Abstract
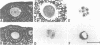
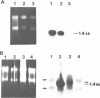
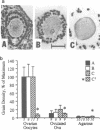
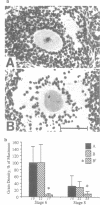
The c-mos proto-oncogene exists as a maternal mRNA in mammalian oocytes, in that it has been shown to accumulate in mouse oocytes during the growth phase and to be present at high levels in fully grown oocytes. The function of c-mos during the subsequent development of the oocytes and embryos was examined by determining the fate of the oocyte c-mos mRNAs by in situ hybridization and Northern blot hybridization analysis. A substantial decrease in the levels of c-mos transcripts was observed in oocytes undergoing meiotic maturation. By the two-cell stage, levels of c-mos transcripts dropped to below the limits of detection using in situ hybridization. c-mos transcripts remained undectable through the blastocyst stage of embryogenesis. Analysis of meiotic maturation in vitro permitted finer temporal resolution of the initial drop in c-mos levels. Between approximately 7 and 17 h of culture, the amount of c-mos mRNA fell to 18-43% of the levels found in the fully grown oocyte. This interval corresponds to the progression of meiotic maturation from metaphase I to metaphase II. Our in vivo studies showed that ovulation per se is not the stimulus for the drop in c-mos transcript levels, since preovulatory metaphase II oocytes exhibited this decline to a degree comparable to that of ovulated metaphase II oocytes. The development specificity of c-mos transcript levels suggests a role of this putative serine kinase in the meiotic maturation of mammalian germ cells.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloom A. M., Mukherjee B. B. RNA synthesis in maturing mouse oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Oct;74(2):577–582. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90421-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornslaeger E. A., Mattei P., Schultz R. M. Involvement of cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein phosphorylation in regulation of mouse oocyte maturation. Dev Biol. 1986 Apr;114(2):453–462. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90209-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bornslaeger E. A., Poueymirou W. T., Mattei P., Schultz R. M. Effects of protein kinase C activators on germinal vesicle breakdown and polar body emission of mouse oocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Aug;165(2):507–517. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90603-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braude P., Pelham H., Flach G., Lobatto R. Post-transcriptional control in the early mouse embryo. Nature. 