Abstract
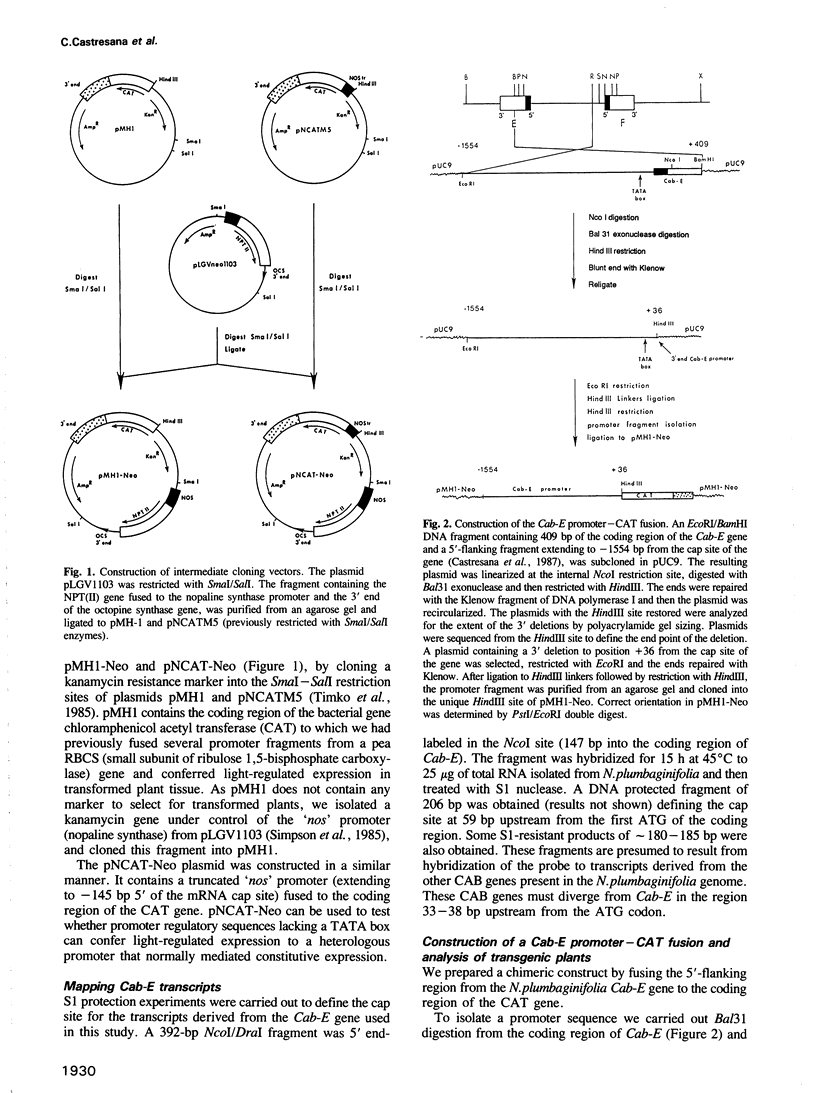
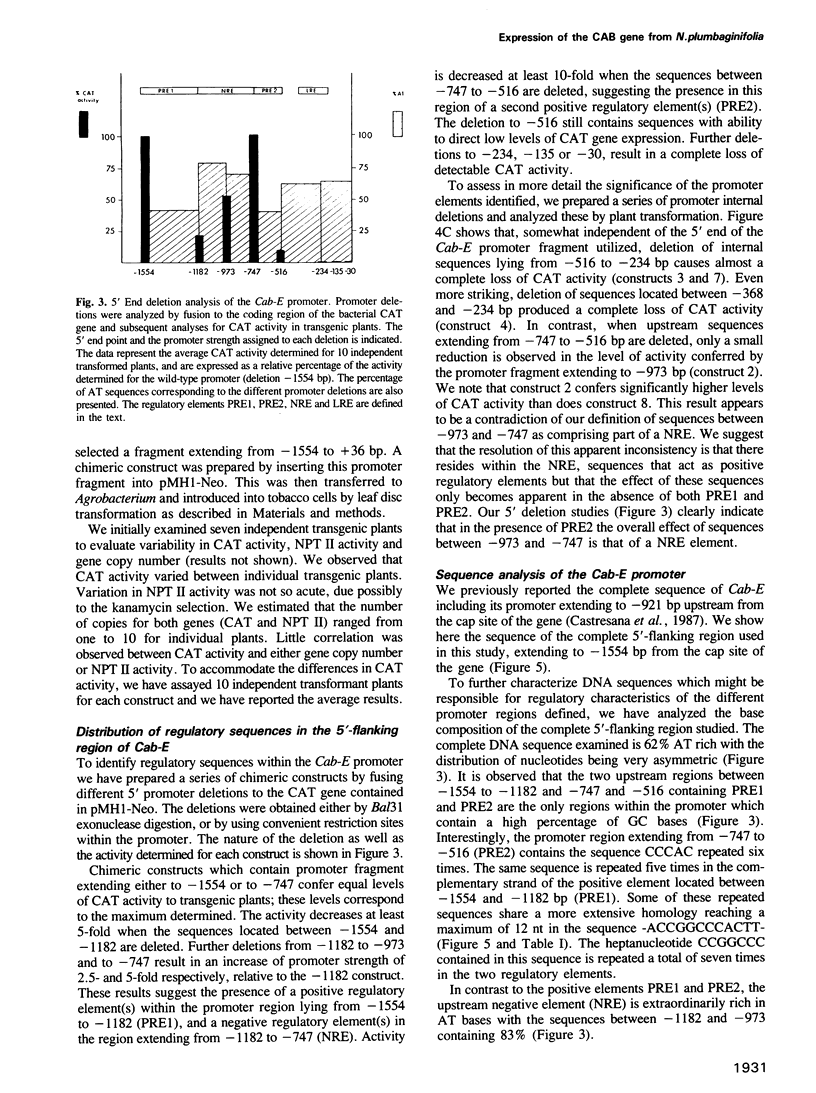
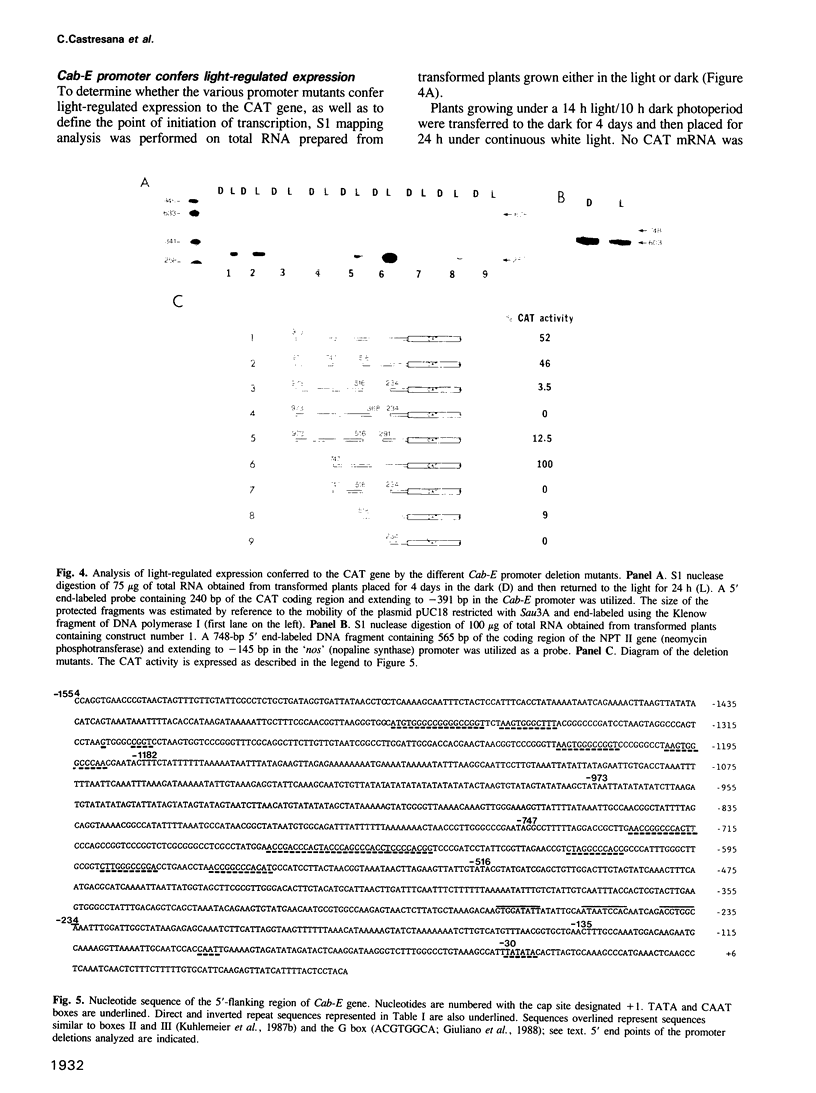
We have analyzed promoter regulatory elements from a photoregulated CAB gene (Cab-E) isolated from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. These studies have been performed by introducing chimeric gene constructs into tobacco cells via Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation. Expression studies on the regenerated transgenic plants have allowed us to characterize three positive and one negative cis-acting elements that influence photoregulated expression of the Cab-E gene. Within the upstream sequences we have identified two positive regulatory elements (PRE1 and PRE2) which confer maximum levels of photoregulated expression. These sequences contain multiple repeated elements related to the sequence-ACCGGCCCACTT-. We have also identified within the upstream region a negative regulatory element (NRE) extremely rich in AT sequences, which reduces the level of gene expression in the light. We have defined a light regulatory element (LRE) within the promoter region extending from -396 to -186 bp which confers photoregulated expression when fused to a constitutive nopaline synthase ('nos') promoter. Within this region there is a 132-bp element, extending from -368 to -234 bp, which on deletion from the Cab-E promoter reduces gene expression from high levels to undetectable levels. Finally, we have demonstrated for a full length Cab-E promoter conferring high levels of photoregulated expression, that sequences proximal to the Cab-E TATA box are not replaceable by corresponding sequences from a 'nos' promoter. This contrasts with the apparent equivalence of these Cab-E and 'nos' TATA box-proximal sequences in truncated promoters conferring low levels of photoregulated expression.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science. 1985 Mar 8;227(4691):1229–1231. doi: 10.1126/science.227.4691.1229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- An G. Development of plant promoter expression vectors and their use for analysis of differential activity of nopaline synthase promoter in transformed tobacco cells. Plant Physiol. 1986 May;81(1):86–91. doi: 10.1104/pp.81.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apel K., Kloppstech K. The plastid membranes of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Light-induced appearance of mRNA coding for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Apr 17;85(2):581–588. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12273.