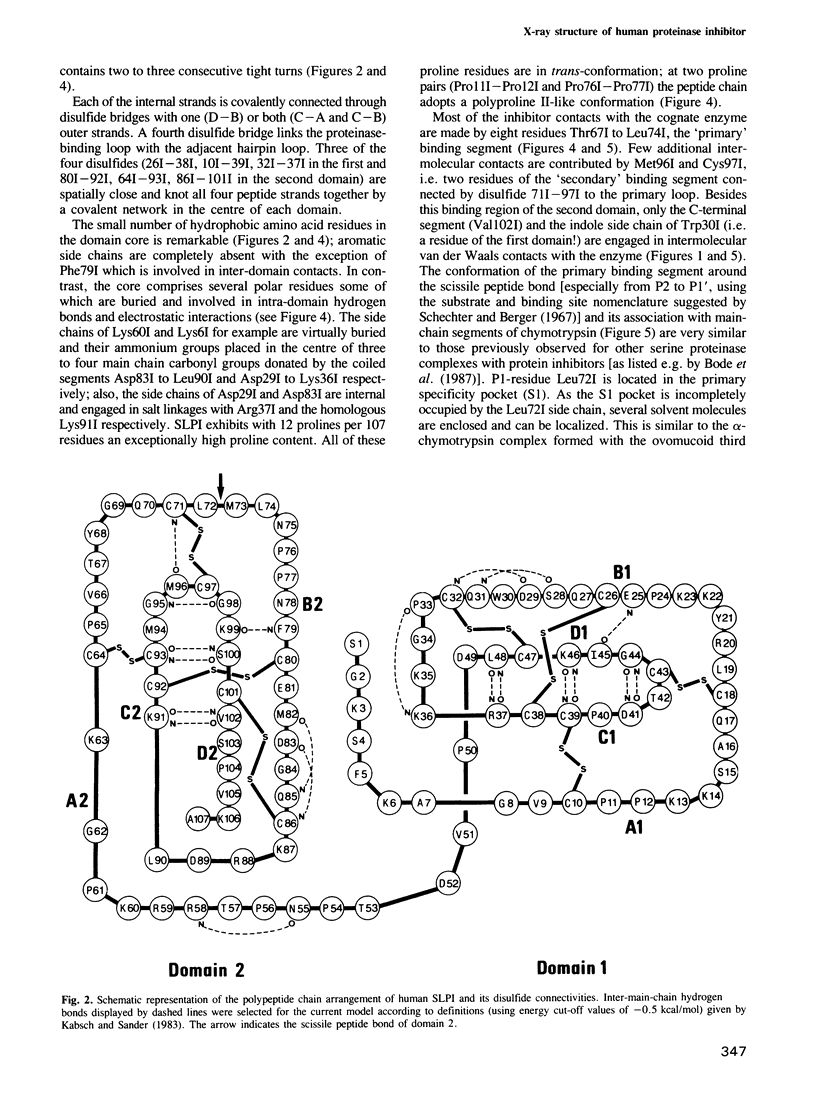
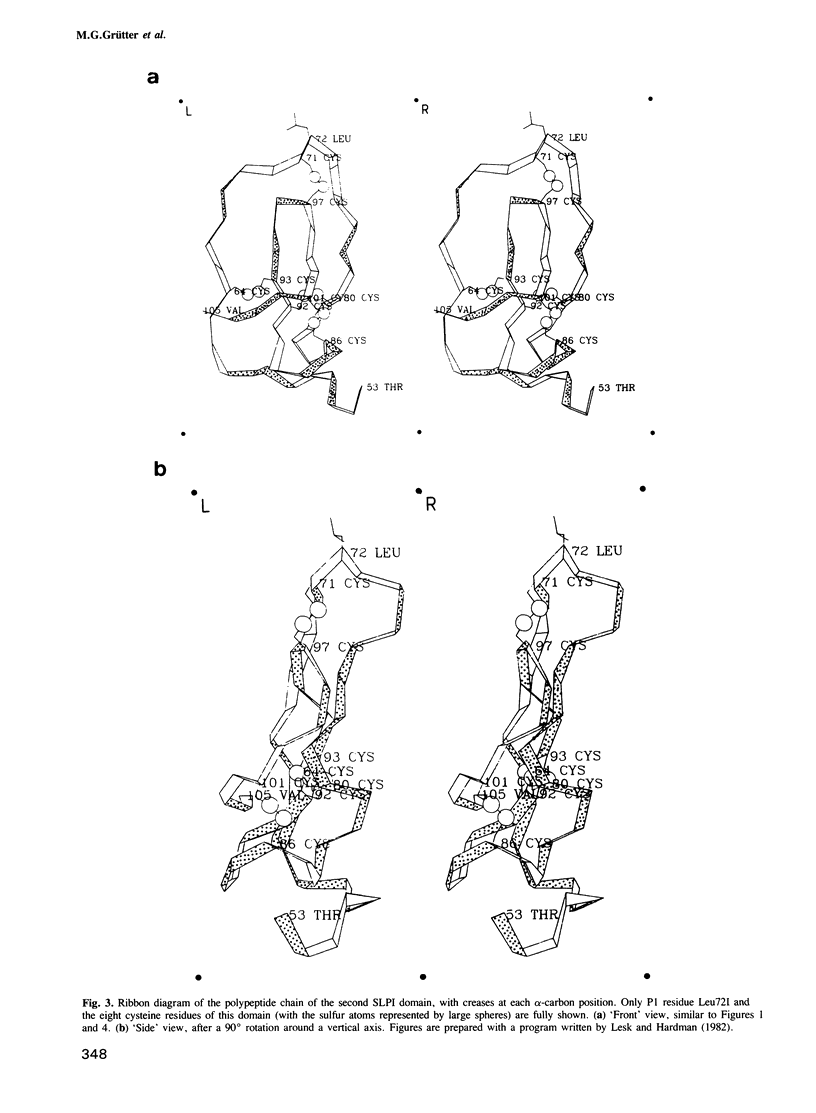
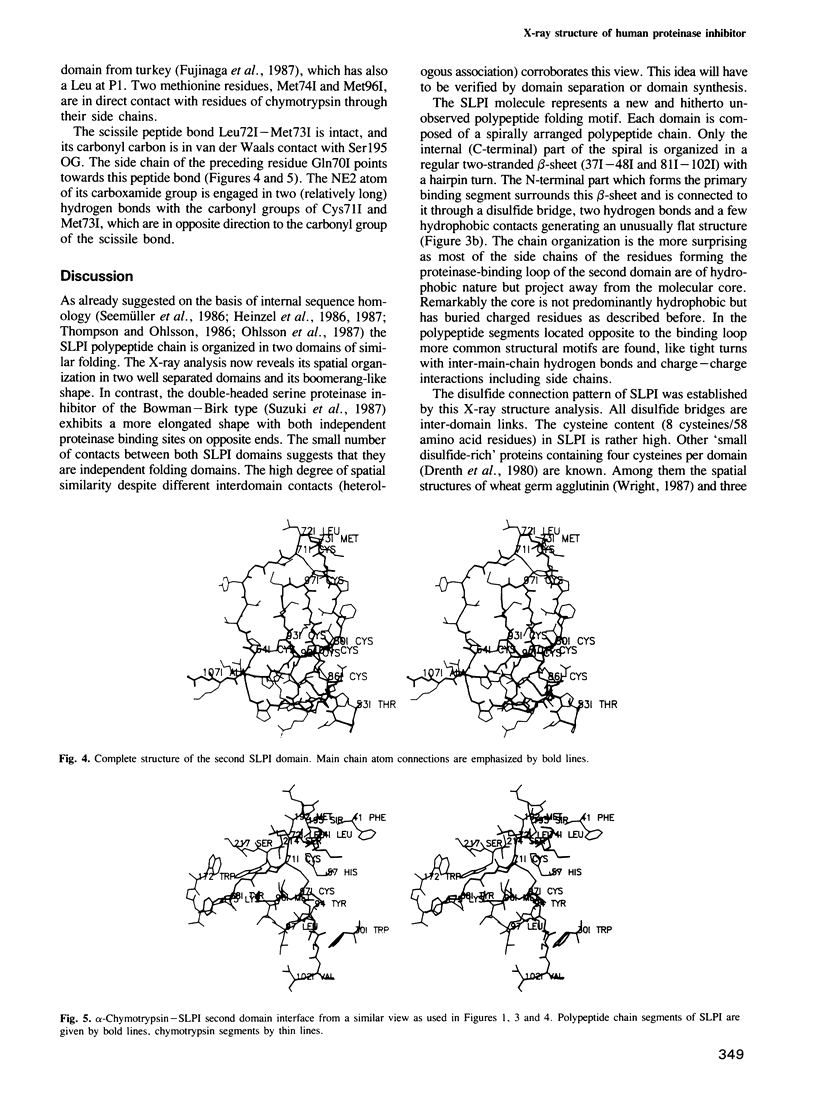
Orthorhombic crystals of the complex formed between bovine alpha-chymotrypsin and a recombinant human mucous proteinase inhibitor (SLPI) were grown. Data to 2.3 A resolution were collected on the area-detector diffractometer FAST. The crystal structure of the complex was solved by Patterson search techniques using chymotrypsin as a search model. A cyclic procedure of modeling and crystallographic refinement enabled the determination of the SLPI structure. The current crystallographic R-value is 0.19. SLPI has a boomerang-like shape with both wings comprising two well separated domains of similar architecture. In each domain the polypeptide chain is arranged like a stretched spiral. Two internal strands form a regular beta-hairpin loop which is accompanied by two external strands linked by the proteinase binding segment. The polypeptide segment of each domain is interconnected by four disulfide bridges with a connectivity pattern hitherto unobserved. The reactive site loop of the second domain has elastase and chymotrypsin binding properties. It contains the scissile peptide bond between Leu72I and Met73I and has a similar conformation to that observed in other serine proteinase protein inhibitors. Eight residues of this loop, two of the adjacent hairpin loop, the C-terminal segment and Trp30I are in direct contact with the cognate enzyme. The binding loop of the first domain (probably with anti-trypsin activity) is disordered due to proteolytic cleavage occurring in the course of crystallization.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Papamokos E., Musil D. The high-resolution X-ray crystal structure of the complex formed between subtilisin Carlsberg and eglin c, an elastase inhibitor from the leech Hirudo medicinalis. Structural analysis, subtilisin structure and interface geometry. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Aug 3;166(3):673–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bode W., Wei A. Z., Huber R., Meyer E., Travis J., Neumann S. X-ray crystal structure of the complex of human leukocyte elastase (PMN elastase) and the third domain of the turkey ovomucoid inhibitor. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2453–2458. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04521.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carp H., Janoff A. Inactivation of bronchial mucous proteinase inhibitor by cigarette smoke and phagocyte-derived oxidants. Exp Lung Res. 1980 Aug;1(3):225–237. doi: 10.3109/01902148009065462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Silverton E. W., Davies D. R. Refined crystal structure of gamma-chymotrypsin at 1.9 A resolution. Comparison with other pancreatic serine proteases. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 5;148(4):449–479. