Abstract
Expression of class I HLA antigen has been shown to be reduced in a number of human tumours. Here we show that in a panel of 11 melanoma cell lines with variable class I HLA expression an inverse correlation exists between the mRNA levels of c-myc and class I HLA. This suggests that high expression of the c-myc oncogene might inhibit the class I HLA expression. To test this hypothesis a melanoma cell line with a low c-myc and high class I HLA mRNA expression was transfected with a c-myc expression vector. All clones expressing the transfected c-myc gene show reduced class I HLA mRNA and beta 2-microglobulin mRNA expression. Reduced class I HLA mRNA levels result in a lowered class I protein expression on the cell surface. Treatment with gamma-interferon fully restores the class I HLA and beta 2-microglobulin expression in these cells. This effect is preceded by a transient decrease of the c-myc mRNA level. These results show that the class I HLA expression is modulated by the level of c-myc expression, thus opening up the possibility that high expression of this oncogene influences the interaction of melanoma cells with the immune system.
Full text
PDF
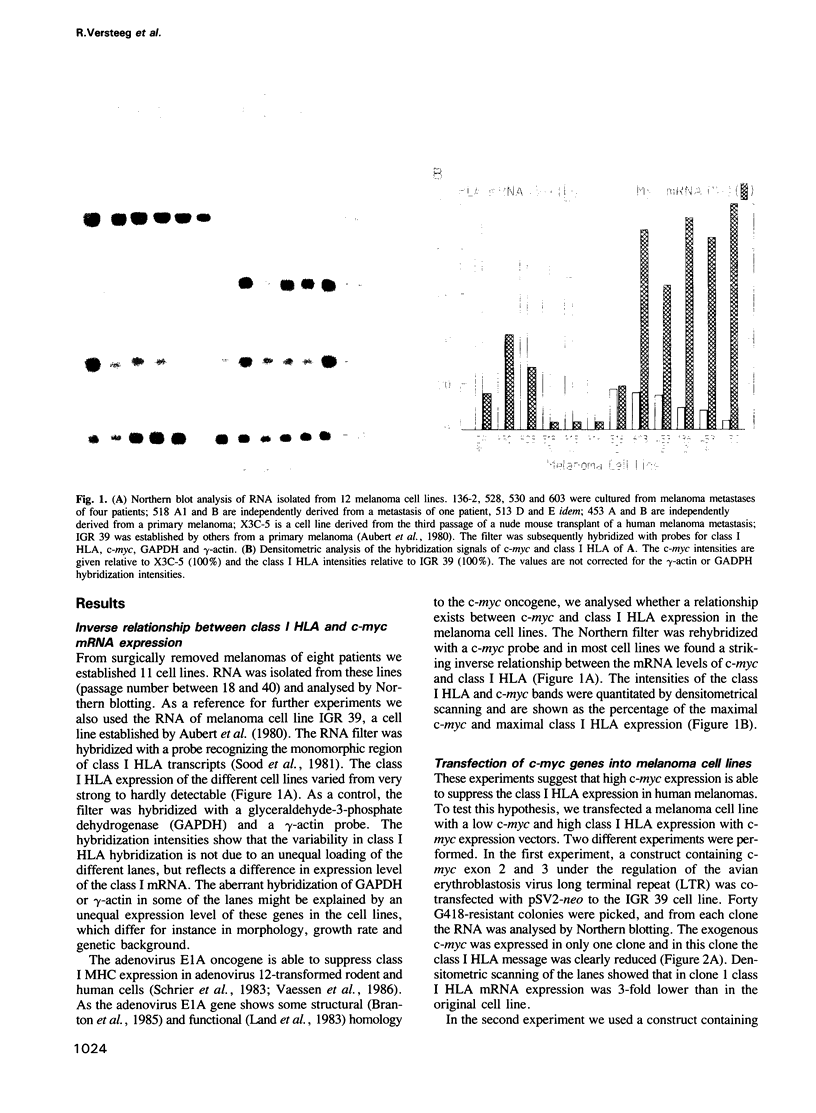
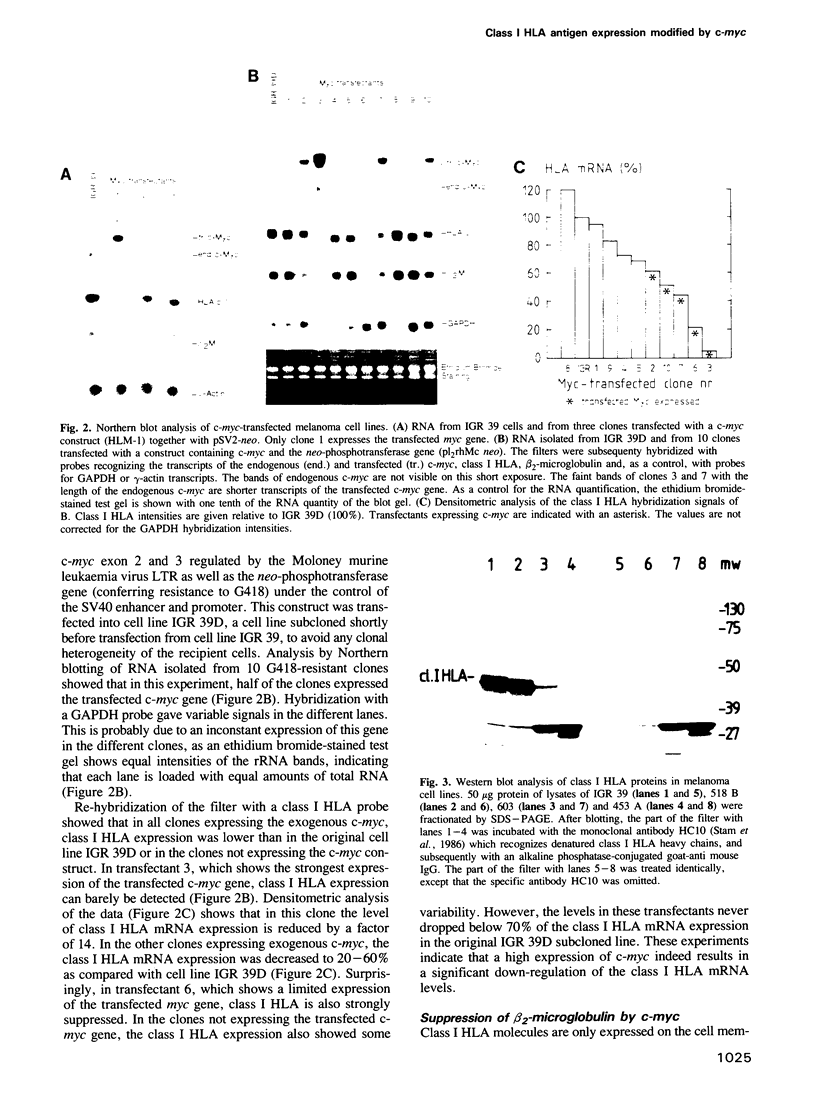




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anichini A., Fossati G., Parmiani G. Clonal analysis of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte response to autologous human metastatic melanoma. Int J Cancer. 1985 May 15;35(5):683–689. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armelin H. A., Armelin M. C., Kelly K., Stewart T., Leder P., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D. Functional role for c-myc in mitogenic response to platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):655–660. doi: 10.1038/310655a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aubert C., Rougé F., Galindo J. R. Tumorigenicity of human malignant melanocytes in nude mice in relation to their differentiation in vitro. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 May;64(5):1029–1040. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basham T. Y., Bourgeade M. F., Creasey A. A., Merigan T. C. Interferon increases HLA synthesis in melanoma cells: interferon-resistant and -sensitive cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3265–3269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Dessain S. K., Weinberg R. A. N-myc amplification causes down-modulation of MHC class I antigen expression in neuroblastoma. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Houweling A., Schrier P. I., Bos J. L., Van der Eb A. J. Characterization of cells transformed by Ad5/Ad12 hybrid early region I plasmids. Virology. 1982 Jul 30;120(2):422–432. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Branton P. E., Bayley S. T., Graham F. L. Transformation by human adenoviruses. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985;780(1):67–94. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(84)90007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bröcker E. B., Suter L., Brüggen J., Ruiter D. J., Macher E., Sorg C. Phenotypic dynamics of tumor progression in human malignant melanoma. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jul 15;36(1):29–35. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colby W. W., Chen E. Y., Smith D. H., Levinson A. D. Identification and nucleotide sequence of a human locus homologous to the v-myc oncogene of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):722–725. doi: 10.1038/301722a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole M. D. The myc oncogene: its role in transformation and differentiation. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:361–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.002045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle A., Martin W. J., Funa K., Gazdar A., Carney D., Martin S. E., Linnoila I., Cuttitta F., Mulshine J., Bunn P. Markedly decreased expression of class I histocompatibility antigens, protein, and mRNA in human small-cell lung cancer. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1135–1151. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Tanaka K., Jay F., Khoury G., Jay G. Modulation of the tumorigenicity of human adenovirus-12-transformed cells by interferon. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hui K., Grosveld F., Festenstein H. Rejection of transplantable AKR leukaemia cells following MHC DNA-mediated cell transformation. Nature. 1984 Oct 25;311(5988):750–752. doi: 10.1038/311750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knuth A., Danowski B., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity against autologous malignant melanoma: analysis with interleukin 2-dependent T-cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3511–3515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kärre K., Ljunggren H. G., Piontek G., Kiessling R. Selective rejection of H-2-deficient lymphoma variants suggests alternative immune defence strategy. Nature. 1986 Feb 20;319(6055):675–678. doi: 10.1038/319675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lampson L. A., Fisher C. A., Whelan J. P. Striking paucity of HLA-A, B, C and beta 2-microglobulin on human neuroblastoma cell lines. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2471–2478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Land H., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Tumorigenic conversion of primary embryo fibroblasts requires at least two cooperating oncogenes. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):596–602. doi: 10.1038/304596a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Murphree A. L., Benedict W. F. Expression and amplification of the N-myc gene in primary retinoblastoma. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):458–460. doi: 10.1038/309458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nau M. M., Brooks B. J., Battey J., Sausville E., Gazdar A. F., Kirsch I. R., McBride O. W., Bertness V., Hollis G. F., Minna J. D. L-myc, a new myc-related gene amplified and expressed in human small cell lung cancer. Nature. 