Abstract
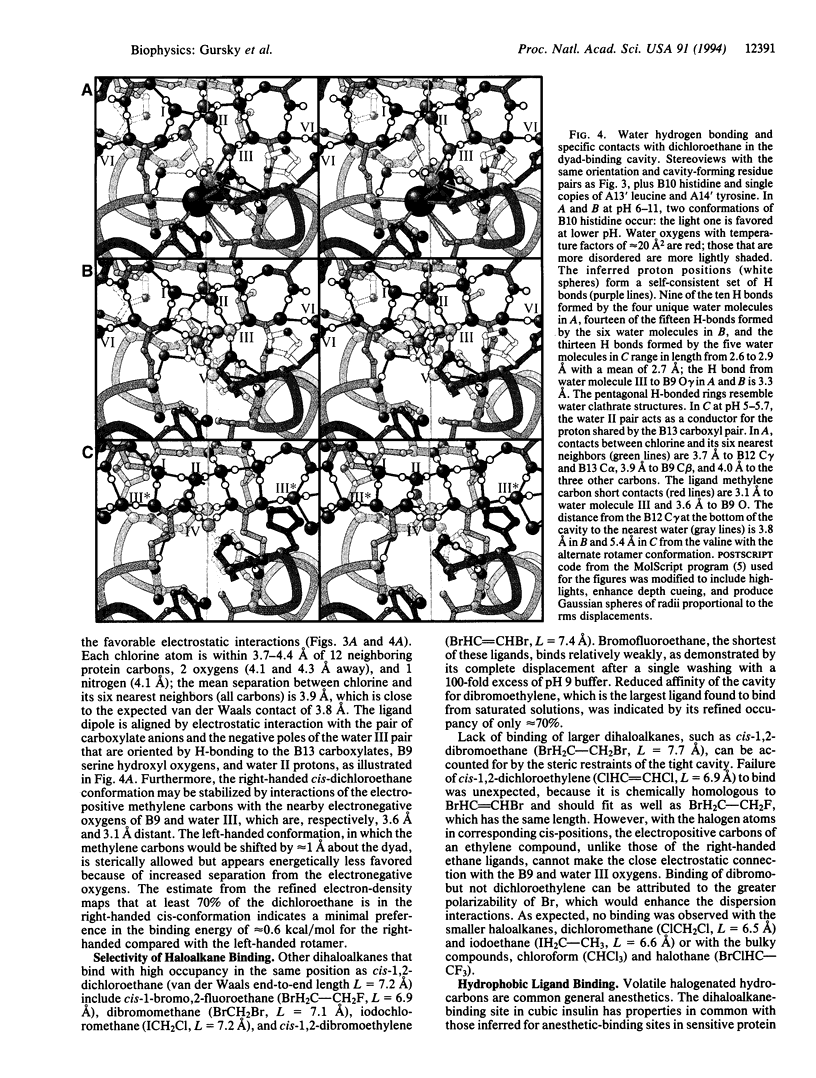
Crystallographic analysis at 2-A resolution of the selective binding of dihalogenated methane, ethane, and ethylene compounds in the cavity on the cubic insulin dimer axis provides a model for anesthetic-protein interactions. At pH 6-11, 1,2-dichloroethane binds isomorphically in the right-handed cis-conformation, displacing four water molecules from the invariant cavity. Lowering the pH to 5.7 in 1 M Na2SO4 without dihaloalkanes induces a cooperative structural transition in which the dyad cavities between B13 glutamate pairs are constricted, and SO4(2-) ions are bound by rearranged triads of B1 NH+3 groups. In the presence of dichloroethane at pH 5-5.5, the equilibrium is shifted to a mixture of the ligand-bound and ligand-excluding cavity structures, with half-occupancy of the sulfate sites, exemplifying how a volatile anesthetic can act as an allosteric effector. Measurements at pH 9 of the occupancies of structurally similar dihaloalkanes demonstrate a high degree of binding selectivity. Induced polarization of the ligand and bound water by the charge distribution in the binding cavity apparently provides the selective electrostatic interactions that discriminate between dihaloalkanes of comparable size and polarity.