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90186-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandekar A. M., Robinson E. A., Appella E., Qasba P. K. Complete sequence analysis of cDNA clones encoding rat whey phosphoprotein: homology to a protease inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3987–3991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drenth J., Low B. W., Richardson J. S., Wright C. S. The toxin-agglutinin fold. A new group of small protein structures organized around a four-disulfide core. J Biol Chem. 1980 Apr 10;255(7):2652–2655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fink E., Jaumann E., Fritz H., Ingrisch H., Werle E. Protease-Inhibitoren im menschichen Spermaplasma. Isolierung durch Affinitätschromatographie und Hemmverhalten. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Nov;352(11):1591–1594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujinaga M., Sielecki A. R., Read R. J., Ardelt W., Laskowski M., Jr, James M. N. Crystal and molecular structures of the complex of alpha-chymotrypsin with its inhibitor turkey ovomucoid third domain at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):397–418. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90659-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haendle H., Fritz H., Trautschold I., Werle E. Uber einen hormonabhängigen Inhibitor für proteolytische Enzyme in männlichen accessorischen Geschlechtsdrüsen und im Sperma. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1965;343(1):185–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinzel R., Appelhans H., Gassen G., Seemüller U., Machleidt W., Fritz H., Steffens G. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA for human antileukoprotease from cervix uterus. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Oct 1;160(1):61–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09940.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennighausen L. G., Sippel A. E. Mouse whey acidic protein is a novel member of the family of 'four-disulfide core' proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2677–2684. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser K., Haendle H., Reichert R., Werle E. Uber Vorkommen und Eigenschaften eines Proteaseninhibitors in menschlichem Nasensekret. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1971 Jul;352(7):954–958. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochstrasser K., Reichert R., Schwarz S., Werle E. isolierung und Charakterisierung eines Proteaseninhibitors aus menschlichen Bronchialsekret. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1972 Feb;353(2):221–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Schneider M., Epp O., Mayr I., Messerschmidt A., Pflugrath J., Kayser H. Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and preliminary molecular model of the bilin binding protein from the insect Pieris brassicae. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):423–434. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90661-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabsch W., Sander C. Dictionary of protein secondary structure: pattern recognition of hydrogen-bonded and geometrical features. Biopolymers. 