1985 Nov 7;318(6041):69–73. doi: 10.1038/318069a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebaï N., Malissen B. Structural and genetic analyses of HLA class I molecules using monoclonal xenoantibodies. Tissue Antigens. 1983 Aug;22(2):107–117. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1983.tb01176.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruiter D. J., Bergman W., Welvaart K., Scheffer E., van Vloten W. A., Russo C., Ferrone S. Immunohistochemical analysis of malignant melanomas and nevocellular nevi with monoclonal antibodies to distinct monomorphic determinants of HLA antigens. Cancer Res. 1984 Sep;44(9):3930–3935. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedmak J. J., Grossberg S. E. A rapid, sensitive, and versatile assay for protein using Coomassie brilliant blue G250. Anal Biochem. 1977 May 1;79(1-2):544–552. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90428-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sood A. K., Pereira D., Weissman S. M. Isolation and partial nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone for human histocompatibility antigen HLA-B by use of an oligodeoxynucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):616–620. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stam N. J., Spits H., Ploegh H. L. Monoclonal antibodies raised against denatured HLA-B locus heavy chains permit biochemical characterization of certain HLA-C locus products. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Isselbacher K. J., Khoury G., Jay G. Reversal of oncogenesis by the expression of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):26–30. doi: 10.1126/science.3975631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi K., Kärre K., Klein G. Lung colonization and metastasis by disseminated B16 melanoma cells: H-2 associated control at the level of the host and the tumor cell. Int J Cancer. 1985 Oct 15;36(4):503–510. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., Israel A., Kourilsky P., van der Eb A. J. Adenovirus E1A-mediated regulation of class I MHC expression. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):335–341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Bulbuc N., Hämmerling G. J., Katzav S., Segal S., Feldman M. Abrogation of metastatic properties of tumour cells by de novo expression of H-2K antigens following H-2 gene transfection. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):301–305. doi: 10.1038/315301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries J. E., Spits H. Cloned human cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) lines reactive with autologous melanoma cells. I. In vitro generation, isolation, and analysis to phenotype and specificity. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):510–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Eb A. J., Graham F. L. Assay of transforming activity of tumor virus DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):826–839. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







