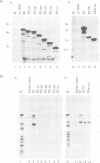
Abstract
The E2 open reading frame of bovine papilloma virus 1 (BPV-1) has been shown to encode both positive and negative acting transcriptional regulatory factors. The DNA binding properties of these factors were analysed to investigate the mechanism by which they might regulate viral gene expression. Polypeptides corresponding to the full-length E2 product and a shorter protein thought to represent the repressor function were synthesized in vitro by translation of T7 polymerase generated transcripts. Using rabbit antisera generated against synthetic peptides from the E2 open reading frame, it was possible to immunoprecipitate each of these products and show that each was capable of binding the same specific sequence located at several sites in the BPV-1 genome. This DNA binding property was mapped to a conserved carboxy-terminal domain of 101 amino acids by analysis of truncated polypeptides synthesized from the E2 open reading frame.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amtmann E., Sauer G. Bovine papilloma virus transcription: polyadenylated RNA species and assessment of the direction of transcription. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):59–66. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.59-66.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Bovine papillomavirus E2 trans-activating gene product binds to specific sites in papillomavirus DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):70–73. doi: 10.1038/325070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Howley P. M. Differential promoter utilization by the bovine papillomavirus in transformed cells and productively infected wart tissues. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1027–1035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04855.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bozkowa K., Siwińska-Gołebiowska H., Lambert I. Badanie właściwości antygenowych treści dwunastniczej u dzieci z mukowiscydoza. Probl Med Wieku Rozwoj. 1975;5:15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dvoretzky I., Shober R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R. A quantitative in vitro focus assay for bovine papilloma virus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):369–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90195-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel L. W., Heilman C. A., Howley P. M. Transcriptional organization of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1983 Sep;47(3):516–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.3.516-528.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri I., Danos O., Yaniv M. Genomic structure of the cottontail rabbit (Shope) papillomavirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(6):1580–1584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.6.1580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haugen T. H., Cripe T. P., Ginder G. D., Karin M., Turek L. P. Trans-activation of an upstream early gene promoter of bovine papilloma virus-1 by a product of the viral E2 gene. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):145–152. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04732.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilman C. A., Engel L., Lowy D. R., Howley P. M. Virus-specific transcription in bovine papillomavirus-transformed mouse cells. Virology. 1982 May;119(1):22–34. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90061-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermonat P. L., Howley P. M. Mutational analysis of the 3' open reading frames and the splice junction at nucleotide 3225 of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Dec;61(12):3889–3895. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.12.3889-3895.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirochika H., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Enhancers and trans-acting E2 transcriptional factors of papillomaviruses. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2599–2606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2599-2606.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4 protein, synthesized in vitro, binds HIS3 regulatory sequences: implications for general control of amino acid biosynthetic genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Spalholz B. A., Howley P. M. A transcriptional repressor encoded by BPV-1 shares a common carboxy-terminal domain with the E2 transactivator. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90663-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. F., Lowy D. R., Dvoretzky I., Howley P. M. Mouse cells transformed by bovine papillomavirus contain only extrachromosomal viral DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2727–2731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay R. D. Binding of a simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein to DNA. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jan 25;145(3):471–488. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90540-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaluk C., Bastia D. The E2 "gene" of bovine papillomavirus encodes an enhancer-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1215–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Howley P. M. Transcriptional trans-activation by the human papillomavirus type 16 E2 gene product. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1630-1638.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabson M. S., Yee C., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus type 1 3' early region transformation and plasmid maintenance functions. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):626–634. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.626-634.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarver N., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Transformation and replication in mouse cells of a bovine papillomavirus--pML2 plasmid vector that can be rescued in bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7147–7151. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Wade M. A synthetic peptide corresponding to the NH2 terminus of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is a pH-dependent hemolysin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4691–4694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Lambert P. F., Yee C. L., Howley P. M. Bovine papillomavirus transcriptional regulation: localization of the E2-responsive elements of the long control region. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2128–2137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2128-2137.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]