1979 Nov 1;282(5734):102–105. doi: 10.1038/282102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cathala G., Savouret J. F., Mendez B., West B. L., Karin M., Martial J. A., Baxter J. D. A method for isolation of intact, translationally active ribonucleic acid. DNA. 1983;2(4):329–335. doi: 10.1089/dna.1983.2.329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho W. K., Stern S., Biggers J. D. Inhibitory effect of dibutyryl cAMP on mouse oocyte maturation in vitro. J Exp Zool. 1974 Mar;187(3):383–386. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401870307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Leon V., Johnson A., Bachvarova R. Half-lives and relative amounts of stored and polysomal ribosomes and poly(A) + RNA in mouse oocytes. Dev Biol. 1983 Aug;98(2):400–408. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90369-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLeon D. V., Cox K. H., Angerer L. M., Angerer R. C. Most early-variant histone mRNA is contained in the pronucleus of sea urchin eggs. Dev Biol. 1983 Nov;100(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90211-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue R. P. Maturation of the mouse oocyte in vitro. I. Sequence and timing of nuclear progression. J Exp Zool. 1968 Oct;169(2):237–249. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401690210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Kopf G. S., Schultz R. M. Stage-specific changes in protein phosphorylation accompanying meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes and fertilization of mouse eggs. J Exp Zool. 1986 Sep;239(3):401–409. doi: 10.1002/jez.1402390311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebelhaus D. H., Heikkila J. J., Schultz G. A. Changes in the quantity of histone and actin messenger RNA during the development of preimplantation mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 1983 Jul;98(1):148–154. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giebelhaus D. H., Weitlauf H. M., Schultz G. A. Actin mRNA content in normal and delayed implanting mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 1985 Feb;107(2):407–413. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golbus M. S., Stein M. P. Qualitative patterns of protein synthesis in the mouse oocyte. J Exp Zool. 1976 Dec;198(3):337–342. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401980306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
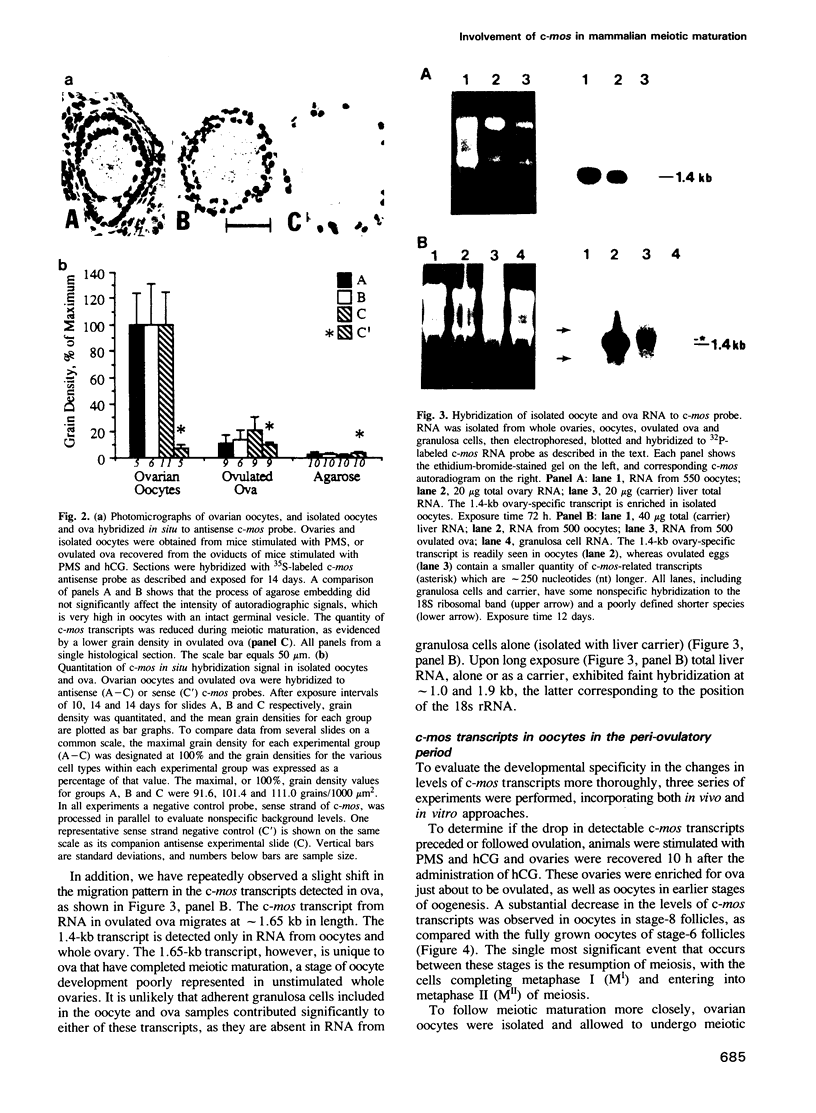
