Abstract
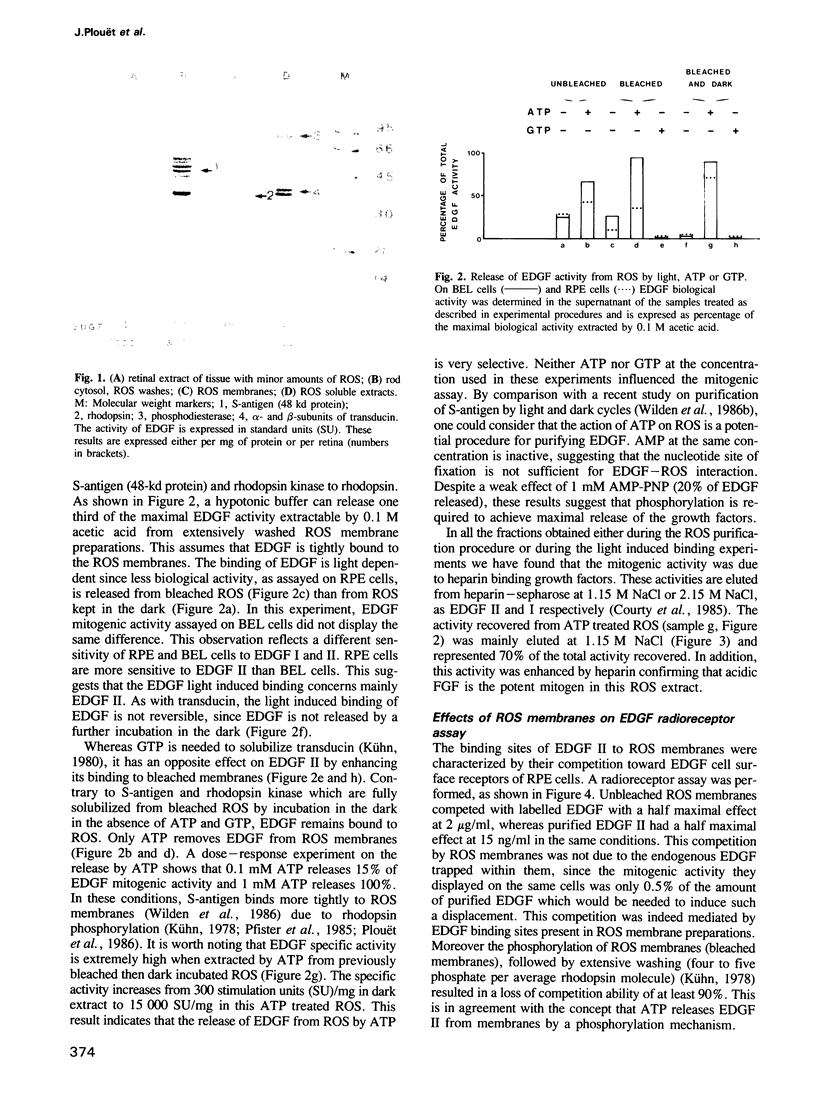
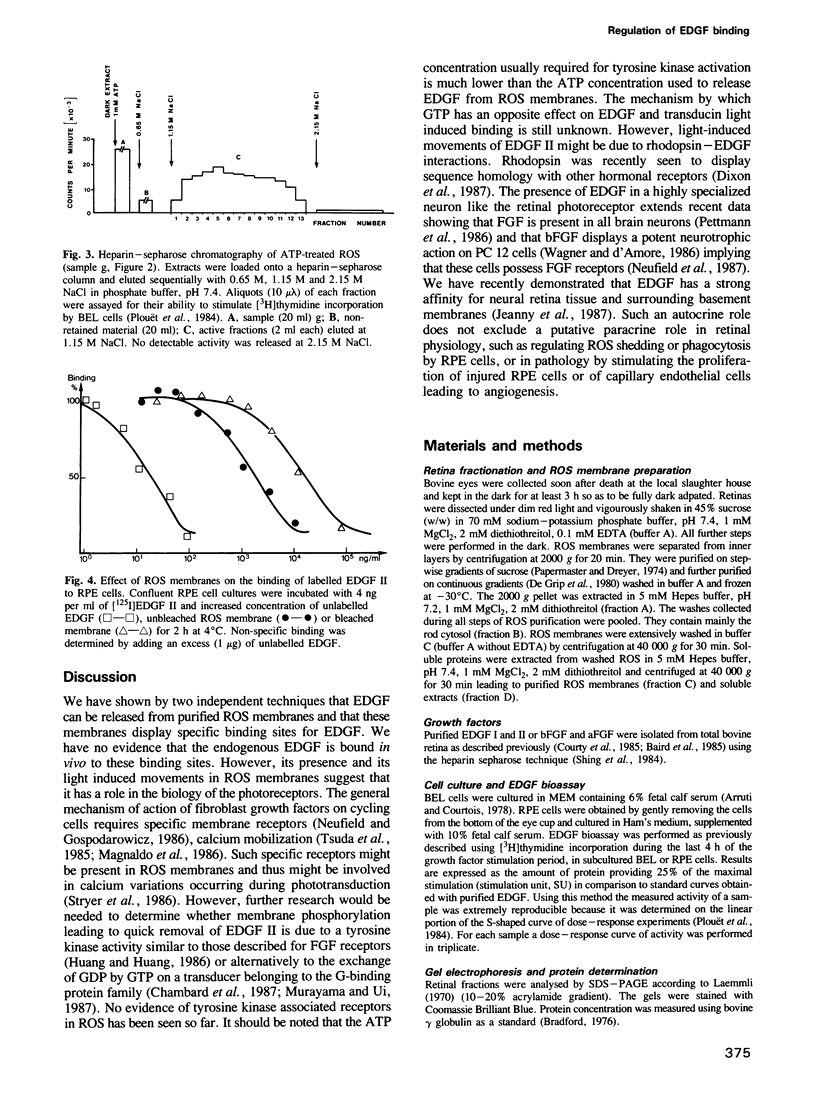
Eye derived growth factor II (EDGF II), the retinal form of acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF) is present in rod outer segments (ROS) purified in the dark, which display higher EDGF specific activity than all other parts of the retina. EDGF binds to ROS disc membranes upon illumination. This binding is not reversible in the dark. ATP, but not GTP, readily releases EDGF from either dark-adapted or previously bleached ROS. The release of EDGF activity from ROS membranes would require a phosphorylation mechanism since AMP-PNP, an ATP analogue, is not efficient. ROS membranes compete with cellular EDGF receptors of retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro for the binding of labelled EDGF II, suggesting that they also possess specific binding sites. These data suggest that EDGF II is involved in photoreceptor cell biology.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arruti C., Courtois Y. Morphological changes and growth stimulation of bovine epithelial lens cells by a retinal extract in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird A., Esch F., Gospodarowicz D., Guillemin R. Retina- and eye-derived endothelial cell growth factors: partial molecular characterization and identity with acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 31;24(27):7855–7860. doi: 10.1021/bi00348a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barritault D., Arruti C., Courtois Y. Is there a ubiquitous growth factor in the eye? Proliferation induced in different cell types by eye-derived growth factors. Differentiation. 1981;18(1):29–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courty J., Loret C., Moenner M., Chevallier B., Lagente O., Courtois Y., Barritault D. Bovine retina contains three growth factor activities with different affinity to heparin: eye derived growth factor I, II, III. Biochimie. 1985 Feb;67(2):265–269. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(85)80056-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuny R., Jeanny J. C., Courtois Y. Lens regeneration from cultured newt irises stimulated by retina-derived growth factors (EDGFs). Differentiation. 1986;32(3):221–229. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. A., Glaser B. M., Brunson S. K., Fenselau A. H. Angiogenic activity from bovine retina: partial purification and characterization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):3068–3072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.3068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Grip W. J., Daemen F. J., Bonting S. L. Isolation and purification of bovine rhodopsin. Methods Enzymol. 1980;67:301–320. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)67038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Sigal I. S., Rands E., Register R. B., Candelore M. R., Blake A. D., Strader C. D. Ligand binding to the beta-adrenergic receptor involves its rhodopsin-like core. Nature. 