1983 Dec;22(12):2577–2637. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasen E. C., Kramps J. A. The N-terminal sequence of antileukoprotease isolated from bronchial secretion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 16;128(1):285–289. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91676-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kueppers F. Proteinase inhibitor in human tears. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Mar 23;229(3):845–849. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90304-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesk A. M., Hardman K. D. Computer-generated schematic diagrams of protein structures. Science. 1982 Apr 30;216(4545):539–540. doi: 10.1126/science.7071602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. W., Preston H. S., Sato A., Rosen L. S., Searl J. E., Rudko A. D., Richardson J. S. Three dimensional structure of erabutoxin b neurotoxic protein: inhibitor of acetylcholine receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2991–2994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner-White E. J., Poet R. Four classes of beta-hairpins in proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Nov 15;240(1):289–292. doi: 10.1042/bj2400289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Tegner H., Akesson U. Isolation and partial characterization of a low molecular weight acid stable protease inhibitor from human bronchial secretion. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1977 May;358(5):583–589. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1977.358.1.583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson M., Rosengren M., Tegner H., Ohlsson K. Quantification of granulocyte elastase inhibitors in human mixed saliva and in pure parotid secretion. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1983 Sep;364(9):1323–1328. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1983.364.2.1323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Berger A. On the size of the active site in proteases. I. Papain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1967 Apr 20;27(2):157–162. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(67)80055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiessler H., Arnhold M., Ohlsson K., Fritz H. Inhibitors of acrosin and granulocyte proteinases from human genital tract secretions. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1976 Sep;357(9):1251–1260. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1976.357.2.1251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seemüller U., Arnhold M., Fritz H., Wiedenmann K., Machleidt W., Heinzel R., Appelhans H., Gassen H. G., Lottspeich F. The acid-stable proteinase inhibitor of human mucous secretions (HUSI-I, antileukoprotease). Complete amino acid sequence as revealed by protein and cDNA sequencing and structural homology to whey proteins and Red Sea turtle proteinase inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1986 Apr 7;199(1):43–48. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibanda B. L., Thornton J. M. Beta-hairpin families in globular proteins. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):170–174. doi: 10.1038/316170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. E., Johnson D. A. Human bronchial leucocyte proteinase inhibitor. Rapid isolation and kinetic analysis with human leucocyte proteinases. Biochem J. 1985 Jan 15;225(2):463–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2250463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stetler G., Brewer M. T., Thompson R. C. Isolation and sequence of a human gene encoding a potent inhibitor of leukocyte proteases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 24;14(20):7883–7896. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.20.7883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki A., Tsunogae Y., Tanaka I., Yamane T., Ashida T., Norioka S., Hara S., Ikenaka T. The structure of Bowman-Birk type protease inhibitor A-II from peanut (Arachis hypogaea) at 3.3 A resolution. J Biochem. 1987 Jan;101(1):267–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Ohlsson K. Isolation, properties, and complete amino acid sequence of human secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor, a potent inhibitor of leukocyte elastase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6692–6696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsernoglou D., Petsko G. A. The crystal structure of a post-synaptic neurotoxin from sea snake at A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1976 Sep 15;68(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80390-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada H., Blow D. M. Structure of alpha-chymotrypsin refined at 1.68 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1985 Aug 20;184(4):703–711. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90314-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallner O., Fritz H. Characterization of an acid-stable proteinase inhibitor in human cervical mucus. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1974 Jun;355(6):709–715. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1974.355.1.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber E., Papamokos E., Bode W., Huber R., Kato I., Laskowski M., Jr Crystallization, crystal structure analysis and molecular model of the third domain of Japanese quail ovomucoid, a Kazal type inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 15;149(1):109–123. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90263-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright C. S. Refinement of the crystal structure of wheat germ agglutinin isolectin 2 at 1.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 5;194(3):501–529. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90678-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



