Abstract
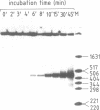
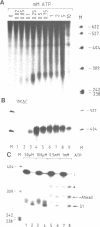
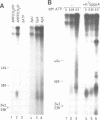
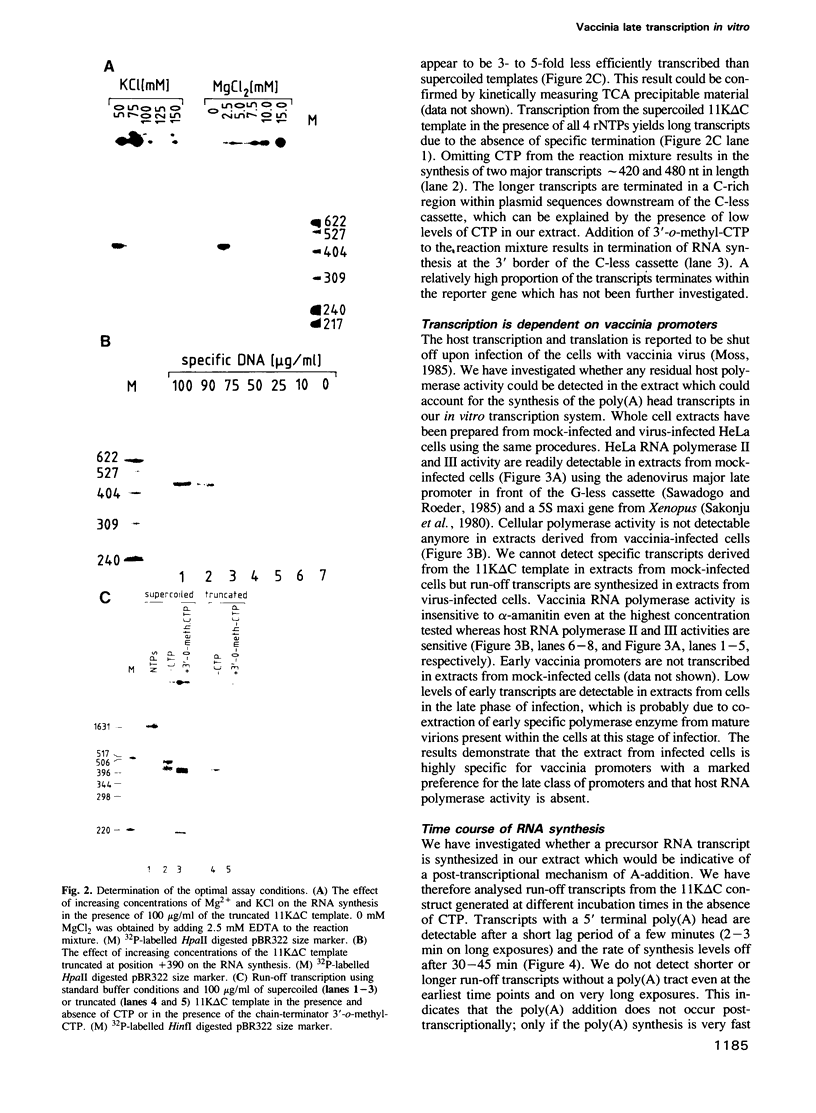
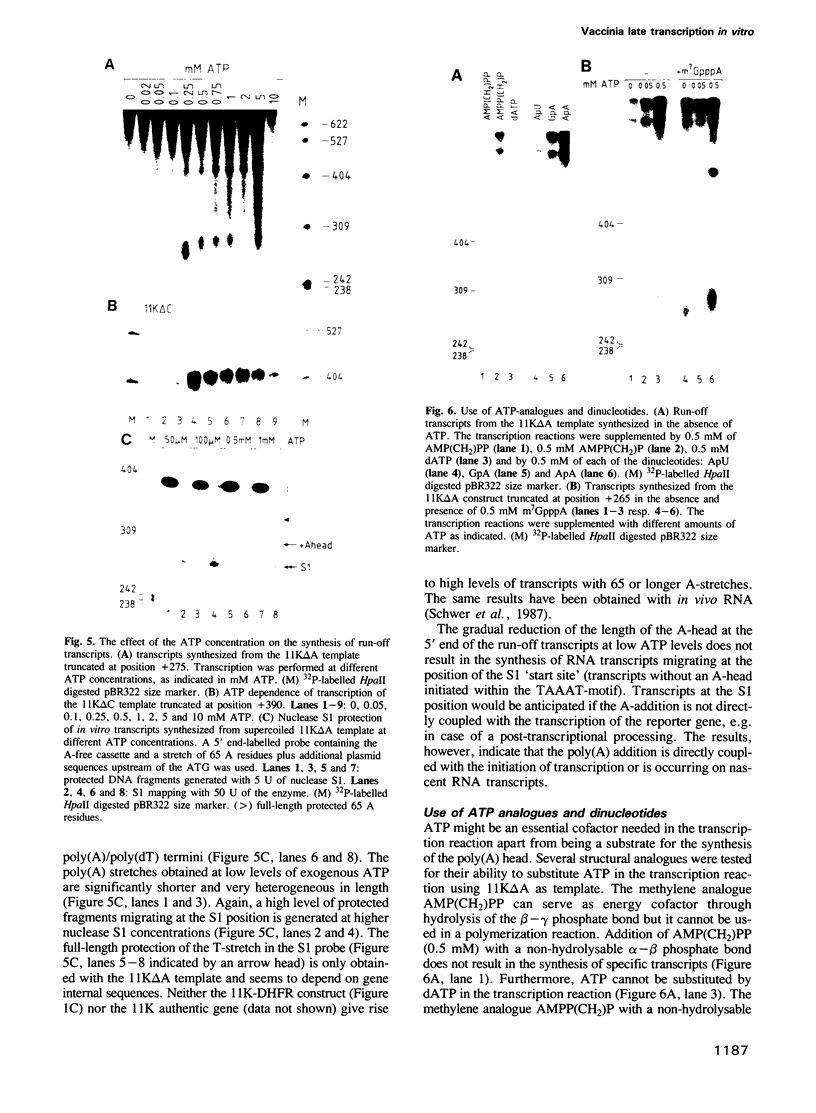
A cell free system mediating accurate transcription of vaccinia virus genes was established using lysates of cells in the late phase of infection. Vaccinia late genes are faithfully transcribed in this extract whereas cellular pol II and pol III promoters are not recognized. The late viral transcripts contain a poly(A) head of approximately 35 nt at the 5' end which is not co-linearly encoded in the externally added template. The transcripts obtained in vitro are indistinguishable from the mature in vivo RNAs. The poly(A) head is synthesized de novo and its formation appears to be directly coupled to the transcription of the gene. The synthesis of the poly(A) head transcripts in vitro is consistent with a proposed slippage model.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beaton A. R., Krug R. M. Selected host cell capped RNA fragments prime influenza viral RNA transcription in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Sep 11;9(17):4423–4436. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.17.4423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benne R., Van den Burg J., Brakenhoff J. P., Sloof P., Van Boom J. H., Tromp M. C. Major transcript of the frameshifted coxII gene from trypanosome mitochondria contains four nucleotides that are not encoded in the DNA. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):819–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90063-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertholet C., Drillien R., Wittek R. One hundred base pairs of 5' flanking sequence of a vaccinia virus late gene are sufficient to temporally regulate late transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):2096–2100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.2096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertholet C., Van Meir E., ten Heggeler-Bordier B., Wittek R. Vaccinia virus produces late mRNAs by discontinuous synthesis. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90211-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Contreras R., Cheroutre H., Degrave W., Fiers W. Simple, efficient in vitro synthesis of capped RNA useful for direct expression of cloned eukaryotic genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6353–6362. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Jasmer D. P., Stuart K. Developmentally regulated addition of nucleotides within apocytochrome b transcripts in Trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):337–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90286-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foglesong P. D. In vitro transcription of a cloned vaccinia virus gene by a soluble extract prepared from vaccinia virus-infected HeLa cells. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):822–826. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.822-826.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furuichi Y., LaFiandra A., Shatkin A. J. 5'-Terminal structure and mRNA stability. Nature. 1977 Mar 17;266(5599):235–239. doi: 10.1038/266235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golini F., Kates J. R. A soluble transcription system derived from purified vaccinia virions. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):205–213. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.205-213.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda A., Mizumoto K., Ishihama A. RNA polymerase of influenza virus. Dinucleotide-primed initiation of transcription at specific positions on viral RNA. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5987–5991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänggi M., Bannwarth W., Stunnenberg H. G. Conserved TAAAT motif in vaccinia virus late promoters: overlapping TATA box and site of transcription initiation. