Abstract
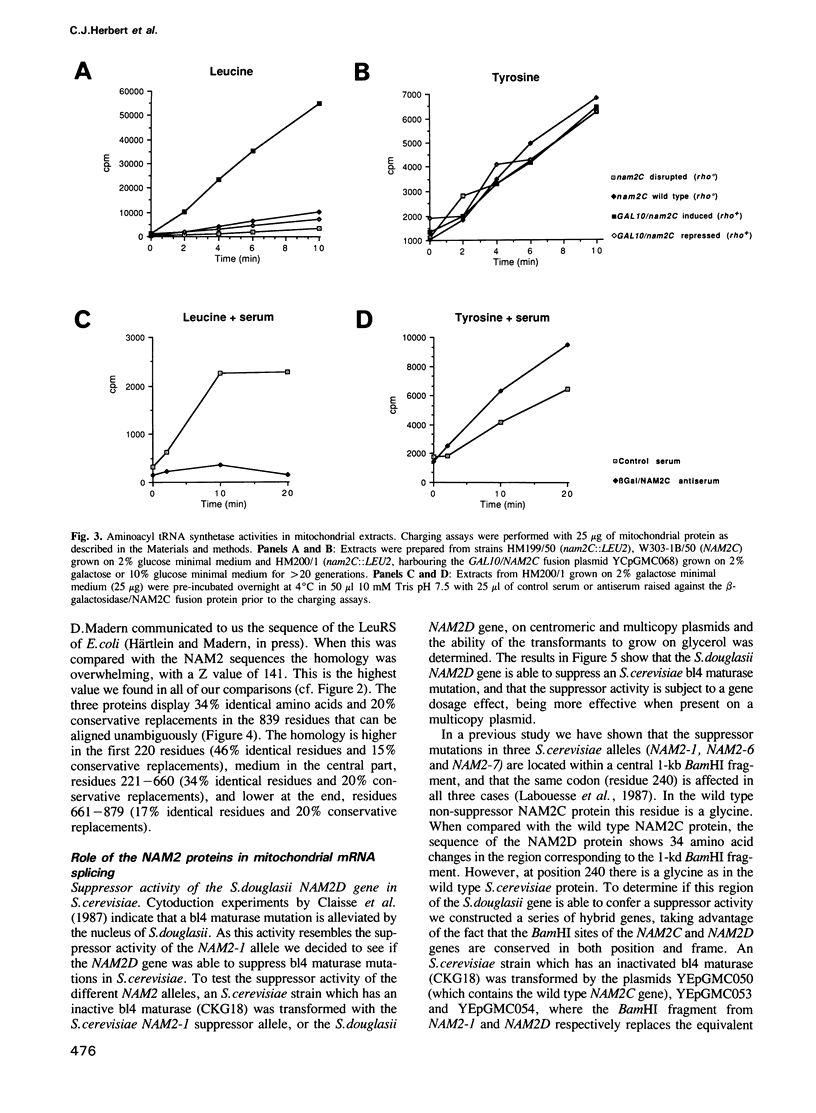
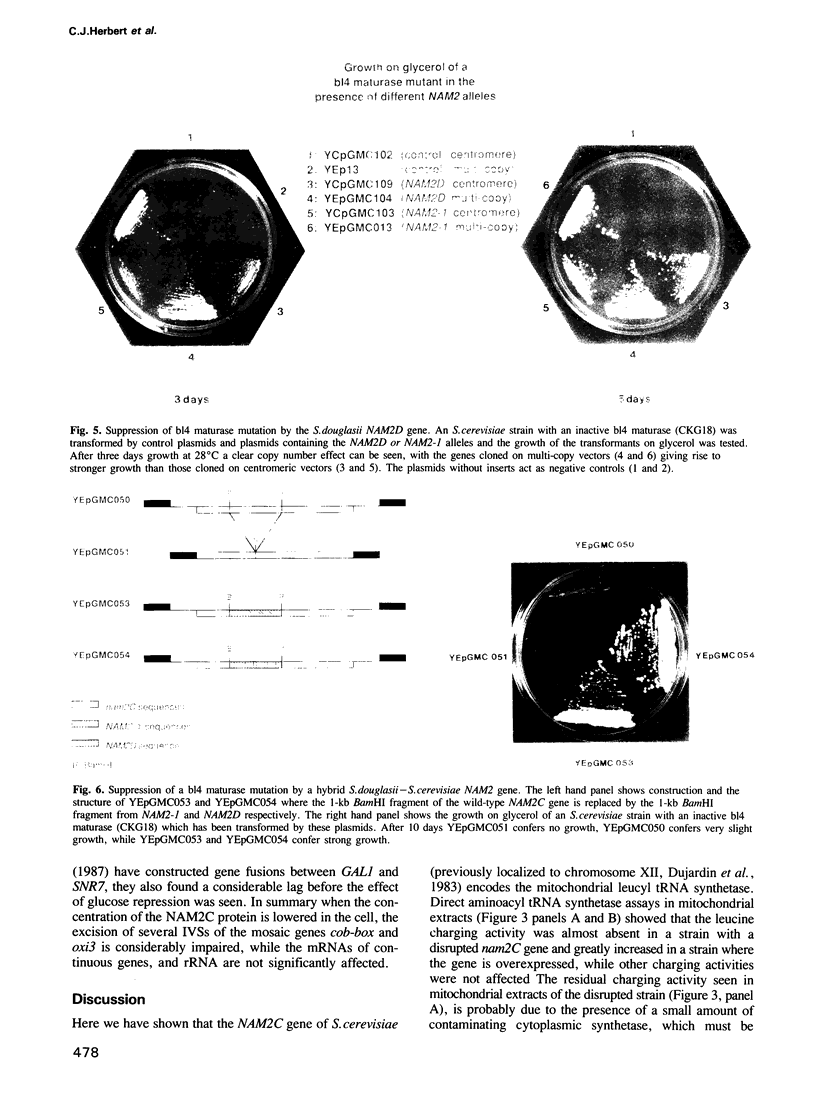
We have cloned and sequenced the NAM2 gene of Saccharomyces douglasii, which is a homologue of the NAM2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The wild-type S.douglasii gene possesses the suppressor functions of the mutant S. cerevisiae NAM2-1 allele, being able to cure a mitochondrial b14 maturase deficiency. By sequence comparisons and direct measurements we have demonstrated that the NAM2 genes encode mitochondrial leucyl tRNA synthetases (EC 6.1.1.4.). Using a derivative of the NAM2 gene, where the expression of the gene is under the control of the UAS GAL10, we have shown that the processing of the pre-mRNA from the two mosaic genes oxi3 and cob-box is impaired when transcription of the gene is repressed. These results lead us to conclude that the mitochondrial leucyl tRNA synthetase is involved in protein synthesis and mRNA splicing. Sequence comparisons show that the mitochondrial and Escherichia coli leucyl tRNA synthetases are highly homologous; however, significant features which may be important for the splicing functions of the mitochondrial enzymes are absent from the bacterial enzyme.