1987 Mar 5;326(6108):73–77. doi: 10.1038/326073a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Neufeld G., Schweigerer L. Molecular and biological characterization of fibroblast growth factor, an angiogenic factor which also controls the proliferation and differentiation of mesoderm and neuroectoderm derived cells. Cell Differ. 1986 Jul;19(1):1–17. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(86)90021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S. S., Huang J. S. Association of bovine brain-derived growth factor receptor with protein tyrosine kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9568–9571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanny J. C., Fayein N., Moenner M., Chevallier B., Barritault D., Courtois Y. Specific fixation of bovine brain and retinal acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors to mouse embryonic eye basement membranes. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jul;171(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light- and GTP-regulated interaction of GTPase and other proteins with bovine photoreceptor membranes. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):587–589. doi: 10.1038/283587a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kühn H. Light-regulated binding of rhodopsin kinase and other proteins to cattle photoreceptor membranes. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4389–4395. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R., Harper J. W., Fett J. W. Purification of heparin-binding growth factors. Anal Biochem. 1986 Apr;154(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90487-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnaldo I., L'Allemain G., Chambard J. C., Moenner M., Barritault D., Pouysségur J. The mitogenic signaling pathway of fibroblast growth factor is not mediated through polyphosphoinositide hydrolysis and protein kinase C activation in hamster fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 25;261(36):16916–16922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Possible involvement of a GTP-binding protein, the substrate of islet-activating protein, in receptor-mediated signaling responsible for cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12463–12467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D. Basic and acidic fibroblast growth factors interact with the same cell surface receptors. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5631–5637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neufeld G., Gospodarowicz D., Dodge L., Fujii D. K. Heparin modulation of the neurotropic effects of acidic and basic fibroblast growth factors and nerve growth factor on PC12 cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Apr;131(1):131–140. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041310119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papermaster D. S., Dreyer W. J. Rhodopsin content in the outer segment membranes of bovine and frog retinal rods. Biochemistry. 