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):1071–1076. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Zentner P. G., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription at bacteriophage T4 variant late promoters. An application of a newly devised promoter-mapping method involving RNA chain retraction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14256–14265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Hirsh D. A trans-spliced leader sequence on actin mRNA in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90613-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Leader sequences of murine coronavirus mRNAs can be freely reassorted: evidence for the role of free leader RNA in transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4204–4208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Gefter M. L. Transcription of mammalian genes in vitro. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:369–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puckett C., Moss B. Selective transcription of vaccinia virus genes in template dependent soluble extracts of infected cells. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90177-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann G., Moss B. Transcription of vaccinia virus early genes by a template-dependent soluble extract of purified virions. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):349–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.349-355.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosel J., Moss B. Transcriptional and translational mapping and nucleotide sequence analysis of a vaccinia virus gene encoding the precursor of the major core polypeptide 4b. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):830–838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.830-838.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwer B., Visca P., Vos J. C., Stunnenberg H. G. Discontinuous transcription or RNA processing of vaccinia virus late messengers results in a 5' poly(A) leader. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90212-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Kodama Y., Hashimoto J., Miura K. I. Importance of 5'-terminal blocking structure to stabilize mRNA in eukaryotic protein synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2734–2738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slattery E., Dignam J. D., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Purification and analysis of a factor which suppresses nick-induced transcription by RNA polymerase II and its identity with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5955–5959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Sequence relationships between the genome and the intracellular RNA species 1, 3, 6, and 7 of mouse hepatitis virus strain A59. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):432–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.432-439.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. E., Boothroyd J. C. Evidence for trans splicing in trypanosomes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90617-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan S., Baroudy B. M., Moss B. Distinctive nucleotide sequences adjacent to multiple initiation and termination sites of an early vaccinia virus gene. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):805–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90188-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen L., Moss B. Multiple 3' ends of mRNA encoding vaccinia virus growth factor occur within a series of repeated sequences downstream of T clusters. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):320–323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.320-323.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]