Abstract
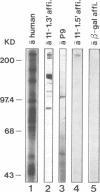
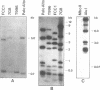
The 11-1 gene of Plasmodium falciparum has been investigated by DNA sequence analysis. It begins at the 5' end with a putative miniexon coding for a polypeptide which has the characteristics of a signal sequence. The miniexon is followed by a small intron. This again is followed by a large exon consisting of 9-, 18- and 27-bp repeats embedded in unique DNA. Specific antibodies isolated by affinity chromatography on a purified recombinant fusion protein expressing the three- and six-amino acid repeats were used to identify the product of the 11-1 gene. In exhibits size variations from 260 to 350 kd in different strains. Southern blot analysis with synthetic DNA as probe demonstrates that the 18-bp repeat is absent or drastically altered in two strains whereas the other repeats are present in all seven strains investigated. The unusual preference for G in the third position of some codons of the repeats but not in the unique sequences indicates rapid evolution of the repeats. Slippage during replication, unequal crossing over and selection are discussed as possible mechanisms leading rapidly to extreme diversity.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aota S., Ikemura T. Diversity in G + C content at the third position of codons in vertebrate genes and its cause. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 26;14(16):6345–6355. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.16.6345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ching G., Inouye M. Evolution of the lipoprotein gene in the enterobacteriaceae. Cloning and DNA sequence of the lpp gene from Proteus mirabilis. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 5;185(3):501–507. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, beta-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):211–222. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark-Lewis I., Aebersold R., Ziltener H., Schrader J. W., Hood L. E., Kent S. B. Automated chemical synthesis of a protein growth factor for hemopoietic cells, interleukin-3. Science. 1986 Jan 10;231(4734):134–139. doi: 10.1126/science.3079915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppel R. L., Culvenor J. G., Bianco A. E., Crewther P. E., Stahl H. D., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Variable antigen associated with the surface of erythrocytes infected with mature stages of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1986 Sep;20(3):265–277. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(86)90107-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowman A. F., Saint R. B., Coppel R. L., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Conserved sequences flank variable tandem repeats in two S-antigen genes of Plasmodium falciparum. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90337-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dame J. B., Williams J. L., McCutchan T. F., Weber J. L., Wirtz R. A., Hockmeyer W. T., Maloy W. L., Haynes J. D., Schneider I., Roberts D. Structure of the gene encoding the immunodominant surface antigen on the sporozoite of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science. 1984 Aug 10;225(4662):593–599. doi: 10.1126/science.6204383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C., Berzofsky J. A. T-cell antigenic sites tend to be amphipathic structures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):7048–7052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.7048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois P., Dedet J. P., Fandeur T., Roussilhon C., Jendoubi M., Pauillac S., Mercereau-Puijalon O., Pereira Da Silva L. Protective immunization of the squirrel monkey against asexual blood stages of Plasmodium falciparum by use of parasite protein fractions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):229–232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elford B. C., Haynes J. D., Chulay J. D., Wilson R. J. Selective stage-specific changes in the permeability to small hydrophilic solutes of human erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Jun;16(1):43–60. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J. M., Coppel R. L., Corcoran L. M., Foote S. J., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. Structure of the RESA gene of Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8265–8277. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg H., Kutner S., Krugliak M., Cabantchik Z. I. Characterization of permeation pathways appearing in the host membrane of Plasmodium falciparum infected red blood cells. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1985 Mar;14(3):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(85)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo L. H., Yang R. C., Wu R. An improved strategy for rapid direct sequencing of both strands of long DNA molecules cloned in a plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 25;11(16):5521–5540. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.16.5521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holder A. A., Lockyer M. J., Odink K. G., Sandhu J. S., Riveros-Moreno V., Nicholls S. C., Hillman Y., Davey L. S., Tizard M. L., Schwarz R. T. Primary structure of the precursor to the three major surface antigens of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):270–273. doi: 10.1038/317270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inselburg J., Bzik D. J., Horii T. Pyrimethamine resistant Plasmodium falciparum: overproduction of dihydrofolate reductase by a gene duplication. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Nov;26(1-2):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90136-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane B., Sibilli L., Scherf A., Jaureguiberry G., Langsley G., Ozaki L. S., Guillotte M., Müller-Hill B., Pereira da Silva L., Mercereau-Puijalon O. The polymorphic 11.1 locus of Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1987 Nov;26(1-2):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(87)90132-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Coppel R. L., Stahl H. D., Bianco A. E., Corcoran L. M., McIntyre P., Langford C. J., Favaloro J. M., Crewther P. E., Brown G. V. The Wellcome Trust lecture. Genes for antigens of Plasmodium falciparum. Parasitology. 1986;92 (Suppl):S83–108. doi: 10.1017/s0031182000085711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobloch J., Schreiber M., Grokhovsky S., Scherf A. Specific and nonspecific immunodiagnostic properties of recombinant and synthetic Plasmodium falciparum antigens. Eur J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Oct;6(5):547–551. doi: 10.1007/BF02014244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kochan J., Perkins M., Ravetch J. V. A tandemly repeated sequence determines the binding domain for an erythrocyte receptor binding protein of P. falciparum. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90834-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenen M., Scherf A., Mercereau O., Langsley G., Sibilli L., Dubois P., Pereira da Silva L., Müller-Hill B. Human antisera detect a Plasmodium falciparum genomic clone encoding a nonapeptide repeat. 1984 Sep 27-Oct 3Nature. 311(5984):382–385. doi: 10.1038/311382a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leech J. H., Barnwell J. W., Miller L. H., Howard R. J. Identification of a strain-specific malarial antigen exposed on the surface of Plasmodium falciparum-infected erythrocytes. J Exp Med. 1984 Jun 1;159(6):1567–1575. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.6.1567. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay M., Goman M., Bone N., Hyde J. E., Scaife J., Certa U., Stunnenberg H., Bujard H. Polymorphism of the precursor for the major surface antigens of Plasmodium falciparum merozoites: studies at the genetic level. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3823–3829. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei D., Langsley G., Braun-Breton C., Guillotte M., Dubremetz J. F., Mercereau-Puijalon O. The S-antigen of Plasmodium falciparum Palo Alto represents a new S-antigen serotype. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1988 Jan 15;27(2-3):171–180. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(88)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Feder R., Pavlovec A., Blobel G. Primary structure and genomic organization of the histidine-rich protein of the malaria parasite Plasmodium lophurae. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):616–620. doi: 10.1038/312616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D., Woollett G., Bergin-Cartwright M., Kay D., Scaife J. A malaria protein exported into a new compartment within the host erythrocyte. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):485–491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04779.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Evolution of repeated DNA sequences by unequal crossover. Science. 1976 Feb 13;191(4227):528–535. doi: 10.1126/science.1251186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Long range periodicities in mouse satellite DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):51–69. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90404-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe K., Mackay M., Goman M., Scaife J. G. Allelic dimorphism in a surface antigen gene of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 20;195(2):273–287. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90649-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triglia T., Stahl H. D., Crewther P. E., Scanlon D., Brown G. V., Anders R. F., Kemp D. J. The complete sequence of the gene for the knob-associated histidine-rich protein from Plasmodium falciparum. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1413–1419. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02382.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Udeinya I. J., Miller L. H., McGregor I. A., Jensen J. B. Plasmodium falciparum strain-specific antibody blocks binding of infected erythrocytes to amelanotic melanoma cells. Nature. 1983 Jun 2;303(5916):429–431. doi: 10.1038/303429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullmann A. One-step purification of hybrid proteins which have beta-galactosidase activity. Gene. 1984 Jul-Aug;29(1-2):27–31. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90162-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. L. Analysis of sequences from the extremely A + T-rich genome of Plasmodium falciparum. Gene. 1987;52(1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wellems T. E., Howard R. J. Homologous genes encode two distinct histidine-rich proteins in a cloned isolate of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6065–6069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Zamaroczy M., Bernardi G. The AT spacers and the var1 genes from the mitochondrial genomes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Torulopsis glabrata: evolutionary origin and mechanism of formation. Gene. 1987;54(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90342-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]