Abstract
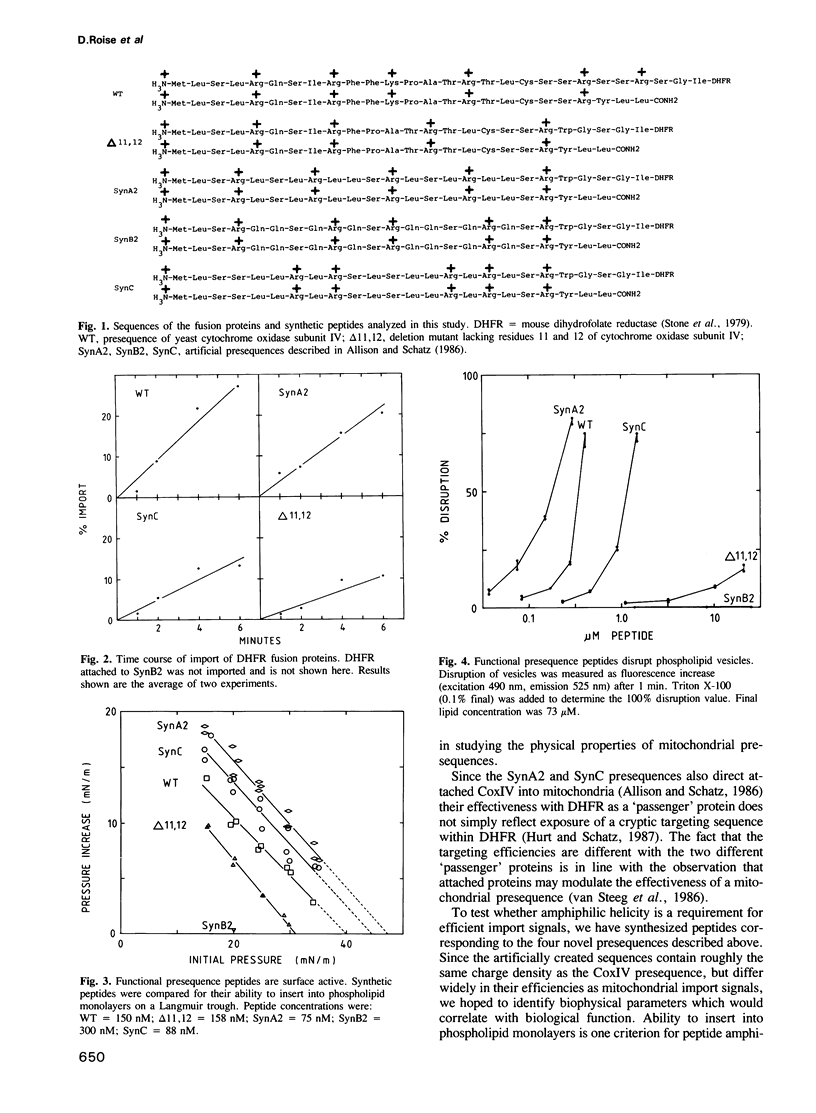
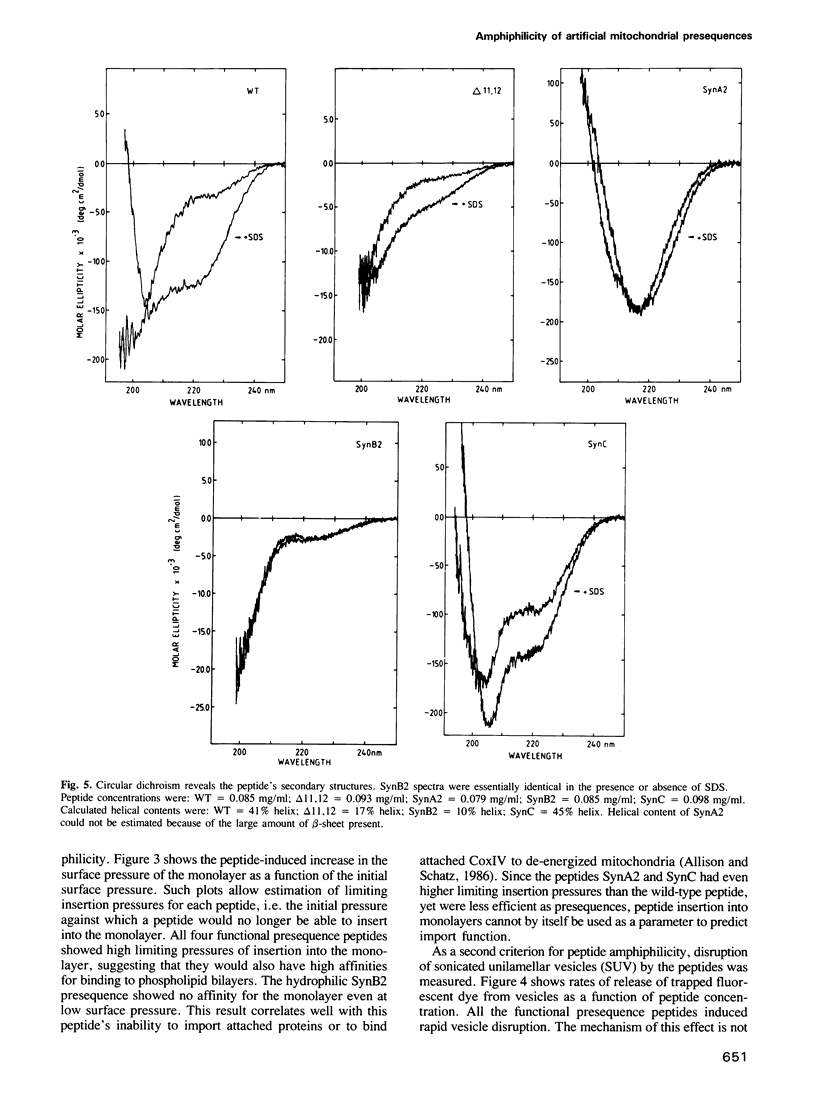
We have shown earlier that a mitochondrial presequence peptide can form an amphiphilic helix. However, the importance of amphiphilicity for mitochondrial presequence function became doubtful when an artificial presequence, designed to be non-amphiphilic, proved to be active as a mitochondrial import signal. We now show experimentally that this 'non-amphiphilic' presequence peptide is, in fact, highly amphiphilic as measured by its ability to insert into phospholipid monolayers and to disrupt phospholipid vesicles. This result, and similar tests on three additional artificial presequences (two functionally active and one inactive), revealed that all active presequences were amphiphilic whereas the inactive presequence was non-amphiphilic. One of the active presequence peptides was non-helical in solution and in the presence of detergent micelles. We conclude that amphiphilicity is necessary for mitochondrial presequence function whereas a helical structure may not be essential.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison D. S., Schatz G. Artificial mitochondrial presequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9011–9015. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A., Schatz G. Sequences from a prokaryotic genome or the mouse dihydrofolate reductase gene can restore the import of a truncated precursor protein into yeast mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3117–3121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernheimer A. W., Rudy B. Interactions between membranes and cytolytic peptides. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 12;864(1):123–141. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(86)90018-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. H., Yang J. T., Chau K. H. Determination of the helix and beta form of proteins in aqueous solution by circular dichroism. Biochemistry. 1974 Jul 30;13(16):3350–3359. doi: 10.1021/bi00713a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epand R. M., Hui S. W., Argan C., Gillespie L. L., Shore G. C. Structural analysis and amphiphilic properties of a chemically synthesized mitochondrial signal peptide. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10017–10020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Daum G., Schatz G. Import of proteins into mitochondria. Energy-dependent uptake of precursors by isolated mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13034–13041. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Kalousek F., Fenton W. A., Pollock R. A., Rosenberg L. E. Targeting of pre-ornithine transcarbamylase to mitochondria: definition of critical regions and residues in the leader peptide. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):451–459. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90466-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Kalousek F., Rosenberg L. E. Arginine in the leader peptide is required for both import and proteolytic cleavage of a mitochondrial precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4930–4933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Allison D. S., Müller U., Schatz G. Amino-terminal deletions in the presequence of an imported mitochondrial protein block the targeting function and proteolytic cleavage of the presequence at the carboxy terminus. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 25;262(3):1420–1424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Schatz G. The amino-terminal region of an imported mitochondrial precursor polypeptide can direct cytoplasmic dihydrofolate reductase into the mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3149–3156. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02272.