Abstract
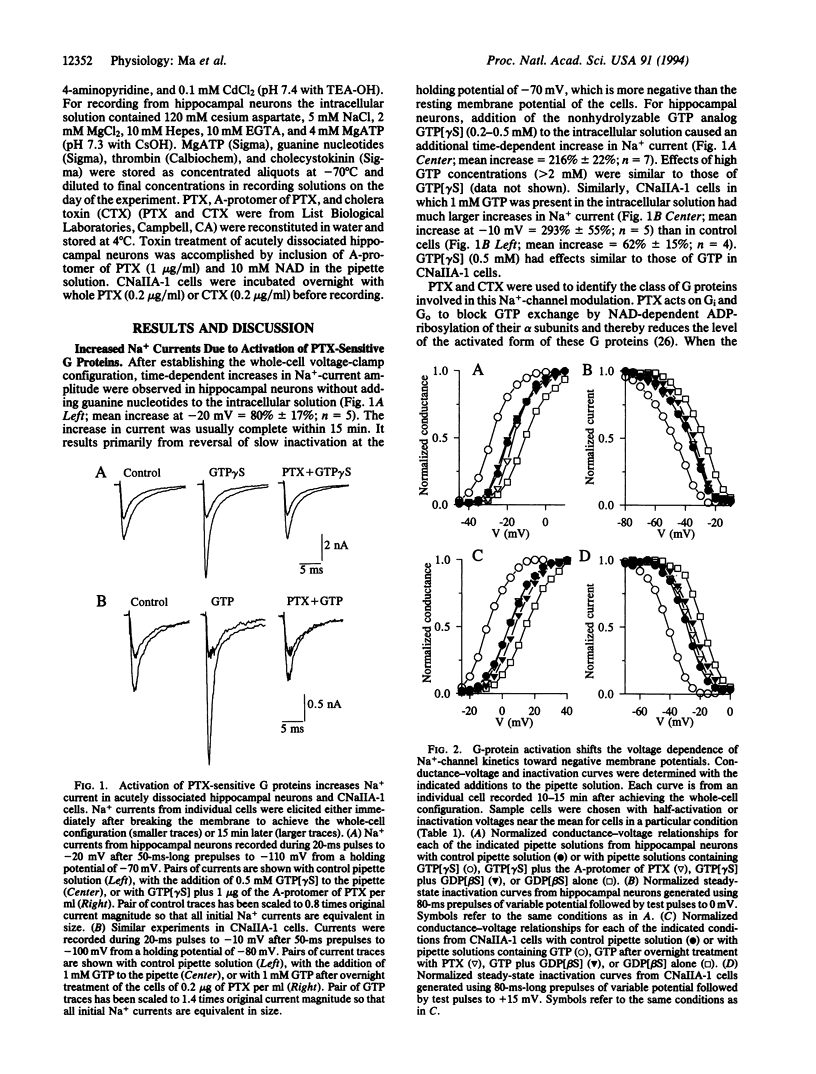
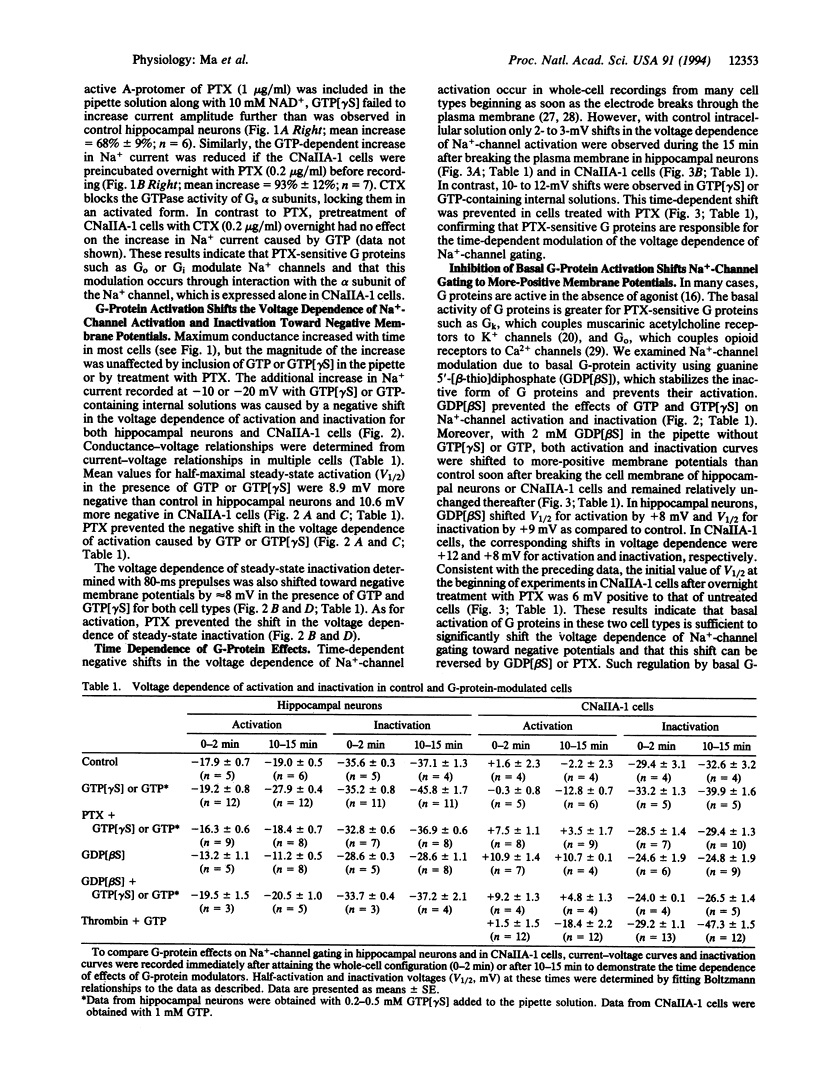
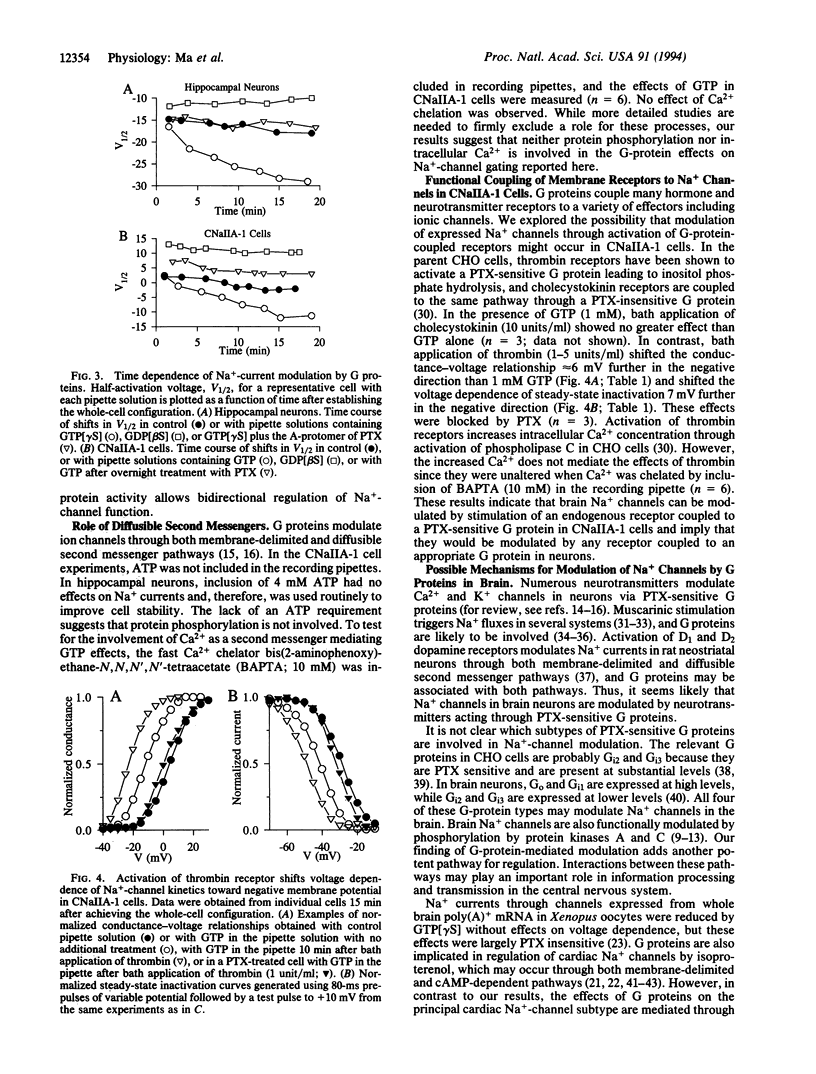
Na+ channels in acutely dissociated rat hippocampal neurons and in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells transfected with a cDNA encoding the alpha subunit of rat brain type IIA Na+ channel (CNaIIA-1 cells) are modulated by guanine nucleotide binding protein (G protein)-coupled pathways under conditions of whole-cell voltage clamp. Activation of G proteins by 0.2-0.5 mM guanosine 5'-[gamma-thio]triphosphate (GTP[gamma S]), a nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, increased Na+ currents recorded in both cell types. The increase in current amplitude was caused by an 8- to 10-mV negative shift in the voltage dependence of both activation and inactivation. The effects of G-protein activators were blocked by treatment with pertussis toxin or guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate (GDP[beta S]), a nonhydrolyzable GDP analog, but not by cholera toxin. GDP[beta S] (2 mM) alone had effects opposite those of GTP[gamma S], shifting Na(+)-channel gating 8-10 mV toward more-positive membrane potentials and suggesting that basal activation of G proteins in the absence of stimulation is sufficient to modulate Na+ channels. In CNaIIA-1 cells, thrombin, which activates pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins in CHO cells, caused a further negative shift in the voltage dependence of Na(+)-channel activation and inactivation beyond that observed with GTP alone. The results in CNaIIA-1 cells indicate that the alpha subunit of the Na+ channel alone is sufficient to mediate G protein effects on gating. The modulation of Na+ channels via a G-protein-coupled pathway acting on Na(+)-channel alpha subunits may regulate electrical excitability through integration of different G-protein-coupled synaptic inputs.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abita J. P., Chicheportiche R., Schweitz H., Lazdunski M. Effects of neurotoxins (veratridine, sea anemone toxin, tetrodotoxin) on transmitter accumulation and release by nerve terminals in vitro. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1838–1844. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anwyl R. Modulation of vertebrate neuronal calcium channels by transmitters. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1991 Sep-Dec;16(3):265–281. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(91)90010-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashkenazi A., Peralta E. G., Winslow J. W., Ramachandran J., Capon D. J. Functionally distinct G proteins selectively couple different receptors to PI hydrolysis in the same cell. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):487–493. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auld V. J., Goldin A. L., Krafte D. S., Marshall J., Dunn J. M., Catterall W. A., Lester H. A., Davidson N., Dunn R. J. A rat brain Na+ channel alpha subunit with novel gating properties. Neuron. 1988 Aug;1(6):449–461. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(88)90176-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitwieser G. E., Szabo G. Uncoupling of cardiac muscarinic and beta-adrenergic receptors from ion channels by a guanine nucleotide analogue. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):538–540. doi: 10.1038/317538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. M. Membrane-delimited cell signaling complexes: direct ion channel regulation by G proteins. J Membr Biol. 1993 Jan;131(2):93–104. doi: 10.1007/BF02791318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cellular and molecular biology of voltage-gated sodium channels. Physiol Rev. 1992 Oct;72(4 Suppl):S15–S48. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1992.72.suppl_4.S15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Armon M., Garty H., Sokolovsky M. G-protein mediates voltage regulation of agonist binding to muscarinic receptors: effects on receptor-Na+ channel interaction. Biochemistry. 1988 Jan 12;27(1):368–374. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Armon M., Kloog Y., Henis Y. I., Sokolovsky M. Batrachotoxin changes the properties of the muscarinic receptor in rat brain and heart: possible interaction(s) between muscarinic receptors and sodium channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3524–3527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Armon M., Sokolovsky M., Dascal N. Modulation of the voltage-dependent sodium channel by agents affecting G-proteins: a study in Xenopus oocytes injected with brain RNA. Brain Res. 1989 Sep 4;496(1-2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91066-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen-Armon M., Sokolovsky M. Interactions between the muscarinic receptors, sodium channels, and guanine nucleotide-binding protein(s) in rat atria. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12498–12505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa T., Herz A. Antagonists with negative intrinsic activity at delta opioid receptors coupled to GTP-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7321–7325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dascal N., Lotan I. Activation of protein kinase C alters voltage dependence of a Na+ channel. Neuron. 1991 Jan;6(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(91)90131-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dell'Acqua M. L., Carroll R. C., Peralta E. G. Transfected m2 muscarinic acetylcholine receptors couple to G alpha i2 and G alpha i3 in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Activation and desensitization of the phospholipase C signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 15;268(8):5676–5685. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernandez J. M., Fox A. P., Krasne S. Membrane patches and whole-cell membranes: a comparison of electrical properties in rat clonal pituitary (GH3) cells. J Physiol. 1984 Nov;356:565–585. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1984.sp015483. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Snutch T., Lübbert H., Dowsett A., Marshall J., Auld V., Downey W., Fritz L. C., Lester H. A., Dunn R. Messenger RNA coding for only the alpha subunit of the rat brain Na channel is sufficient for expression of functional channels in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7503–7507. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. G protein-coupled mechanisms and nervous signaling. Neuron. 1992 Aug;9(2):187–195. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90158-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato E., Anwyl R., Quandt F. N., Narahashi T. Acetylcholine-induced electrical responses in neuroblastoma cells. Neuroscience. 1983 Mar;8(3):643–651. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y., Itoh H., Kozasa T., Nakafuku M., Satoh T. Structure and function of signal-transducing GTP-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:349–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keryer G., Herman G., Rossignol B. Sodium requirement in secretory processes regulated through muscarinic receptors in rat parotid glands: its effect on amylase secretion and phosphatidylinositol labelling. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):4–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80916-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korth M., Kühlkamp V. Muscarinic receptor-mediated increase of intracellular Na+-ion activity and force of contraction. Pflugers Arch. 1985 Mar;403(3):266–272. doi: 10.1007/BF00583598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger B. K., Blaustein M. P., Ratzlaff R. W. Sodium channels in presynaptic nerve terminals. Regulation by neurotoxins. J Gen Physiol. 1980 Sep;76(3):287–313. doi: 10.1085/jgp.76.3.287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze D. L., Lacerda A. E., Wilson D. L., Brown A. M. Cardiac Na currents and the inactivating, reopening, and waiting properties of single cardiac Na channels. J Gen Physiol. 1985 Nov;86(5):691–719. doi: 10.1085/jgp.86.5.691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuo C. C., Bean B. P. Na+ channels must deactivate to recover from inactivation. Neuron. 1994 Apr;12(4):819–829. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., West J. W., Lai Y., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by cAMP-dependent phosphorylation. Neuron. 1992 Jun;8(6):1151–1159. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90135-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M., West J. W., Numann R., Murphy B. J., Scheuer T., Catterall W. A. Convergent regulation of sodium channels by protein kinase C and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1439–1442. doi: 10.1126/science.8396273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel A. W., Raymond J. R., Fitz J. G. Regulation of high-conductance anion channels by G proteins and 5-HT1A receptors in CHO cells. Am J Physiol. 1993 Mar;264(3 Pt 2):F490–F495. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.3.F490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda J. J., Lee H., Shibata E. F. Enhancement of rabbit cardiac sodium channels by beta-adrenergic stimulation. Circ Res. 1992 Jan;70(1):199–207. doi: 10.1161/01.res.70.1.199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Ikeda T., Suzuki H., Takeshima H., Takahashi T., Kuno M., Numa S. Expression of functional sodium channels from cloned cDNA. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):826–828. doi: 10.1038/322826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Numann R., Catterall W. A., Scheuer T. Functional modulation of brain sodium channels by protein kinase C phosphorylation. Science. 1991 Oct 4;254(5028):115–118. doi: 10.1126/science.1656525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Fozzard H. A., Hanck D. A. Mechanism of cAMP-dependent modulation of cardiac sodium channel current kinetics. Circ Res. 1993 Apr;72(4):807–815. doi: 10.1161/01.res.72.4.807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono K., Kiyosue T., Arita M. Isoproterenol, DBcAMP, and forskolin inhibit cardiac sodium current. Am J Physiol. 1989 Jun;256(6 Pt 1):C1131–C1137. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1989.256.6.C1131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfaffinger P. J., Martin J. M., Hunter D. D., Nathanson N. M., Hille B. GTP-binding proteins couple cardiac muscarinic receptors to a K channel. Nature. 1985 Oct 10;317(6037):536–538. doi: 10.1038/317536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheuer T., Auld V. J., Boyd S., Offord J., Dunn R., Catterall W. A. Functional properties of rat brain sodium channels expressed in a somatic cell line. Science. 1990 Feb 16;247(4944):854–858. doi: 10.1126/science.2154850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert B., VanDongen A. M., Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M. Beta-adrenergic inhibition of cardiac sodium channels by dual G-protein pathways. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):516–519. doi: 10.1126/science.2547248. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert B., Vandongen A. M., Kirsch G. E., Brown A. M. Inhibition of cardiac Na+ currents by isoproterenol. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 2):H977–H982. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1990.258.4.H977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soejima M., Noma A. Mode of regulation of the ACh-sensitive K-channel by the muscarinic receptor in rabbit atrial cells. Pflugers Arch. 1984 Apr;400(4):424–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00587544. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surmeier D. J., Kitai S. T. D1 and D2 dopamine receptor modulation of sodium and potassium currents in rat neostriatal neurons. Prog Brain Res. 1993;99:309–324. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6123(08)61354-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West J. W., Scheuer T., Maechler L., Catterall W. A. Efficient expression of rat brain type IIA Na+ channel alpha subunits in a somatic cell line. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):59–70. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90108-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yatani A., Mattera R., Codina J., Graf R., Okabe K., Padrell E., Iyengar R., Brown A. M., Birnbaumer L. The G protein-gated atrial K+ channel is stimulated by three distinct Gi alpha-subunits. Nature. 1988 Dec 15;336(6200):680–682. doi: 10.1038/336680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