Full text
PDF



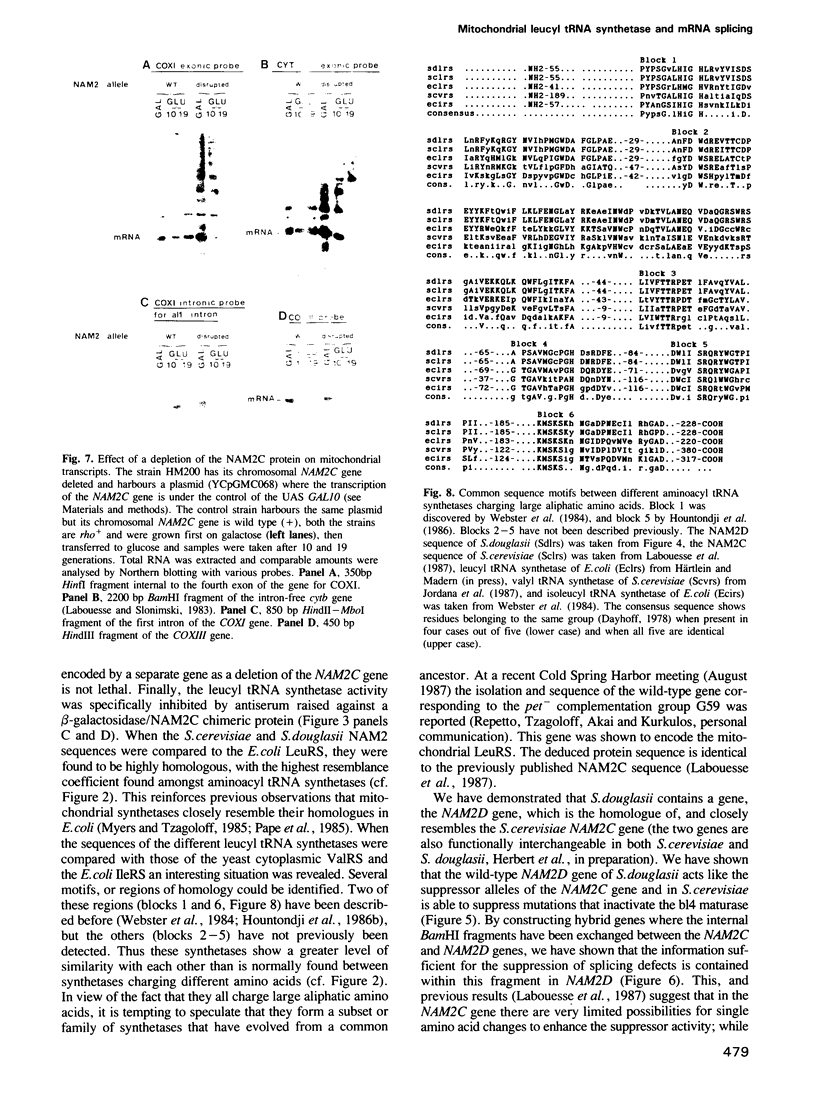




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akins R. A., Lambowitz A. M. A protein required for splicing group I introns in Neurospora mitochondria is mitochondrial tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase or a derivative thereof. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):331–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90488-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banroques J., Delahodde A., Jacq C. A mitochondrial RNA maturase gene transferred to the yeast nucleus can control mitochondrial mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):837–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90065-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Botstein D. Two differentially regulated mRNAs with different 5' ends encode secreted with intracellular forms of yeast invertase. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90384-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cech T. R., Bass B. L. Biological catalysis by RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:599–629. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cryer D. R., Eccleshall R., Marmur J. Isolation of yeast DNA. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;12:39–44. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60950-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dale R. M., McClure B. A., Houchins J. P. A rapid single-stranded cloning strategy for producing a sequential series of overlapping clones for use in DNA sequencing: application to sequencing the corn mitochondrial 18 S rDNA. Plasmid. 1985 Jan;13(1):31–40. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(85)90053-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De La Salle H., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Critical sequences within mitochondrial introns: pleiotropic mRNA maturase and cis-dominant signals of the box intron controlling reductase and oxidase. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujardin G., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Single base substitution in an intron of oxidase gene compensates splicing defects of the cytochrome b gene. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):628–632. doi: 10.1038/298628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujardin G., Pajot P., Groudinsky O., Slonimski P. P. Long range control circuits within mitochondria and between nucleus and mitochondria. I. Methodology and phenomenology of suppressors. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;179(3):469–482. doi: 10.1007/BF00271736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groudinsky O., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. Long range control circuits within mitochondria and between nucleus and mitochondria. II. Genetic and biochemical analyses of suppressors which selectively alleviate the mitochondrial intron mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):493–503. doi: 10.1007/BF00352529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hountondji C., Blanquet S., Lederer F. Methionyl-tRNA synthetase from Escherichia coli: primary structure at the binding site for the 3'-end of tRNAfMet. Biochemistry. 1985 Feb 26;24(5):1175–1180. doi: 10.1021/bi00326a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hountondji C., Dessen P., Blanquet S. Sequence similarities among the family of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Biochimie. 1986 Sep;68(9):1071–1078. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80181-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hountondji C., Lederer F., Dessen P., Blanquet S. Escherichia coli tyrosyl- and methionyl-tRNA synthetases display sequence similarity at the binding site for the 3'-end of tRNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 14;25(1):16–21. doi: 10.1021/bi00349a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacq C., Banroques J., Becam A. M., Slonimski P. P., Guiso N., Danchin A. Antibodies against a fused 'lacZ-yeast mitochondrial intron' gene product allow identification of the mRNA maturase encoded by the fourth intron of the yeast cob-box gene. EMBO J. 1984 Jul;3(7):1567–1572. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02012.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordana X., Chatton B., Paz-Weisshaar M., Buhler J. M., Cramer F., Ebel J. P., Fasiolo F. Structure of the yeast valyl-tRNA synthetase gene (VASI) and the homology of its translated amino acid sequence with Escherichia coli isoleucyl-tRNA synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7189–7194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. The yeast nuclear gene NAM2 is essential for mitochondrial DNA integrity and can cure a mitochondrial RNA-maturase deficiency. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):133–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90068-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Herbert C. J., Dujardin G., Slonimski P. P. Three suppressor mutations which cure a mitochondrial RNA maturase deficiency occur at the same codon in the open reading frame of the nuclear NAM2 gene. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):713–721. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04812.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Netter P., Schroeder R. Molecular basis of the 'box effect', A maturase deficiency leading to the absence of splicing of two introns located in two split genes of yeast mitochondrial DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 1;144(1):85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labouesse M., Slonimski P. P. Construction of novel cytochrome b genes in yeast mitochondria by subtraction or addition of introns. EMBO J. 1983;2(2):269–276. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01416.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazowska J., Jacq C., Slonimski P. P. Sequence of introns and flanking exons in wild-type and box3 mutants of cytochrome b reveals an interlaced splicing protein coded by an intron. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):333–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90344-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw P., Tzagoloff A. Assembly of the mitochondrial membrane system. Characterization of a yeast nuclear gene involved in the processing of the cytochrome b pre-mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9459–9468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Jacquier A., Dujon B. Comparison of fungal mitochondrial introns reveals extensive homologies in RNA secondary structure. Biochimie. 1982 Oct;64(10):867–881. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(82)80349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Pape L. K., Tzagoloff A. Mitochondrial protein synthesis is required for maintenance of intact mitochondrial genomes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2087–2092. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03896.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pape L. K., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Characterization of a yeast nuclear gene (MST1) coding for the mitochondrial threonyl-tRNA1 synthetase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):15362–15370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson B., Guthrie C. An essential yeast snRNA with a U5-like domain is required for splicing in vivo. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):613–624. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90537-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roise D., Horvath S. J., Tomich J. M., Richards J. H., Schatz G. A chemically synthesized pre-sequence of an imported mitochondrial protein can form an amphiphilic helix and perturb natural and artificial phospholipid bilayers. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1327–1334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneller J. M., Schneller C., Martin R., Stahl A. J. Nuclear origin of specific yeast mitochondrial aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1976 May;3(5):1151–1165. doi: 10.1093/nar/3.5.1151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster T., Tsai H., Kula M., Mackie G. A., Schimmel P. Specific sequence homology and three-dimensional structure of an aminoacyl transfer RNA synthetase. Science. 1984 Dec 14;226(4680):1315–1317. doi: 10.1126/science.6390679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss-Brummer B., Hüttenhofer A., Kaudewitz F. Leakiness of termination codons in mitochondrial mutants of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):62–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00328702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H., Maroudas N. G., Wilkie D. Induction of the cytoplasmic petite mutation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the antibacterial antibiotics erythromycin and chloramphenicol. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;111(3):209–223. doi: 10.1007/BF00433106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]