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Pesold-Hurt B., Suda K., Oppliger W., Schatz G. The first twelve amino acids (less than half of the pre-sequence) of an imported mitochondrial protein can direct mouse cytosolic dihydrofolate reductase into the yeast mitochondrial matrix. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):2061–2068. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurt E. C., Schatz G. A cytosolic protein contains a cryptic mitochondrial targeting signal. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):499–503. doi: 10.1038/325499a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kempf C., Klausner R. D., Weinstein J. N., Van Renswoude J., Pincus M., Blumenthal R. Voltage-dependent trans-bilayer orientation of melittin. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 10;257(5):2469–2476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzin M. I. Khirurgicheskaia pomosch' v Sovetskom Soize (k 50-letiiu obrazoaniia SSSR. Klin Med (Mosk) 1972 Dec;50(12):7–10. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers M., Mayorga O. L., Emtage J., Freire E. Thermodynamic characterization of interactions between ornithine transcarbamylase leader peptide and phospholipid bilayer membranes. Biochemistry. 1987 Jul 14;26(14):4309–4315. doi: 10.1021/bi00388a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfanner N., Neupert W. Transport of proteins into mitochondria: a potassium diffusion potential is able to drive the import of ADP/ATP carrier. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2819–2825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04009.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilgrim D., Young E. T. Primary structure requirements for correct sorting of the yeast mitochondrial protein ADH III to the yeast mitochondrial matrix space. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roise D., Horvath S. J., Tomich J. M., Richards J. H., Schatz G. A chemically synthesized pre-sequence of an imported mitochondrial protein can form an amphiphilic helix and perturb natural and artificial phospholipid bilayers. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1327–1334. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04363.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone D., Paterson S. J., Raper J. H., Phillips A. W. The amino acid sequence of dihydrofolate reductase from the mouse lymphoma L1210. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jan 25;254(2):480–488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stueber D., Ibrahimi I., Cutler D., Dobberstein B., Bujard H. A novel in vitro transcription-translation system: accurate and efficient synthesis of single proteins from cloned DNA sequences. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3143–3148. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02271.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Steeg H., Oudshoorn P., Van Hell B., Polman J. E., Grivell L. A. Targeting efficiency of a mitochondrial pre-sequence is dependent on the passenger protein. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3643–3650. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04694.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassarotti A., Stroud R., Douglas M. Independent mutations at the amino terminus of a protein act as surrogate signals for mitochondrial import. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):705–711. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04811.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson M. E. Compilation of published signal sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 11;12(13):5145–5164. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.13.5145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Heijne G. Mitochondrial targeting sequences may form amphiphilic helices. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1335–1342. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04364.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


