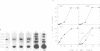Abstract
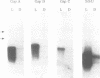
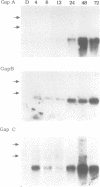
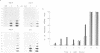
When tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) plants were transferred from the dark to continuous white light, the steady-state mRNA levels transcribed from the nuclear genes encoding chloroplast (GapA and GapB) glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase increased at least 30- to 50-fold, while the mRNA level for the cytosolic enzyme (GapC) increased only 10-fold. Kinetic analyses show that the rates of mRNA accumulation for GapA and GapB are identical reaching steady-state levels after 24-48 h in light. In contrast, mRNA accumulation for the GapC gene shows a completely different kinetic pattern, accumulating much faster than that of GapA and GapB. These results suggest that expression of GapC and GapA/B genes are controlled by different light regulated mechanisms and nuclear run-on analyses suggest that these effects are primarily due to increased transcription.
Keywords: light induction, plant gene expression
Full text
PDF

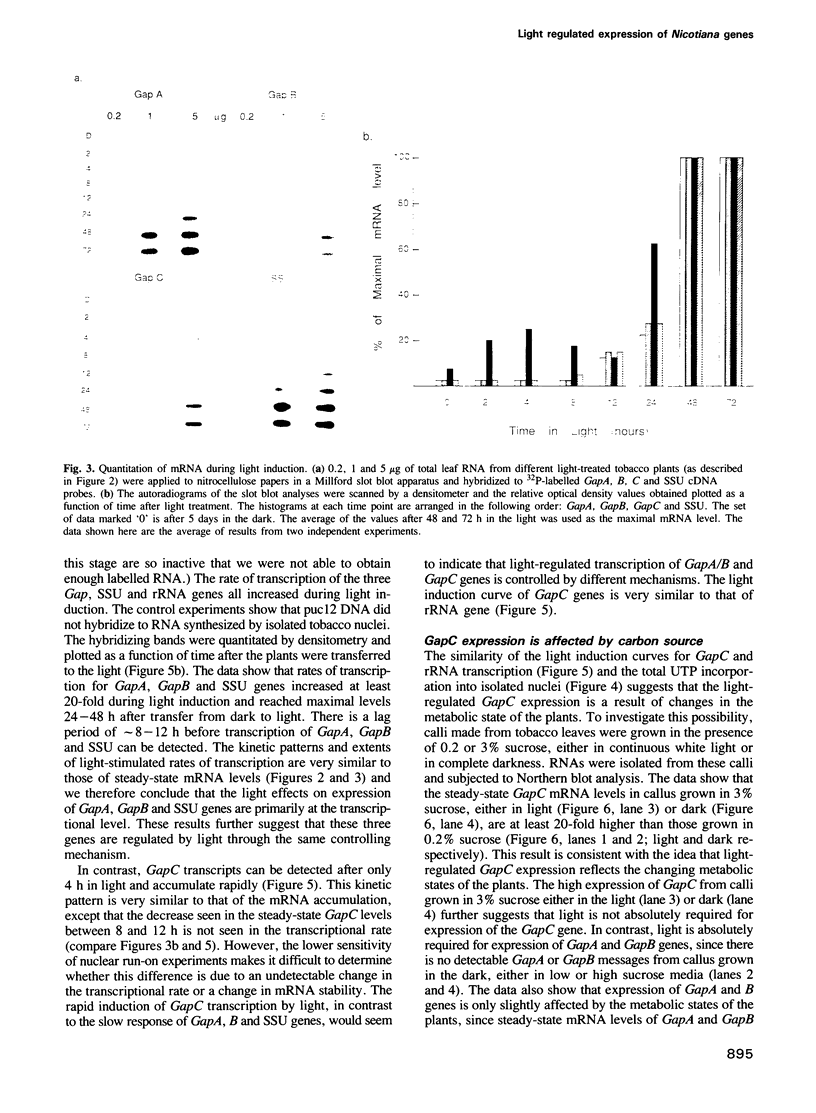
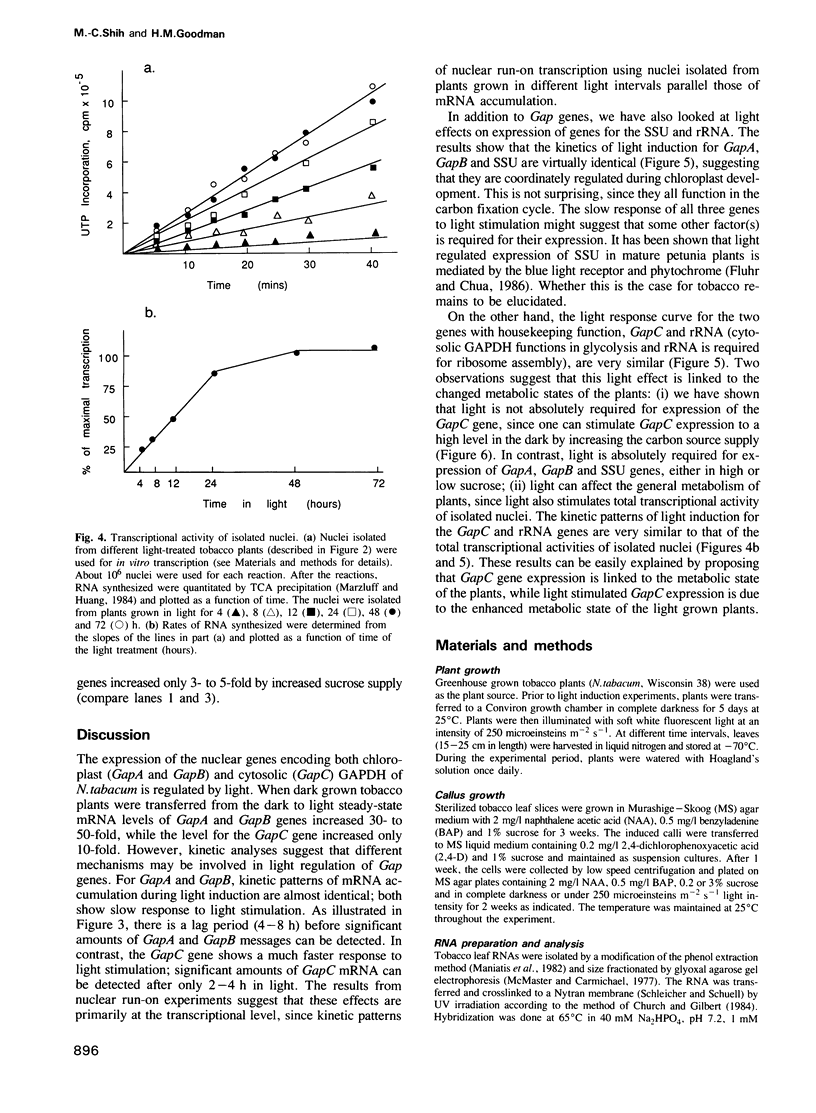
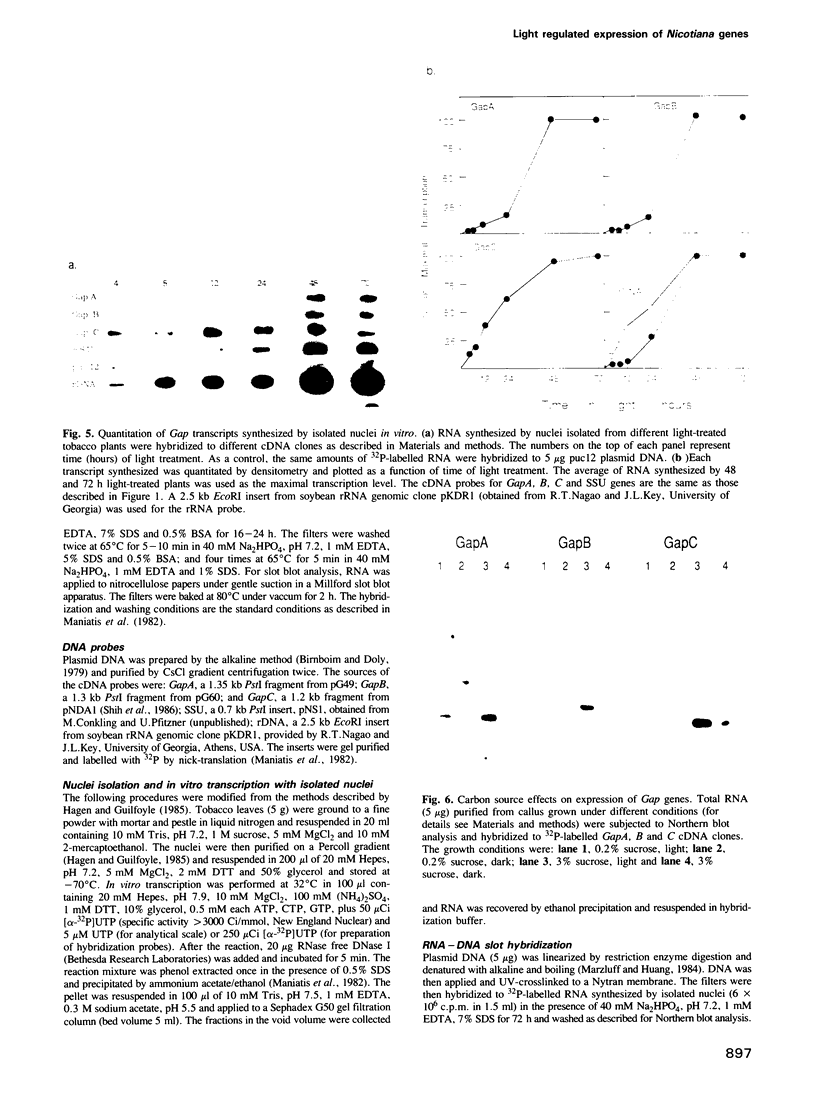

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bennett J., Jenkins G. I., Hartley M. R. Differential regulation of the accumulation of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b complex and ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in greening pea leaves. J Cell Biochem. 1984;25(1):1–13. