Abstract
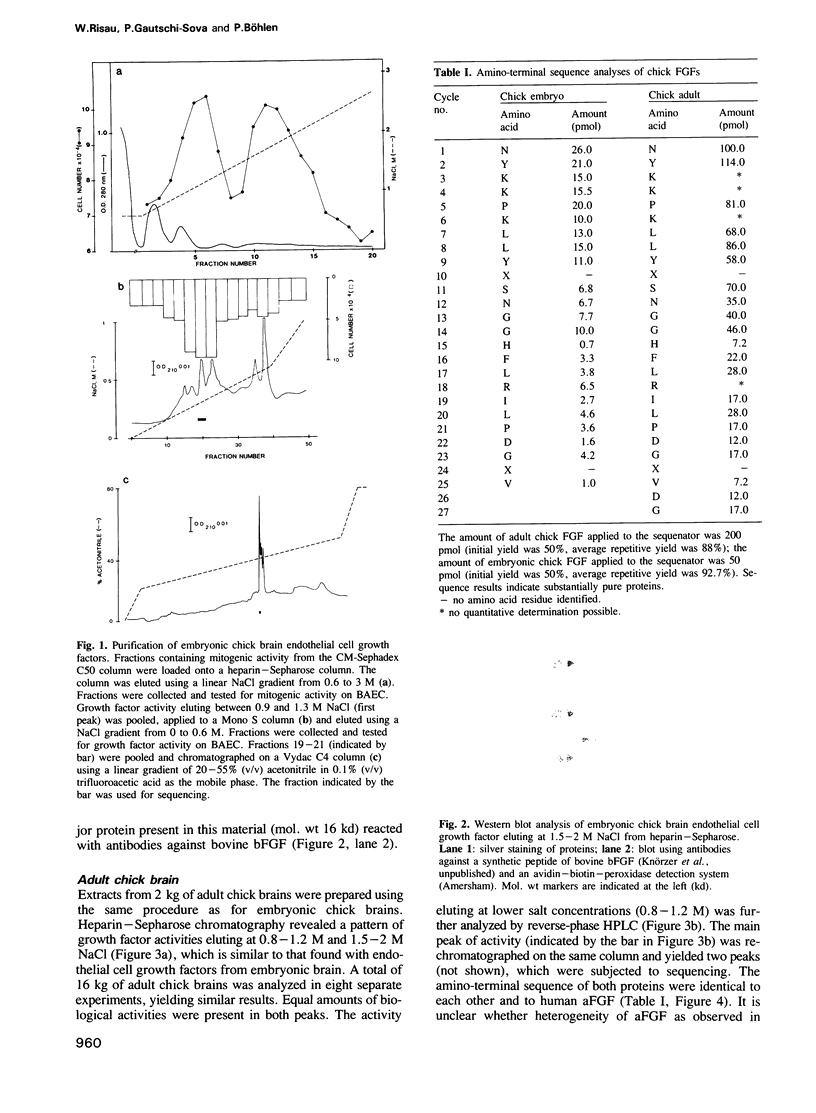
We have investigated the nature of endothelial cell growth factors in 14-day embryonic and adult chick brain extracts. Mitogenic activity was isolated by a combination of cation-exchange, heparin-Sepharose affinity, and reverse-phase HPLC. Two major mitogenic fractions eluted from heparin-Sepharose at 0.8-1.3 M and 1.5-2 M. Biologically active proteins eluting at 0.8-1.3 M NaCl, after purification to homogeneity from embryonic and adult brain, were found to possess the same amino-terminal sequence as human acidic fibroblast growth factor (aFGF). The notion that the isolated mitogens represent chick aFGF is further supported by the findings that their affinity for heparin and their retention behavior in highly resolutive HPLC are indistinguishable from those of genuine aFGF. Mitogenic activities eluting at 1.5-2 M NaCl were also present in embryonic and adult brain, but in quantities insufficient for preliminary characterization. The high specific mitogenic activity for endothelial cells, high affinity for heparin and cross-reactivity with antibodies against bovine basic FGF (bFGF) suggest a relationship of those materials with basic FGF. Our data also suggest that the sequence of aFGF is highly conserved among vertebrates. While angiogenesis occurs predominantly in the embryonic brain, the absence of notable differences in the contents of the potent angiogenic factors aFGF and bFGF in embryonic versus adult chick brain is interesting.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham J. A., Mergia A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Friedman J., Hjerrild K. A., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Nucleotide sequence of a bovine clone encoding the angiogenic protein, basic fibroblast growth factor. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):545–548. doi: 10.1126/science.2425435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abraham J. A., Whang J. L., Tumolo A., Mergia A., Friedman J., Gospodarowicz D., Fiddes J. C. Human basic fibroblast growth factor: nucleotide sequence and genomic organization. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2523–2528. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04530.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Baird A., Esch F., Ling N., Gospodarowicz D. Isolation and partial molecular characterization of pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5364–5368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böhlen P., Esch F., Baird A., Gospodarowicz D. Acidic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) from bovine brain: amino-terminal sequence and comparison with basic FGF. EMBO J. 1985 Aug;4(8):1951–1956. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03876.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crabb J. W., Armes L. G., Carr S. A., Johnson C. M., Roberts G. D., Bordoli R. S., McKeehan W. L. Complete primary structure of prostatropin, a prostate epithelial cell growth factor. Biochemistry. 1986 Sep 9;25(18):4988–4993. doi: 10.1021/bi00366a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delli Bovi P., Curatola A. M., Kern F. G., Greco A., Ittmann M., Basilico C. An oncogene isolated by transfection of Kaposi's sarcoma DNA encodes a growth factor that is a member of the FGF family. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):729–737. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90331-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denekamp J. Vascular endothelium as the vulnerable element in tumours. Acta Radiol Oncol. 1984;23(4):217–225. doi: 10.3109/02841868409136015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson C., Peters G. Potential oncogene product related to growth factors. 1987 Apr 30-May 6Nature. 326(6116):833–833. doi: 10.1038/326833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):442–447. doi: 10.1126/science.2432664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautschi-Sova P., Jiang Z. P., Fràter-Schröder M., Böhlen P. Acidic fibroblast growth factor is present in nonneural tissue: isolation and chemical characterization from bovine kidney. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5844–5847. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gautschi-Sova P., Müller T., Böhlen P. Amino acid sequence of human acidic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Nov 14;140(3):874–880. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90716-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimenez-Gallego G., Conn G., Hatcher V. B., Thomas K. A. The complete amino acid sequence of human brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 31;138(2):611–617. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80540-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Neufeld G., Schweigerer L. Fibroblast growth factor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1986 Aug;46(3):187–204. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(86)90001-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Howk R., Burgess W., Ricca G. A., Chiu I. M., Ravera M. W., O'Brien S. J., Modi W. S., Maciag T., Drohan W. N. Human endothelial cell growth factor: cloning, nucleotide sequence, and chromosome localization. Science. 1986 Aug 1;233(4763):541–545. doi: 10.1126/science.3523756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risau W. Developing brain produces an angiogenesis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taira M., Yoshida T., Miyagawa K., Sakamoto H., Terada M., Sugimura T. cDNA sequence of human transforming gene hst and identification of the coding sequence required for transforming activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Fitzpatrick S. Purification and characterization of acidic fibroblast growth factor from bovine brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):357–361. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlodavsky I., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Fridman R., Ishai-Michaeli R., Sasse J., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell-derived basic fibroblast growth factor: synthesis and deposition into subendothelial extracellular matrix. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2292–2296. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



