Abstract
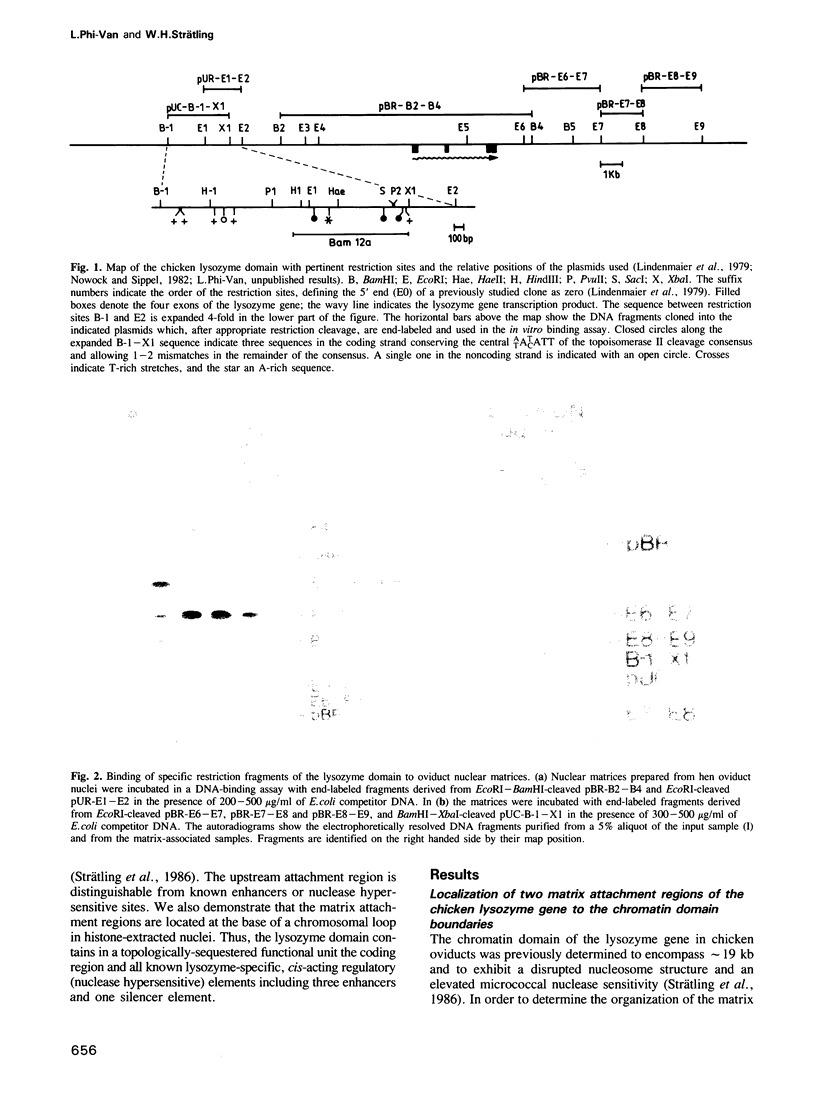
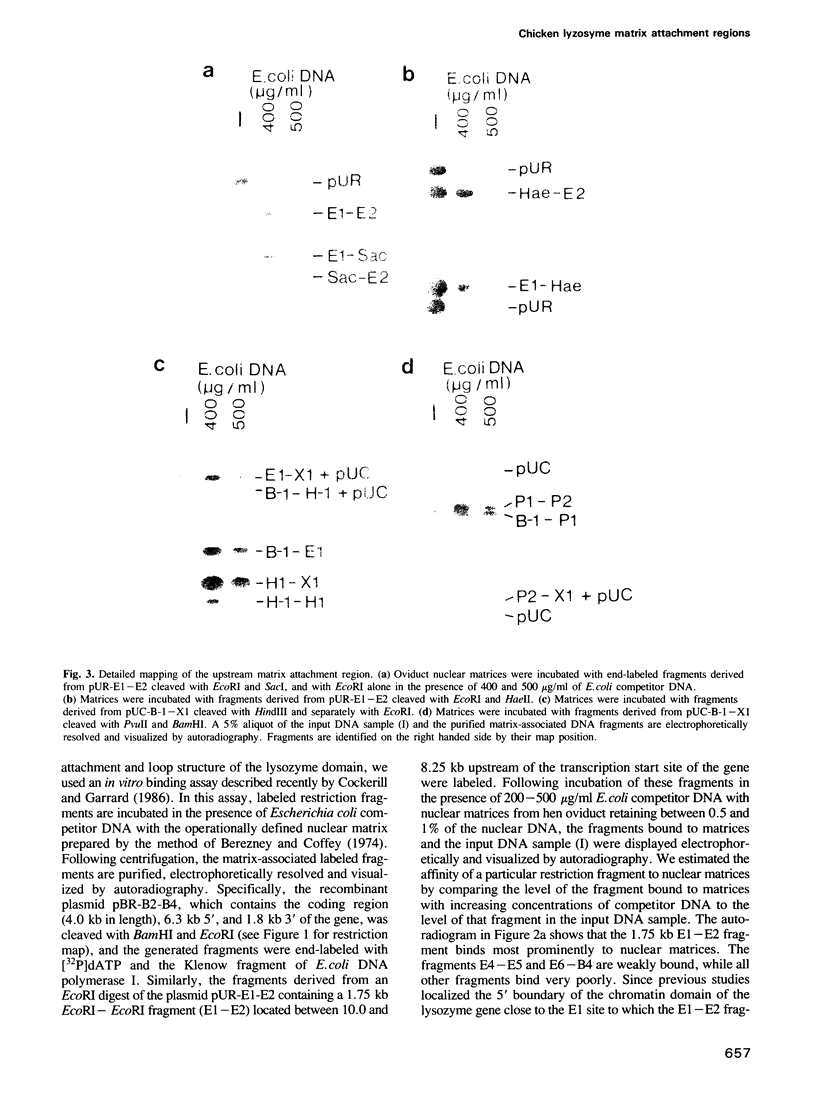
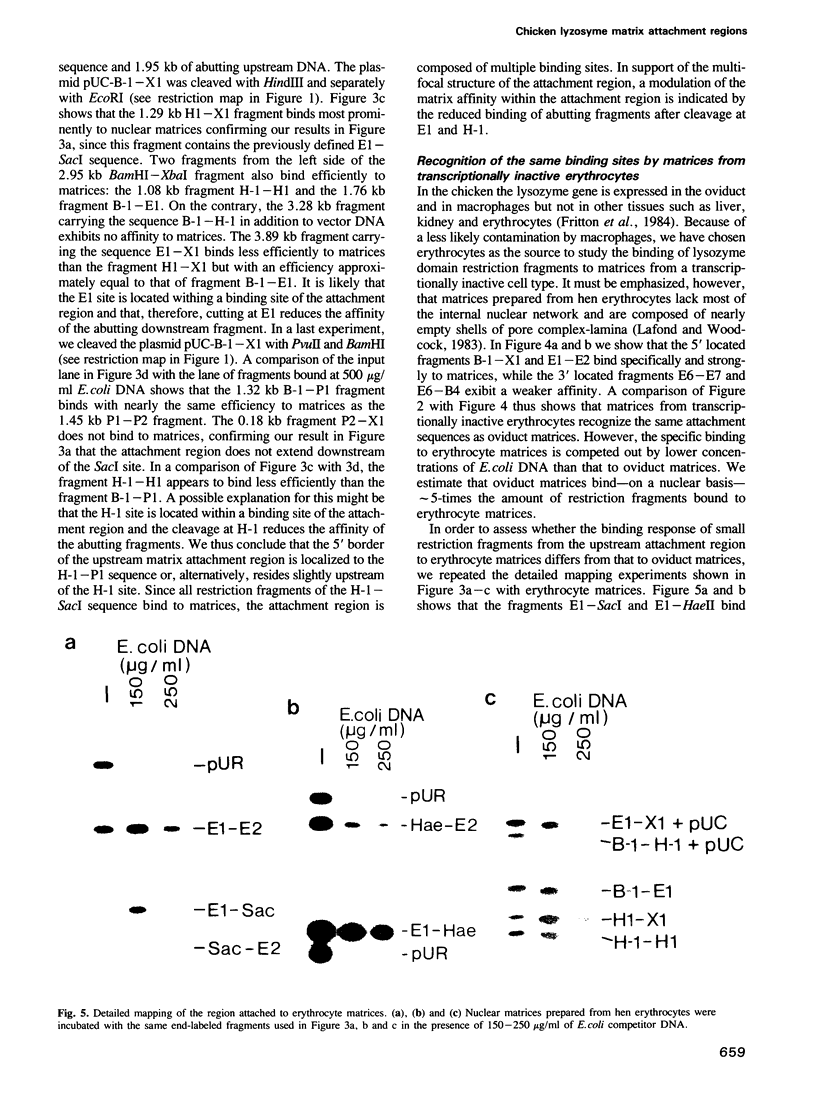
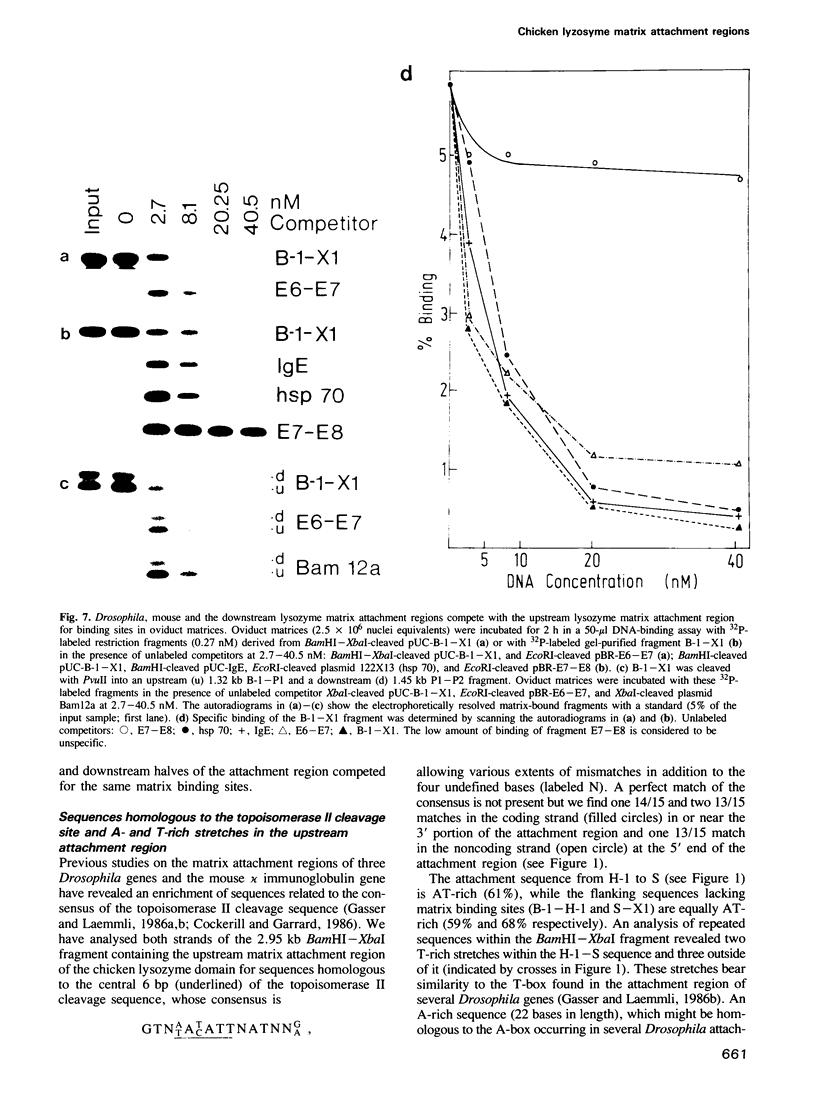
The matrix attachment regions of the chicken lysozyme domain were studied in an in vitro DNA binding assay by incubating oviduct nuclear matrices with labeled restriction fragments. A strong attachment region was localized between 11.1 and 8.85 kb upstream of the transcription start site and a weaker one between 1.3 and 5.0 kb downstream of the poly(A)+ addition site. Both attachment regions co-map with the previously established boundaries of the chromatin domain. The upstream matrix attachment region is distinguishable from known enhancers and is composed of multiple binding sites. We find specific but weaker binding of the same restriction fragments to matrix preparations from transcriptionally inactive chicken erythrocytes indicating a cell-type and transcription-independent conservation of the sites for specific binding of matrix attachment sequences. We also demonstrate that the matrix attachment regions are located at the base of a chromosomal loop in histone-extracted nuclei. Thus, the lysozyme domain represents a topologically-sequestered functional unit containing the coding region and all known lysozyme-specific, cis-acting regulatory elements.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baldacci P., Royal A., Brégégère F., Abastado J. P., Cami B., Daniel F., Kourilsky P. DNA organisation in the chicken lysozyme gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3575–3588. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benyajati C., Worcel A. Isolation, characterization, and structure of the folded interphase genome of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell. 1976 Nov;9(3):393–407. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90084-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Identification of a nuclear protein matrix. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Oct 23;60(4):1410–1417. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berrios M., Osheroff N., Fisher P. A. In situ localization of DNA topoisomerase II, a major polypeptide component of the Drosophila nuclear matrix fraction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4142–4146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burch J. B., Weintraub H. Temporal order of chromatin structural changes associated with activation of the major chicken vitellogenin gene. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):65–76. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90335-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Garrard W. T. Chromosomal loop anchorage of the kappa immunoglobulin gene occurs next to the enhancer in a region containing topoisomerase II sites. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90761-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockerill P. N., Yuen M. H., Garrard W. T. The enhancer of the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus is flanked by presumptive chromosomal loop anchorage elements. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5394–5397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. R., Brazell I. A. Conformational constraints in nuclear DNA. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):287–302. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Earnshaw W. C., Halligan B., Cooke C. A., Heck M. M., Liu L. F. Topoisomerase II is a structural component of mitotic chromosome scaffolds. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1706–1715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T., Nowock J., Strech-Jurk U., Theisen M., Sippel A. E. Alternative sets of DNase I-hypersensitive sites characterize the various functional states of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):163–165. doi: 10.1038/311163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritton H. P., Sippel A. E., Igo-Kemenes T. Nuclease-hypersensitive sites in the chromatin domain of the chicken lysozyme gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jun 11;11(11):3467–3485. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.11.3467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. Cohabitation of scaffold binding regions with upstream/enhancer elements of three developmentally regulated genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):521–530. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90877-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laemmli U. K. The organisation of chromatin loops: characterization of a scaffold attachment site. EMBO J. 1986 Mar;5(3):511–518. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasser S. M., Laroche T., Falquet J., Boy de la Tour E., Laemmli U. K. Metaphase chromosome structure. Involvement of topoisomerase II. J Mol Biol. 1986 Apr 20;188(4):613–629. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(86)80010-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heck M. M., Earnshaw W. C. Topoisomerase II: A specific marker for cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 2):2569–2581. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igó-Kemenes T., Zachau H. G. Domains in chromatin structure. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1978;42(Pt 1):109–118. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1978.042.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen K., Fritton H. P., Igo-Kemenes T. The DNase I sensitive domain of the chicken lysozyme gene spans 24 kb. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6085–6099. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann S. H., Gibson W., Shaper J. H. Characterization of the major polypeptides of the rat liver nuclear envelope. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2710–2719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafond R. E., Woodcock C. L. Status of the nuclear matrix in mature and embryonic chick erythrocyte nuclei. Exp Cell Res. 1983 Aug;147(1):31–39. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(83)90268-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawson G. M., Knoll B. J., March C. J., Woo S. L., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Definition of 5' and 3' structural boundaries of the chromatin domain containing the ovalbumin multigene family. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1501–1507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebkowski J. S., Laemmli U. K. Evidence for two levels of DNA folding in histone-depleted HeLa interphase nuclei. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 5;156(2):309–324. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutz A., Beug H., Graf T. Purification and characterization of cMGF, a novel chicken myelomonocytic growth factor. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3191–3197. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02278.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenmaier W., Nguyen-Huu M. C., Lurz R., Stratmann M., Blin N., Wurtz T., Hauser H. J., Sippel A. E., Schütz G. Arrangement of coding and intervening sequences of chicken lysozyme gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6196–6200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luchnik A. N., Bakayev V. V., Zbarsky I. B., Georgiev G. P. Elastic torsional strain in DNA within a fraction of SV40 minichromosomes: relation to transcriptionally active chromatin. EMBO J. 1982;1(11):1353–1358. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01322.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Mirault M. E., Laemmli U. K. Organization of the higher-order chromatin loop: specific DNA attachment sites on nuclear scaffold. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):223–232. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mirkovitch J., Spierer P., Laemmli U. K. Genes and loops in 320,000 base-pairs of the Drosophila melanogaster chromosome. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 20;190(2):255–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90296-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowock J., Sippel A. E. Specific protein-DNA interaction at four sites flanking the chicken lysozyme gene. Cell. 1982 Sep;30(2):607–615. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90257-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryoji M., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vivo studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90297-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U. Construction and properties of a new cloning vehicle, allowing direct screening for recombinant plasmids. Mol Gen Genet. 1980;178(2):475–477. doi: 10.1007/BF00270503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samal B., Worcel A., Louis C., Schedl P. Chromatin structure of the histone genes of D. melanogaster. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):401–409. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Drosophila topoisomerase II double-strand DNA cleavage: analysis of DNA sequence homology at the cleavage site. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1057–1072. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner C., Muller M., Baniahmad A., Renkawitz R. Lysozyme gene activity in chicken macrophages is controlled by positive and negative regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4163–4178. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strätling W. H., Dölle A., Sippel A. E. Chromatin structure of the chicken lysozyme gene domain as determined by chromatin fractionation and micrococcal nuclease digestion. Biochemistry. 1986 Jan 28;25(2):495–502. doi: 10.1021/bi00350a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theisen M., Stief A., Sippel A. E. The lysozyme enhancer: cell-specific activation of the chicken lysozyme gene by a far-upstream DNA element. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):719–724. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04273.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udvardy A., Schedl P., Sander M., Hsieh T. S. Novel partitioning of DNA cleavage sites for Drosophila topoisomerase II. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):933–941. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90353-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villeponteau B., Lundell M., Martinson H. Torsional stress promotes the DNAase I sensitivity of active genes. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):469–478. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90454-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voellmy R., Rungger D. Transcription of a Drosophila heat shock gene is heat-induced in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1776–1780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Larsen A., Groudine M. Alpha-Globin-gene switching during the development of chicken embryos: expression and chromosome structure. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):333–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90323-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]