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240250102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry-Lowe S. L., Meagher R. B. Transcriptional regulation of a gene encoding the small subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase in soybean tissue is linked to the phytochrome response. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1910–1917. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry J. O., Nikolau B. J., Carr J. P., Klessig D. F. Translational regulation of light-induced ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase gene expression in amaranth. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2347–2353. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Chua N. H. Developmental regulation of two genes encoding ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase small subunit in pea and transgenic petunia plants: Phytochrome response and blue-light induction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2358–2362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Kuhlemeier C., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Organ-specific and light-induced expression of plant genes. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1106–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4754.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher T. F., Ellis R. J. Light-stimulated transcription of genes for two chloroplast polypeptides in isolated pea leaf nuclei. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1493–1498. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01345.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen G., Guilfoyle T. J. Rapid induction of selective transcription by auxins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1197–1203. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman L. S., Thompson W. F., Briggs W. R. Different Red Light Requirements for Phytochrome-Induced Accumulation of cab RNA and rbcS RNA. Science. 1984 Dec 21;226(4681):1447–1449. doi: 10.1126/science.226.4681.1447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih M. C., Lazar G., Goodman H. M. Evidence in favor of the symbiotic origin of chloroplasts: primary structure and evolution of tobacco glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenases. Cell. 1986 Oct 10;47(1):73–80. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90367-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverthorne J., Tobin E. M. Demonstration of transcriptional regulation of specific genes by phytochrome action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1112–1116. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J., Timko M. P., Cashmore A. R., Schell J., Montagu M. V., Herrera-Estrella L. Light-inducible and tissue-specific expression of a chimaeric gene under control of the 5'-flanking sequence of a pea chlorophyll a/b-binding protein gene. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2723–2729. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone E. M., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Intron-dependent evolution of chicken glyceraldehyde phosphate dehydrogenase gene. Nature. 1985 Feb 7;313(6002):498–500. doi: 10.1038/313498a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]