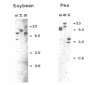
Abstract
We have isolated cDNA clones from soybean and pea that specify nuclear-encoded heat shock proteins (HSPs) which localize to chloroplasts. The mRNAs for these HSPs are undetectable at control temperatures, but increase approximately 150-fold during a 2-h heat shock. Hybridization-selection followed by in vitro translation demonstrates that these HSPs are synthesized as precursor proteins which are processed by the removal of 5-6.5 kd during import into isolated chloroplasts. The nucleotide sequence of the cDNAs shows the derived amino acid sequences of the mature pea and soybean proteins are 79% identical. While the predicted transit peptide encoded by the pea cDNA has some characteristics typical of transit sequences, including high Ser content, multiple basic residues and no acidic residues, it lacks two domains proposed to be important for import and maturation of other chloroplast proteins. The carboxy-terminal region of the chloroplast HSP has significant homology to cytoplasmic HSPs from soybean and other eukaryotes. We hypothesize that the chloroplast HSP shares a common structural and functional domain with low mol. wt HSPs which localize to other parts of the cell, and may have evolved from a nuclear gene.
Full text
PDF
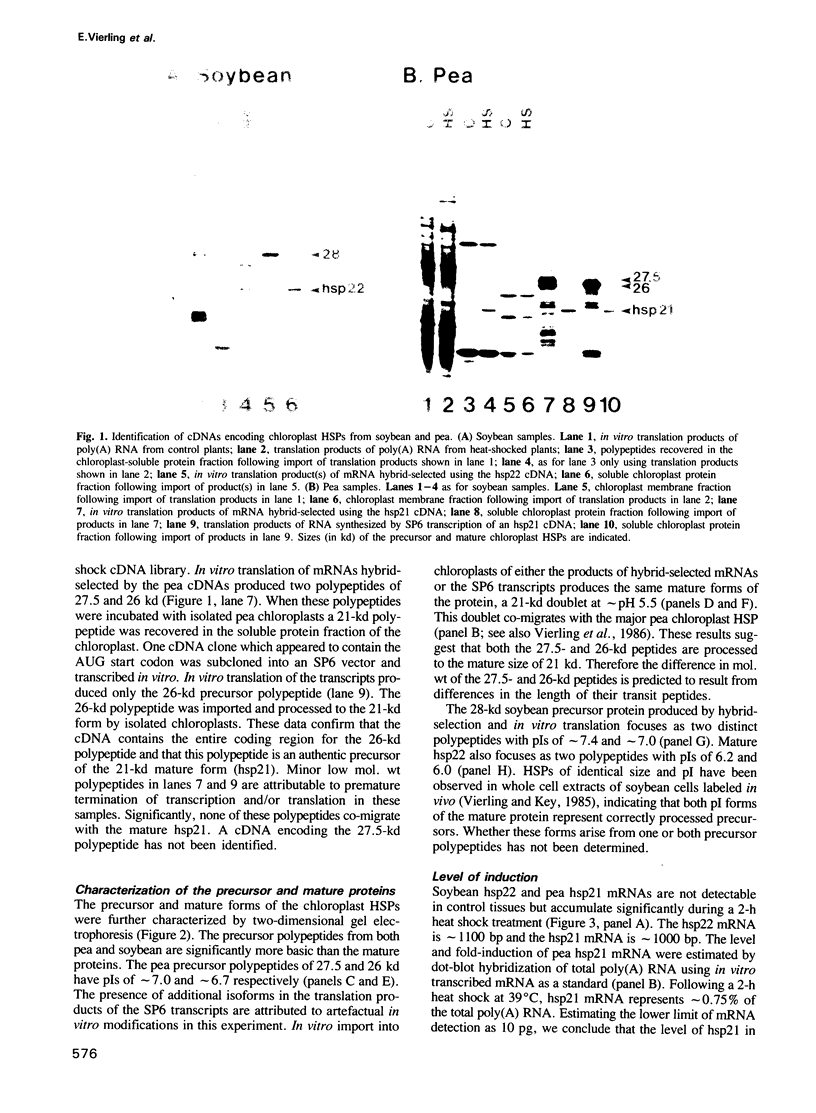
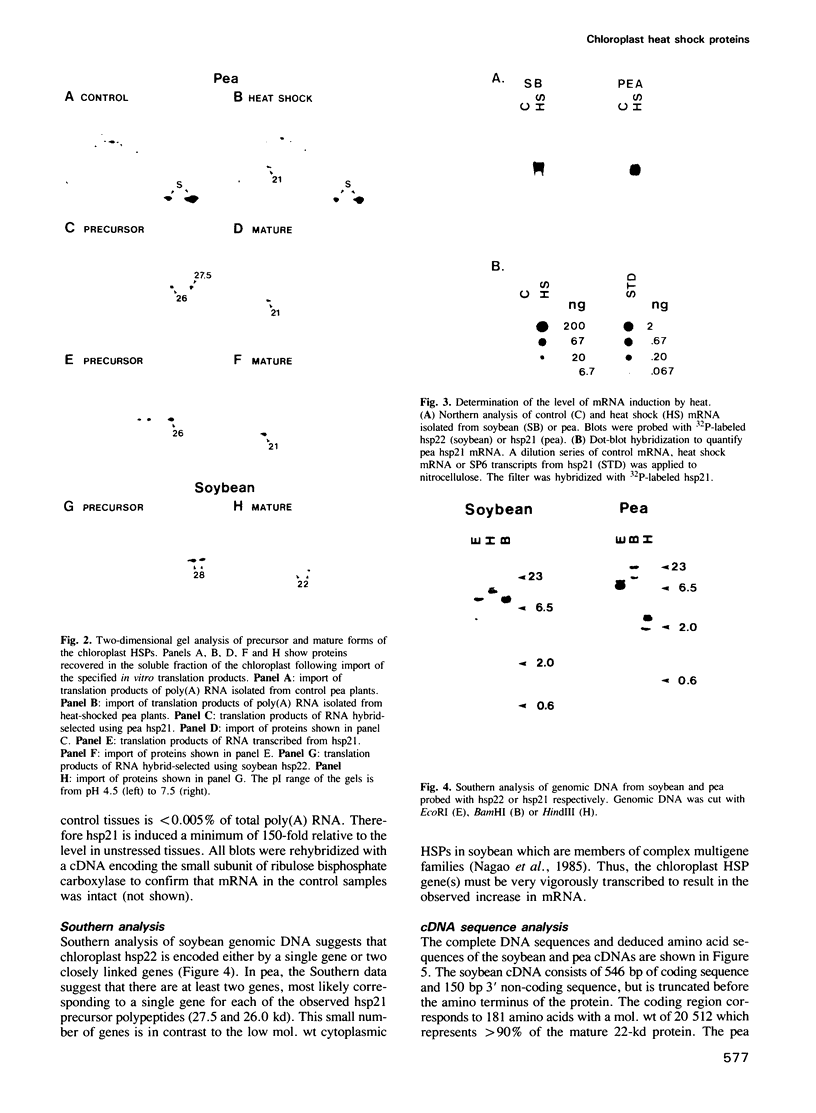

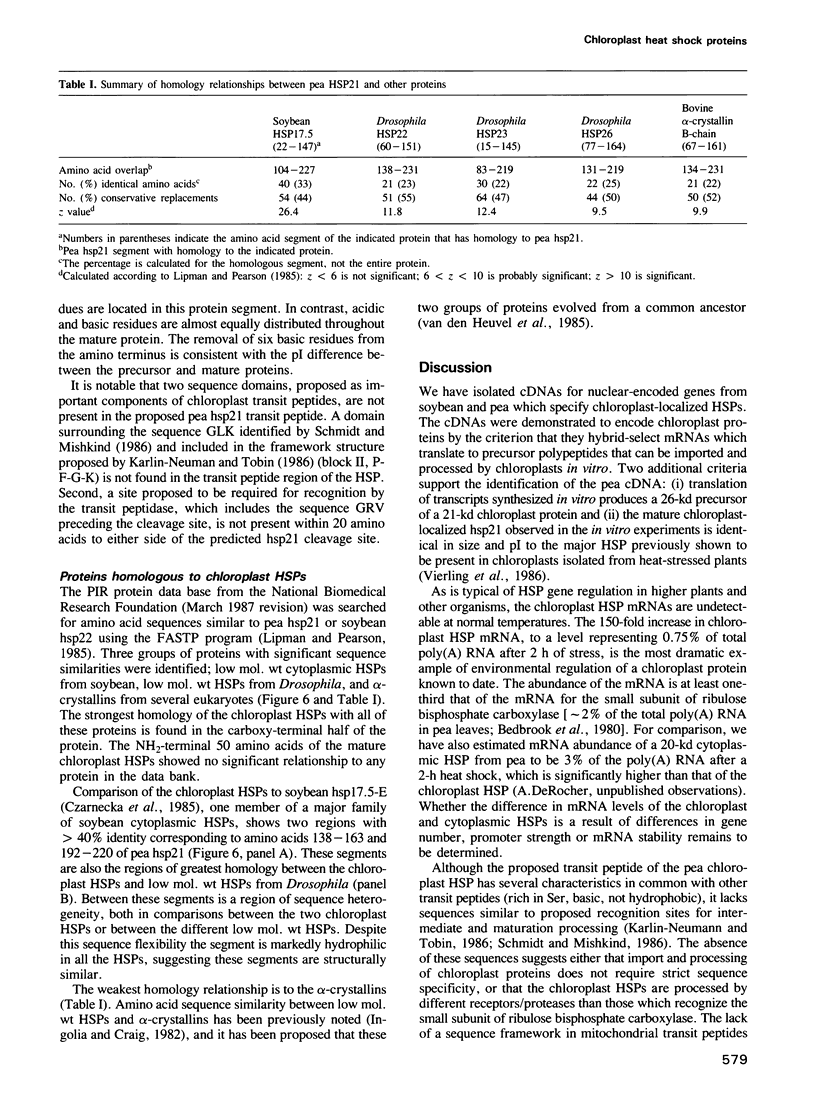


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berry-Lowe S. L., Mc Knight T. D., Shah D. M., Meagher R. B. The nucleotide sequence, expression, and evolution of one member of a multigene family encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in soybean. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(6):483–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. O., Rosbash M. Polynucleotide sequences in eukaryotic DNA and RNA that form ribonuclease-resistant complexes with polyuridylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1974 May 5;85(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarnecka E., Gurley W. B., Nagao R. T., Mosquera L. A., Key J. L. DNA sequence and transcript mapping of a soybean gene encoding a small heat shock protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3726–3730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt J. S., Key J. L. Coordinate expression of ribosomal protein mRNAs following auxin treatment of soybean hypocotyls. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6175–6181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingolia T. D., Craig E. A. Four small Drosophila heat shock proteins are related to each other and to mammalian alpha-crystallin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2360–2364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin-Neumann G. A., Tobin E. M. Transit peptides of nuclear-encoded chloroplast proteins share a common amino acid framework. EMBO J. 1986 Jan;5(1):9–13. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04170.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloppstech K., Meyer G., Schuster G., Ohad I. Synthesis, transport and localization of a nuclear coded 22-kd heat-shock protein in the chloroplast membranes of peas and Chlamydomonas reinhardi. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1901–1909. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S. The heat-shock response. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1151–1191. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loomis W. F., Wheeler S. Heat shock response of Dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1980 Oct;79(2):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagao R. T., Czarnecka E., Gurley W. B., Schöffl F., Key J. L. Genes for low-molecular-weight heat shock proteins of soybeans: sequence analysis of a multigene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3417–3428. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petko L., Lindquist S. Hsp26 is not required for growth at high temperatures, nor for thermotolerance, spore development, or germination. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90563-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss B, Wasmann C C, Bohnert H J. Regions in the transit peptide of SSU essential for transport into chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Aug;209(1):116–121. doi: 10.1007/BF00329845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Mishkind M. L. The transport of proteins into chloroplasts. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:879–912. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.004311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwindinger W. F., Warner J. R. DNA sequence analysis on the IBM-PC. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 2):601–604. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part2.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Wessler S., Fedoroff N. Molecular identification and isolation of the Waxy locus in maize. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90225-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Süss K. H., Yordanov I. T. Biosynthetic cause of in vivo acquired thermotolerance of photosynthetic light reactions and metabolic responses of chloroplasts to heat stress. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):192–199. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tingey S. V., Walker E. L., Coruzzi G. M. Glutamine synthetase genes of pea encode distinct polypeptides which are differentially expressed in leaves, roots and nodules. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):1–9. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierling E., Key J. L. Ribulose 1,5-Bisphosphate Carboxylase Synthesis during Heat Shock. Plant Physiol. 1985 May;78(1):155–162. doi: 10.1104/pp.78.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vierling E., Mishkind M. L., Schmidt G. W., Key J. L. Specific heat shock proteins are transported into chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):361–365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Heuvel R., Hendriks W., Quax W., Bloemendal H. Complete structure of the hamster alpha A crystallin gene. Reflection of an evolutionary history by means of exon shuffling. J Mol Biol. 1985 Sep 20;185(2):273–284. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90403-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Mitochondrial targeting sequences may form amphiphilic helices. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]