Full text
PDF


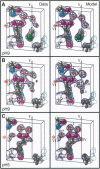
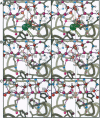
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abraham M. H., Lieb W. R., Franks N. P. Role of hydrogen bonding in general anesthesia. J Pharm Sci. 1991 Aug;80(8):719–724. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600800802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badger J., Harris M. R., Reynolds C. D., Evans A. C., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., North A. C. Structure of the pig insulin dimer in the cubic crystal. Acta Crystallogr B. 1991 Feb 1;47(Pt 1):127–136. doi: 10.1107/s0108768190009570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. N., Blundell T. L., Cutfield J. F., Cutfield S. M., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Hodgkin D. M., Hubbard R. E., Isaacs N. W., Reynolds C. D. The structure of 2Zn pig insulin crystals at 1.5 A resolution. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 6;319(1195):369–456. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASPAR D. L. ASSEMBLY AND STABILITY OF THE TOBACCO MOSAIC VIRUS PARTICLE. Adv Protein Chem. 1963;18:37–121. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti P. Anion binding sites in protein structures. J Mol Biol. 1993 Nov 20;234(2):463–482. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R. The structure and function of the aspartic proteinases. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1990;19:189–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.19.060190.001201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derewenda U., Derewenda Z., Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Bing X., Markussen J. X-ray analysis of the single chain B29-A1 peptide-linked insulin molecule. A completely inactive analogue. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jul 20;220(2):425–433. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90022-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson R., Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Thermodynamics of anesthetic/protein interactions. Temperature studies on firefly luciferase. Biophys J. 1993 Apr;64(4):1264–1271. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(93)81491-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodson E. J., Dodson G. G., Lewitova A., Sabesan M. Zinc-free cubic pig insulin: crystallization and structure determination. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 5;125(3):387–396. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Mapping of general anaesthetic target sites provides a molecular basis for cutoff effects. Nature. 1985 Jul 25;316(6026):349–351. doi: 10.1038/316349a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of general anaesthesia. Nature. 1994 Feb 17;367(6464):607–614. doi: 10.1038/367607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Stereospecific effects of inhalational general anesthetic optical isomers on nerve ion channels. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):427–430. doi: 10.1126/science.1925602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gursky O., Badger J., Li Y., Caspar D. L. Conformational changes in cubic insulin crystals in the pH range 7-11. Biophys J. 1992 Nov;63(5):1210–1220. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81697-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gursky O., Li Y., Badger J., Caspar D. L. Monovalent cation binding to cubic insulin crystals. Biophys J. 1992 Mar;61(3):604–611. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81865-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrickson W. A. Stereochemically restrained refinement of macromolecular structures. Methods Enzymol. 1985;115:252–270. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(85)15021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hua Q. X., Shoelson S. E., Kochoyan M., Weiss M. A. Receptor binding redefined by a structural switch in a mutant human insulin. Nature. 1991 Nov 21;354(6350):238–241. doi: 10.1038/354238a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Namba K., Stubbs G. Structure of tobacco mosaic virus at 3.6 A resolution: implications for assembly. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1401–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3952490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoenborn B. P. Dichloromethane as an antisickling agent in sickle cell hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):4195–4199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.4195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. D., Dodson G. G. Structure of a rhombohedral R6 insulin/phenol complex. Proteins. 1992 Nov;14(3):401–408. doi: 10.1002/prot.340140309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilton R. F., Jr, Singh U. C., Kuntz I. D., Jr, Kollman P. A. Protein-ligand dynamics. A 96 picosecond simulation of a myoglobin-xenon complex. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):195–211. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90389-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verschueren K. H., Seljée F., Rozeboom H. J., Kalk K. H., Dijkstra B. W. Crystallographic analysis of the catalytic mechanism of haloalkane dehalogenase. Nature. 1993 Jun 24;363(6431):693–698. doi: 10.1038/363693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]