- Goldman D. S., Kiessling A. A., Millette C. F., Cooper G. M. Expression of c-mos RNA in germ cells of male and female mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(13):4509–4513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.13.4509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F., Giebelhaus D. H., Schultz G. A. Quantitative and qualitative changes in histone gene expression during early mouse embryo development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5685–5689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli A., Strickland S., Vassalli J. D. Meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes triggers the translation and polyadenylation of dormant tissue-type plasminogen activator mRNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1201–1211. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leon J., Guerrero I., Pellicer A. Differential expression of the ras gene family in mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1535–1540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell S. A., Arlinghaus R. B. Serine kinase activity associated with Maloney murine sarcoma virus-124-encoded p37mos. Virology. 1985 May;143(1):321–333. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90119-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutter G. L., Wolgemuth D. J. Distinct developmental patterns of c-mos protooncogene expression in female and male mouse germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5301–5305. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskarsson M., McClements W. L., Blair D. G., Maizel J. V., Vande Woude G. F. Properties of a normal mouse cell DNA sequence (sarc) homologous to the src sequence of Moloney sarcoma virus. Science. 1980 Mar 14;207(4436):1222–1224. doi: 10.1126/science.6243788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
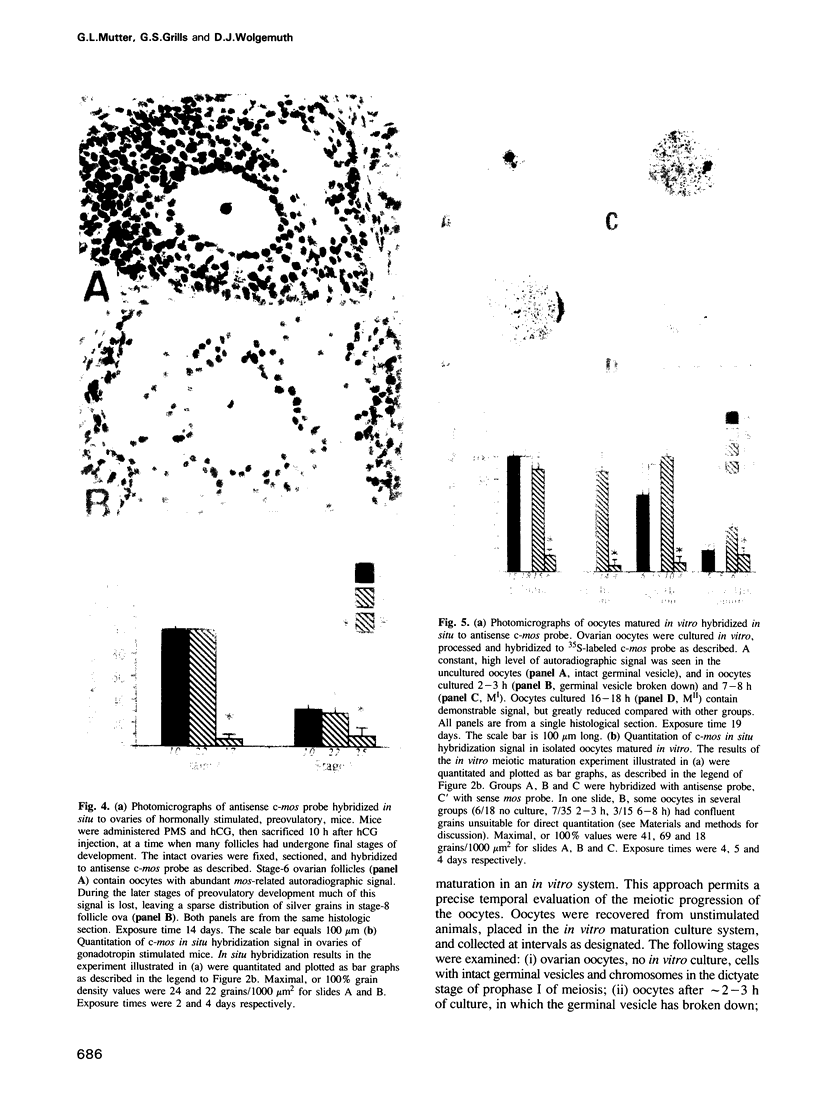
- Papkoff J., Lai M. H., Hunter T., Verma I. M. Analysis of transforming gene products from Moloney murine sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):109–119. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90365-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papkoff J., Nigg E. A., Hunter T. The transforming protein of Moloney murine sarcoma virus is a soluble cytoplasmic protein. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90345-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen T., Peters H. Proposal for a classification of oocytes and follicles in the mouse ovary. J Reprod Fertil. 1968 Dec;17(3):555–557. doi: 10.1530/jrf.0.0170555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pikó L., Clegg K. B. Quantitative changes in total RNA, total poly(A), and ribosomes in early mouse embryos. Dev Biol. 1982 Feb;89(2):362–378. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90325-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponzetto C., Wolgemuth D. J. Haploid expression of a unique c-abl transcript in the mouse male germ line. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1791–1794. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Propst F., Rosenberg M. P., Iyer A., Kaul K., Vande Woude G. F. c-mos proto-oncogene RNA transcripts in mouse tissues: structural features, developmental regulation, and localization in specific cell types. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1629–1637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
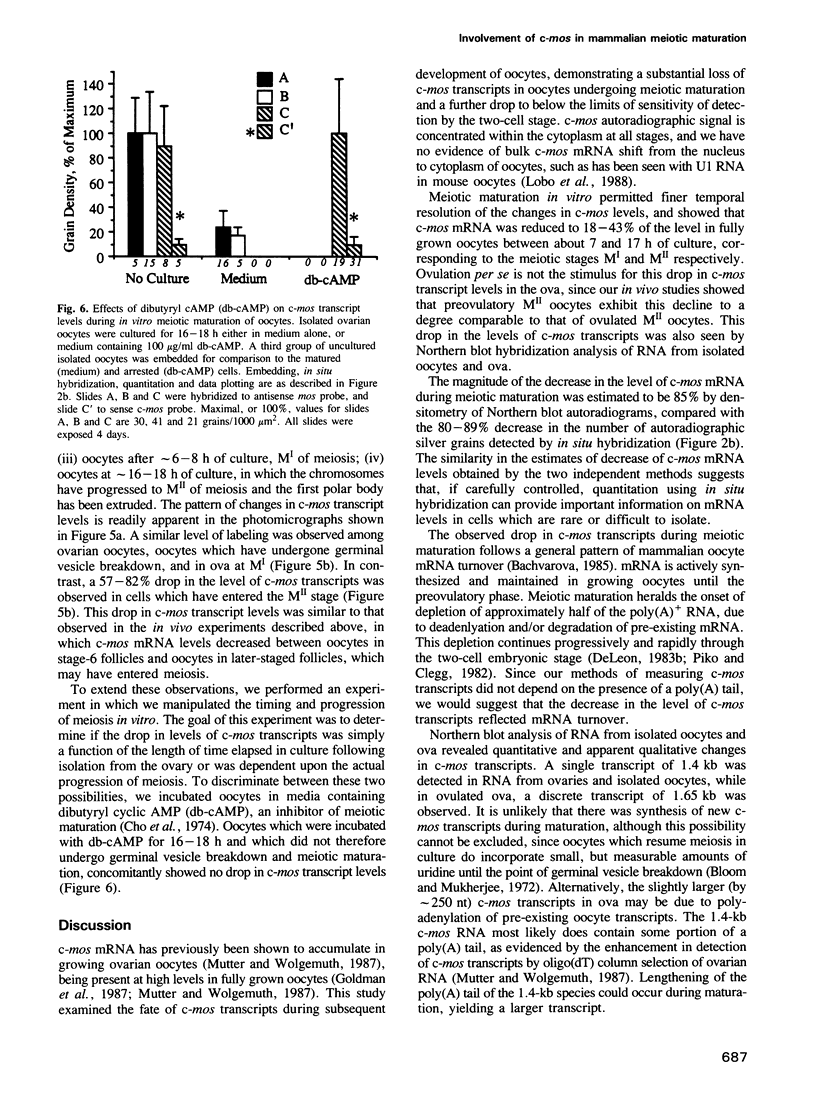
- Propst F., Vande Woude G. F. Expression of c-mos proto-oncogene transcripts in mouse tissues. Nature. 1985 Jun 6;315(6019):516–518. doi: 10.1038/315516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Ruderman J. V. Widespread changes in the translation and adenylation of maternal messenger RNAs following fertilization of Spisula oocytes. Dev Biol. 1987 May;121(1):237–246. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90155-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Tansey T. R., Ruderman J. V. Sequence-specific adenylations and deadenylations accompany changes in the translation of maternal messenger RNA after fertilization of Spisula oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):309–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Montgomery R. R., Belanoff J. R. Regulation of mouse oocyte meiotic maturation: implication of a decrease in oocyte cAMP and protein dephosphorylation in commitment to resume meiosis. Dev Biol. 1983 Jun;97(2):264–273. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Wassarman P. M. Biochemical studies of mammalian oogenesis: Protein synthesis during oocyte growth and meiotic maturation in the mouse. J Cell Sci. 1977 Apr;24:167–194. doi: 10.1242/jcs.24.1.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz R. M., Wassarman P. M. Specific changes in the pattern of protein synthesis during meiotic maturation of mammalian oocytes in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):538–541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shackleford G. M., Varmus H. E. Expression of the proto-oncogene int-1 is restricted to postmeiotic male germ cells and the neural tube of mid-gestational embryos. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):89–95. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90665-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh B., Hannink M., Donoghue D. J., Arlinghaus R. B. p37mos-associated serine/threonine protein kinase activity correlates with the cellular transformation function of v-mos. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):1148–1152. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.1148-1152.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]