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apel K. Phytochrome-induced appearance of mRNA activity for the apoprotein of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein of barley (Hordeum vulgare). Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jun;97(1):183–188. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13101.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Chambon P. In vivo sequence requirements of the SV40 early promotor region. Nature. 1981 Mar 26;290(5804):304–310. doi: 10.1038/290304a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cashmore A. R. Structure and expression of a pea nuclear gene encoding a chlorophyll a/b-binding polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2960–2964. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. L., Schuler M. A., Beachy R. N. Functional analysis of regulatory elements in a plant embryo-specific gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8560–8564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coruzzi G., Broglie R., Cashmore A., Chua N. H. Nucleotide sequences of two pea cDNA clones encoding the small subunit of ribulose 1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase and the major chlorophyll a/b-binding thylakoid polypeptide. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1399–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuming A. C., Bennett J. Biosynthesis of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein. Control of messenger RNA activity by light. Eur J Biochem. 1981 Aug;118(1):71–80. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05487.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhaese P., De Greve H., Decraemer H., Schell J., Van Montagu M. Rapid mapping of transposon insertion and deletion mutations in the large Ti-plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1837–1849. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunsmuir P., Smith S. M., Bedbrook J. The major chlorophyll a/b binding protein of petunia is composed of several polypeptides encoded by a number of distinct nuclear genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1983;2(3):285–300. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebert P. R., Ha S. B., An G. Identification of an essential upstream element in the nopaline synthase promoter by stable and transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5745–5749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fluhr R., Kuhlemeier C., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Organ-specific and light-induced expression of plant genes. Science. 