Abstract
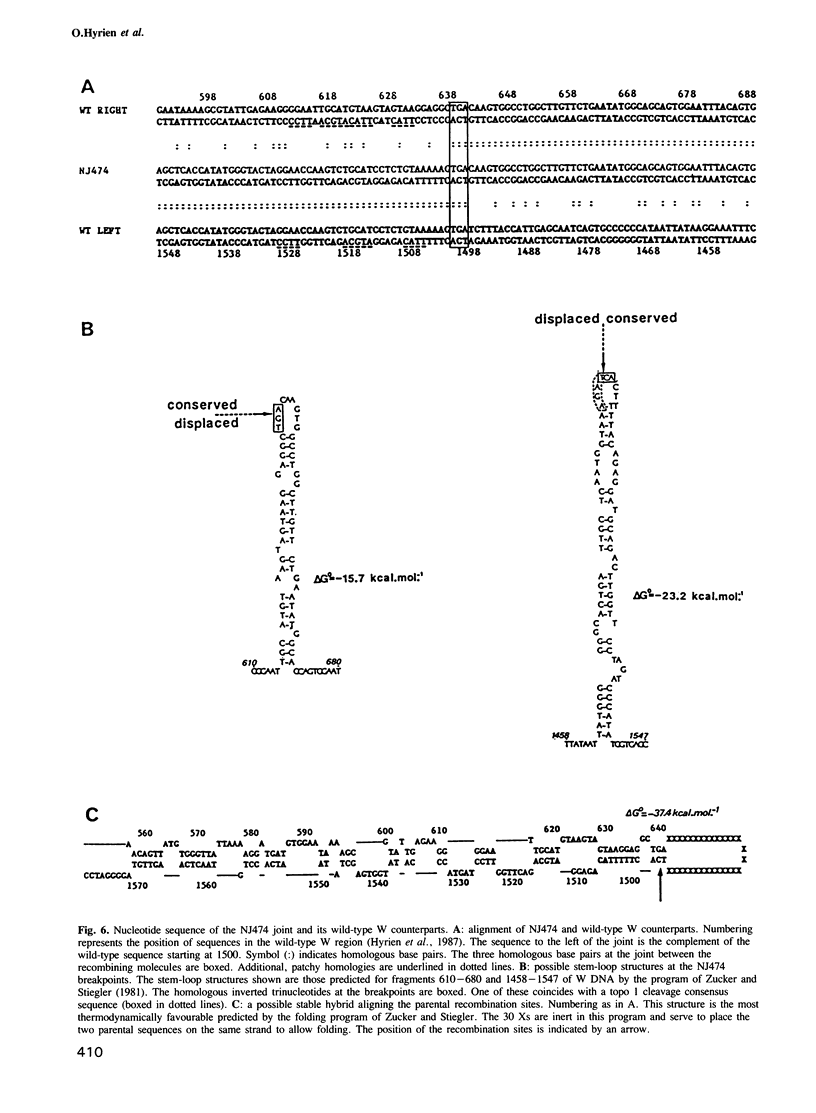
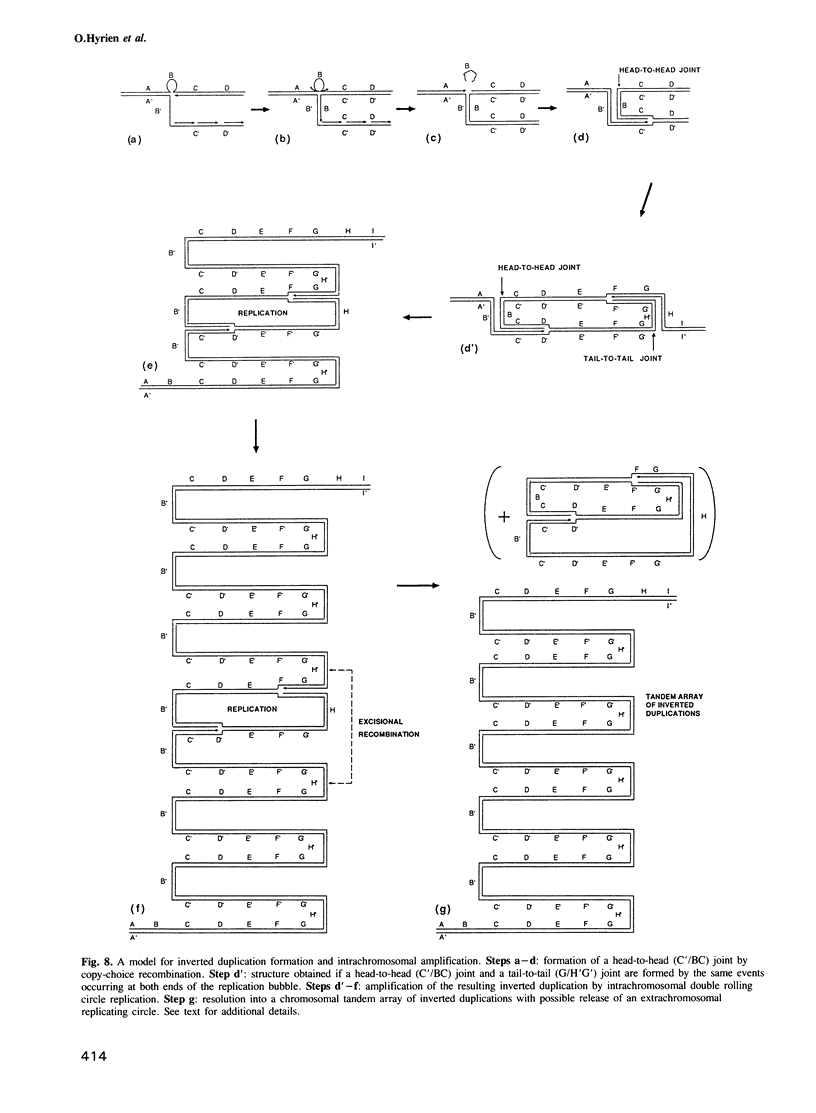
The amplified DNA of HC50474, a Chinese hamster fibroblast cell line selected in three steps for high resistance to coformycin, consists chiefly of 150 copies of a large inverted duplication including the adenylate deaminase gene. Most if not all of these units are more than 2 x 120 kb long. The inverted duplication was first detected in the cells recovered from the second selection step, at the same chromosomal location as the first step amplified units. Its formation and amplification appear to be coupled since the second step cell line already contained 40 copies of this novel structure. Reamplification of the inverted duplication occurred at the third step of selection concomitant with the loss of amplified DNA acquired during the first step. The head-to-head junction has been formed by recombination within a recombinational hotspot described previously [Hyrien, O., Debatisse, M., Buttin, G. and Robert de Saint Vincent, B. (1987) EMBO J., 6, 2401-2408]. Sequences at the joint and in the corresponding wild-type region reveal that the crossover sites, one of which occurs in the putative promoter region of B2 repeat, are located at the top of significant stem-loop structures and that patchy homologies between the parental molecules on one side of the breakpoints allow alignment of these crossover sites. We present a model which explains the formation and amplification of this and other large inverted duplications by errors in DNA replication.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ardeshir F., Giulotto E., Zieg J., Brison O., Liao W. S., Stark G. R. Structure of amplified DNA in different Syrian hamster cell lines resistant to N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;3(11):2076–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.11.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Been M. D., Burgess R. R., Champoux J. J. Nucleotide sequence preference at rat liver and wheat germ type 1 DNA topoisomerase breakage sites in duplex SV40 DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3097–3114. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Selman G. G., Hickman J., Black L., Saunders R. D., Clark A. J. The 45-kb unit of major urinary protein gene organization is a gigantic imperfect palindrome. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1591–1600. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst P., Van der Bliek A. M., Van der Velde-Koerts T., Hes E. Structure of amplified DNA, analyzed by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. J Cell Biochem. 1987 Aug;34(4):247–258. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240340404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P., Champoux J. J., Botchan M. Association of crossover points with topoisomerase I cleavage sites: a model for nonhomologous recombination. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):954–958. doi: 10.1126/science.2997924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock P., Forrester W., Botchan M. DNA sequence studies of simian virus 40 chromosomal excision and integration in rat cells. J Mol Biol. 1984 Mar 25;174(1):55–84. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90365-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caizzi R., Bostock C. J. Gene amplification in methotrexate-resistant mouse cells. IV. Different DNA sequences are amplified in different resistant lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6597–6618. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo M., Cervenka J. Pattern of chromosomal replication in synchronized lymphocytes. I. Evaluation and application of methotrexate block. Hum Genet. 1980;54(1):47–53. doi: 10.1007/BF00279048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., McCoubrey W. K., Jr, Been M. D. DNA structural features that lead to strand breakage by eukaryotic type-I topoisomerase. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:435–442. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claverie J. M. A common philosophy and FORTRAN 77 software package for implementing and searching sequence databases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):397–407. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Wang J. C. Cruciform formation in a negatively supercoiled DNA may be kinetically forbidden under physiological conditions. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debatisse M., Hyrien O., Petit-Koskas E., de Saint-Vincent B. R., Buttin G. Segregation and rearrangement of coamplified genes in different lineages of mutant cells that overproduce adenylate deaminase. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1776–1781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debatisse M., de Saint Vincent B. R., Buttin G. Expression of several amplified genes in an adenylate-deaminase overproducing variant of Chinese hamster fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3123–3127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02268.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federspiel N. A., Beverley S. M., Schilling J. W., Schimke R. T. Novel DNA rearrangements are associated with dihydrofolate reductase gene amplification. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 25;259(14):9127–9140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M., Davies B., Griffiths M., Wilson J., Fried M. Isolation of a gene enhancer within an amplified inverted duplication after "expression selection". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3370–3374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford M., Fried M. Large inverted duplications are associated with gene amplification. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):425–430. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90328-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Futcher A. B. Copy number amplification of the 2 micron circle plasmid of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Theor Biol. 1986 Mar 21;119(2):197–204. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(86)80074-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giulotto E., Saito I., Stark G. R. Structure of DNA formed in the first step of CAD gene amplification. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2115–2121. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04474.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glickman B. W., Ripley L. S. Structural intermediates of deletion mutagenesis: a role for palindromic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):512–516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlin J. L., Milbrandt J. D., Heintz N. H., Azizkhan J. C. DNA sequence amplification in mammalian cells. Int Rev Cytol. 1984;90:31–82. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61487-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyrien O., Debatisse M., Buttin G., de Saint Vincent B. R. A hotspot for novel amplification joints in a mosaic of Alu-like repeats and palindromic A + T-rich DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2401–2408. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02518.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikoku A. S., Hearst J. E. Identification of a structural hairpin in the filamentous chimeric phage M13Gori1. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 15;151(2):245–259. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90514-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaguni L. S., Clayton D. A. Template-directed pausing in in vitro DNA synthesis by DNA polymerase a from Drosophila melanogaster embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):983–987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieny M. P., Lathe R., Lecocq J. P. New versatile cloning and sequencing vectors based on bacteriophage M13. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90039-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach D., Lindsey J. In vivo loss of supercoiled DNA carrying a palindromic sequence. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Aug;204(2):322–327. doi: 10.1007/BF00425517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrman M. A., Goldstein J. L., Russell D. W., Brown M. S. Duplication of seven exons in LDL receptor gene caused by Alu-Alu recombination in a subject with familial hypercholesterolemia. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90079-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Looney J. E., Hamlin J. L. Isolation of the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain from methotrexate-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):569–577. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mouchès C., Pasteur N., Bergé J. B., Hyrien O., Raymond M., de Saint Vincent B. R., de Silvestri M., Georghiou G. P. Amplification of an esterase gene is responsible for insecticide resistance in a California Culex mosquito. Science. 1986 Aug 15;233(4765):778–780. doi: 10.1126/science.3755546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalbantoglu J., Meuth M. DNA amplification--deletion in a spontaneous mutation of the hamster aprt locus: structure and sequence of the novel joint. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8361–8371. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paolella G., Lucero M. A., Murphy M. H., Baralle F. E. The Alu family repeat promoter has a tRNA-like bipartite structure. EMBO J. 1983;2(5):691–696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01486.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Passananti C., Davies B., Ford M., Fried M. Structure of an inverted duplication formed as a first step in a gene amplification event: implications for a model of gene amplification. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1697–1703. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schimke R. T. Gene amplification in cultured animal cells. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):705–713. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90406-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L. A., Gefter M. L. Studies on the mechanism of enzymatic DNA elongation by Escherichia coli DNA polymerase II. J Mol Biol. 1976 May 5;103(1):61–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurvinton C. E., Stahl M. M., Stahl F. W. Large palindromes in the lambda phage genome are preserved in a rec+ host by inhibiting lambda DNA replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sor F., Fukuhara H. Unequal excision of complementary strands is involved in the generation of palindromic repetitions of rho- mitochondrial DNA in yeast. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):391–396. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90458-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spradling A. C., Mahowald A. P. Amplification of genes for chorion proteins during oogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1096–1100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stark G. R., Wahl G. M. Gene amplification. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:447–491. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Vitto L., Padgett R. A., Stark G. R. Single-copy and amplified CAD genes in Syrian hamster chromosomes localized by a highly sensitive method for in situ hybridization. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Mar;2(3):308–319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.3.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss U., Wilson J. H. Repair of single-stranded loops in heteroduplex DNA transfected into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao M. C., Zhu S. G., Yao C. H. Gene amplification in Tetrahymena thermophila: formation of extrachromosomal palindromic genes coding for rRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1260–1267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]