Abstract
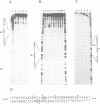
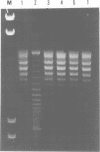
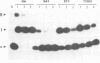
The DNA invertase Gin encoded by bacteriophage Mu catalyses efficient site-specific recombination between inverted repeat sequences (IR) in vivo and in vitro in the presence of the host factor FIS and the recombinational enhancer. We demonstrate that Gin alone is able to introduce single strand breaks into duplex DNA fragments which contain the IR sequence. Strand cleavage is site-specific and can occur on either strand within the IR. Cleaved molecules contain Gin covalently attached to DNA. The covalent complex is formed through linkage of Gin to the 5' DNA phosphate at the site of the break via a phosphoserine. Extensive site-directed mutational analysis showed that all mutants altered at serine position 9 were completely recombination deficient in vivo and in vitro. The mutant proteins bind to DNA but lack topoisomerase activity and are unable to introduce nicks. This holds true even for a conservative amino acid substitution at position 9. We conclude that serine at position 9 is part of the catalytic domain of Gin. The intriguing finding that the DNA invertase Gin has the same catalytic center as the DNA resolvases that promote deletions without recombinational enhancer and host factor FIS is discussed.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Grindley N. D., Templeton N. S., Steitz T. A. Cleavage of the site-specific recombination protein gamma delta resolvase: the smaller of two fragments binds DNA specifically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2001–2005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Trachmann C., Jansen H. W., Schroeer B., Patschinsky T. Structure of mutant and wild-type MC29 v-myc alleles and biochemical properties of their protein products. Oncogene. 1987 May;1(2):97–109. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruist M. F., Horvath S. J., Hood L. E., Steitz T. A., Simon M. I. Synthesis of a site-specific DNA-binding peptide. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):777–780. doi: 10.1126/science.3027895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bushman W., Yin S., Thio L. L., Landy A. Determinants of directionality in lambda site-specific recombination. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):699–706. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90477-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Horiuchi K. Replication of a plasmid containing two origins of bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 25;153(1):169–176. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H. J., Belagaje R., Brown E. L., Fritz R. H., Jones R. A., Lees R. G., Khorana H. G. High-pressure liquid chromatography in polynucleotide synthesis. Biochemistry. 1978 Apr 4;17(7):1257–1267. doi: 10.1021/bi00600a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D. Analysis of gamma delta resolvase mutants in vitro: evidence for an interaction between serine-10 of resolvase and site I of res. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5429–5433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiestand-Nauer R., Iida S. Sequence of the site-specific recombinase gene cin and of its substrates serving in the inversion of the C segment of bacteriophage P1. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1733–1740. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01650.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holzer H., Wohlhueter R. (Glutamine synthetase) tyrosyl-O-adenylate: a new energy-rich phosphate bond. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1972;10:121–132. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(72)90009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber H. E., Iida S., Arber W., Bickle T. A. Site-specific DNA inversion is enhanced by a DNA sequence element in cis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3776–3780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S. Bacteriophage P1 carries two related sets of genes determining its host range in the invertible C segment of its genome. Virology. 1984 Apr 30;134(2):421–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Hiestand-Nauer R. Localized conversion at the crossover sequences in the site-specific DNA inversion system of bacteriophage P1. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90539-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iida S., Hiestand-Nauer R. Role of the central dinucleotide at the crossover sites for the selection of quasi sites in DNA inversion mediated by the site-specific Cin recombinase of phage P1. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jul;208(3):464–468. doi: 10.1007/BF00328140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Bruist M. B., Glaccum M. B., Simon M. I. In vitro analysis of Hin-mediated site-specific recombination. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:751–760. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.085. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Glasgow A. C., Simon M. I. Spatial relationship of the Fis binding sites for Hin recombinational enhancer activity. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):462–465. doi: 10.1038/329462a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson R. C., Simon M. I. Hin-mediated site-specific recombination requires two 26 bp recombination sites and a 60 bp recombinational enhancer. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):781–791. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahmann R., Rudt F., Koch C., Mertens G. G inversion in bacteriophage Mu DNA is stimulated by a site within the invertase gene and a host factor. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):771–780. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Kahmann R. The relationship of two invertible segments in bacteriophage Mu and Salmonella typhimurium DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;184(3):564–566. doi: 10.1007/BF00352543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamp D., Kahmann R., Zipser D., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Inversion of the G DNA segment of phage Mu controls phage infectivity. Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):577–580. doi: 10.1038/271577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitts P. A., Nash H. A. Homology-dependent interactions in phage lambda site-specific recombination. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):346–348. doi: 10.1038/329346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Kahmann R. Purification and properties of the Escherichia coli host factor required for inversion of the G segment in bacteriophage Mu. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15673–15678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer W., Drutsa V., Jansen H. W., Kramer B., Pflugfelder M., Fritz H. J. The gapped duplex DNA approach to oligonucleotide-directed mutation construction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9441–9456. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell A., Gellert M. Mechanistic aspects of DNA topoisomerases. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:69–107. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60526-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens G., Fuss H., Kahmann R. Purification and properties of the DNA invertase gin encoded by bacteriophage Mu. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15668–15672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertens G., Hoffmann A., Blöcker H., Frank R., Kahmann R. Gin-mediated site-specific recombination in bacteriophage Mu DNA: overproduction of the protein and inversion in vitro. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2415–2421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A., Bauer C. E., Gardner J. F. Role of homology in site-specific recombination of bacteriophage lambda: evidence against joining of cohesive ends. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4049–4053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4049. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunes-Düby S. E., Matsumoto L., Landy A. Site-specific recombination intermediates trapped with suicide substrates. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):779–788. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90336-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Brinkman A., van de Putte P. DNA inversions in the chromosome of Escherichia coli and in bacteriophage Mu: relationship to other site-specific recombination systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(17):5355–5358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.17.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Ilmer T. A., Van de Putte P. Site-specific recombination by Gin of bacteriophage Mu: inversions and deletions. Virology. 1983 May;127(1):24–36. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90367-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., Kanaar R., van de Putte P. A genetic switch in vitro: DNA inversion by Gin protein of phage Mu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2689–2692. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plasterk R. H., van de Putte P. Inversion of DNA in vivo and in vitro by gin and pin proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:295–300. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Grindley N. D. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination in vitro: DNA cleavage and protein-DNA linkage at the recombination site. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Moser C. D. Resolvase-mediated recombination intermediates contain a serine residue covalently linked to DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:245–249. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski P. Site-specific recombinases: changing partners and doing the twist. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):341–347. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.341-347.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shure M., Pulleyblank D. E., Vinograd J. The problems of eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA packaging and in vivo conformation posed by superhelix density heterogeneity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1183–1205. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Silverman M., Hilmen M., Simon M. Recombinational switch for gene expression. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):170–172. doi: 10.1126/science.322276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zieg J., Simon M. Analysis of the nucleotide sequence of an invertible controlling element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4196–4200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Putte P., Cramer S., Giphart-Gassler M. Invertible DNA determines host specificity of bacteriophage mu. Nature. 1980 Jul 17;286(5770):218–222. doi: 10.1038/286218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]