1986 May 30;232(4754):1106–1112. doi: 10.1126/science.232.4754.1106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazer A. N. Comparative biochemistry of photosynthetic light-harvesting systems. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:125–157. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlin-Neumann G. A., Kohorn B. D., Thornber J. P., Tobin E. M. A chlorophyll a/b-protein encoded by a gene containing an intron with characteristics of a transposable element. J Mol Appl Genet. 1985;3(1):45–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kay R., Chan A., Daly M., McPherson J. Duplication of CaMV 35S Promoter Sequences Creates a Strong Enhancer for Plant Genes. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1299–1302. doi: 10.1126/science.236.4806.1299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C., Fluhr R., Green P. J., Chua N. H. Sequences in the pea rbcS-3A gene have homology to constitutive mammalian enhancers but function as negative regulatory elements. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):247–255. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamppa G., Nagy F., Chua N. H. Light-regulated and organ-specific expression of a wheat Cab gene in transgenic tobacco. Nature. 1985 Aug 22;316(6030):750–752. doi: 10.1038/316750a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leutwiler L. S., Meyerowitz E. M., Tobin E. M. Structure and expression of three light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding protein genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4051–4064. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Boutry M., Hsu M. Y., Wong M., Chua N. H. The 5'-proximal region of the wheat Cab-1 gene contains a 268-bp enhancer-like sequence for phytochrome response. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagy F., Kay S. A., Boutry M., Hsu M. Y., Chua N. H. Phytochrome-controlled expression of a wheat Cab gene in transgenic tobacco seedlings. EMBO J. 1986 Jun;5(6):1119–1124. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04335.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ow D. W., Jacobs J. D., Howell S. H. Functional regions of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35S RNA promoter determined by use of the firefly luciferase gene as a reporter of promoter activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4870–4874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichersky E., Bernatzky R., Tanksley S. D., Breidenbach R. B., Kausch A. P., Cashmore A. R. Molecular characterization and genetic mapping of two clusters of genes encoding chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins in Lycopersicon esculentum (tomato). Gene. 1985;40(2-3):247–258. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiss B., Sprengel R., Will H., Schaller H. A new sensitive method for qualitative and quantitative assay of neomycin phosphotransferase in crude cell extracts. Gene. 1984 Oct;30(1-3):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90122-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt G. W., Bartlett S. G., Grossman A. R., Cashmore A. R., Chua N. H. Biosynthetic pathways of two polypeptide subunits of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b protein complex. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):468–478. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson J., Timko M. P., Cashmore A. R., Schell J., Montagu M. V., Herrera-Estrella L. Light-inducible and tissue-specific expression of a chimaeric gene under control of the 5'-flanking sequence of a pea chlorophyll a/b-binding protein gene. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2723–2729. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03995.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Naturally occurring poly(dA-dT) sequences are upstream promoter elements for constitutive transcription in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8419–8423. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timko M. P., Kausch A. P., Castresana C., Fassler J., Herrera-Estrella L., Van den Broeck G., Van Montagu M., Schell J., Cashmore A. R. Light regulation of plant gene expression by an upstream enhancer-like element. Nature. 1985 Dec 12;318(6046):579–582. doi: 10.1038/318579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Haute E., Joos H., Maes M., Warren G., Van Montagu M., Schell J. Intergeneric transfer and exchange recombination of restriction fragments cloned in pBR322: a novel strategy for the reversed genetics of the Ti plasmids of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):411–417. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01438.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambryski P., Joos H., Genetello C., Leemans J., Montagu M. V., Schell J. Ti plasmid vector for the introduction of DNA into plant cells without alteration of their normal regeneration capacity. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2143–2150. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01715.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