1974 May 21;13(11):2438–2444. doi: 10.1021/bi00708a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petroutsos G., Courty J., Guimaraes R., Pouliquen Y., Barritault D., Plouët J., Courtois Y. Comparison of the effects of EGF, pFGF and EDGF on corneal epithelium wound healing. Curr Eye Res. 1984 Apr;3(4):593–598. doi: 10.3109/02713688409003059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pettmann B., Labourdette G., Weibel M., Sensenbrenner M. The brain fibroblast growth factor (FGF) is localized in neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1986 Jul 24;68(2):175–180. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(86)90137-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfister C., Chabre M., Plouet J., Tuyen V. V., De Kozak Y., Faure J. P., Kühn H. Retinal S antigen identified as the 48K protein regulating light-dependent phosphodiesterase in rods. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):891–893. doi: 10.1126/science.2988124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plouët J., Courty J., Olivié M., Courtois Y., Barritault D. A highly reliable and sensitive assay for the purification of cellular growth factors. Cell Mol Biol. 1984;30(2):105–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Kenney J., Kowalski J., Thomas K. A., Gimenez-Gallego G., Rios-Candelore M., Di Salvo J., Barritault D., Courty J., Courtois Y. A unique family of endothelial cell polypeptide mitogens: the antigenic and receptor cross-reactivity of bovine endothelial cell growth factor, brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor, and eye-derived growth factor-II. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1623–1626. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. Cyclic GMP cascade of vision. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:87–119. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda T., Kaibuchi K., Kawahara Y., Fukuzaki H., Takai Y. Induction of protein kinase C activation and Ca2+ mobilization by fibroblast growth factor in Swiss 3T3 cells. FEBS Lett. 1985 Oct 28;191(2):205–210. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhlrich S., Lagente O., Lenfant M., Courtois Y. Effect of heparin on the stimulation of non-vascular cells by human acidic and basic FGF. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jun 30;137(3):1205–1213. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner J. A., D'Amore P. A. Neurite outgrowth induced by an endothelial cell mitogen isolated from retina. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1363–1367. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Hall S. W., Kühn H. Phosphodiesterase activation by photoexcited rhodopsin is quenched when rhodopsin is phosphorylated and binds the intrinsic 48-kDa protein of rod outer segments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilden U., Wüst E., Weyand I., Kühn H. Rapid affinity purification of retinal arrestin (48 kDa protein) via its light-dependent binding to phosphorylated rhodopsin. FEBS Lett. 1986 Oct 27;207(2):292–295. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81507-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]