Abstract
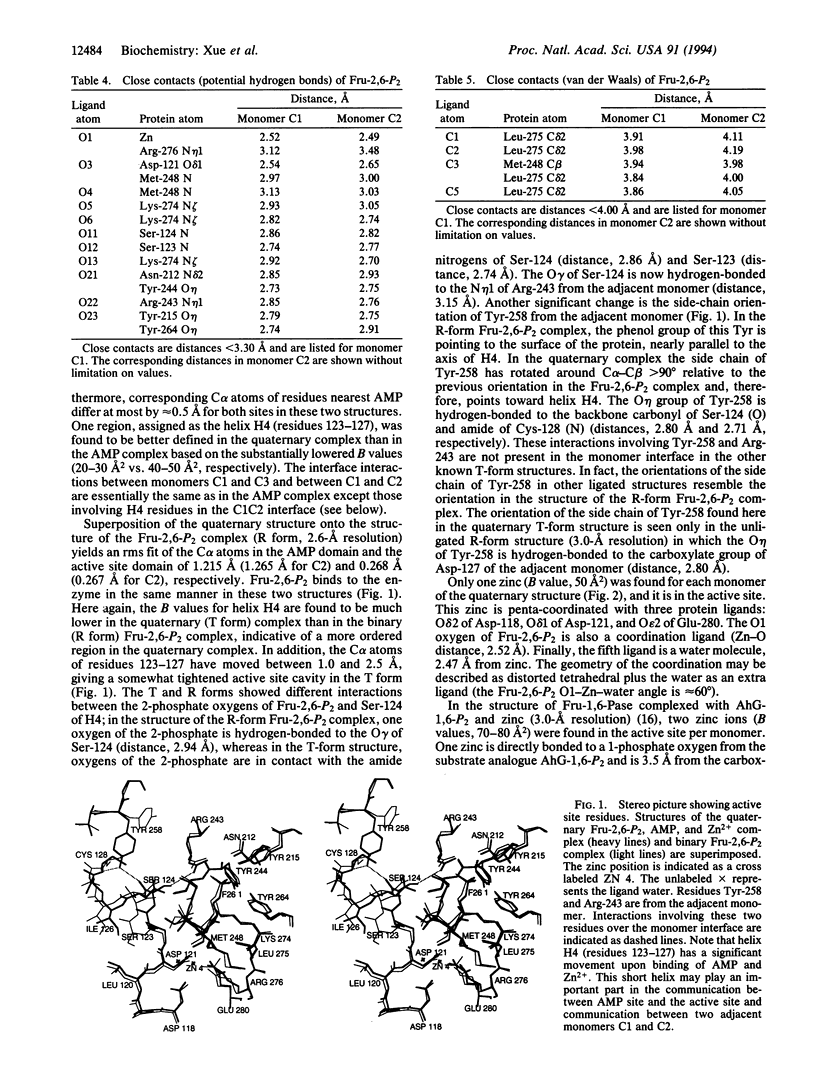
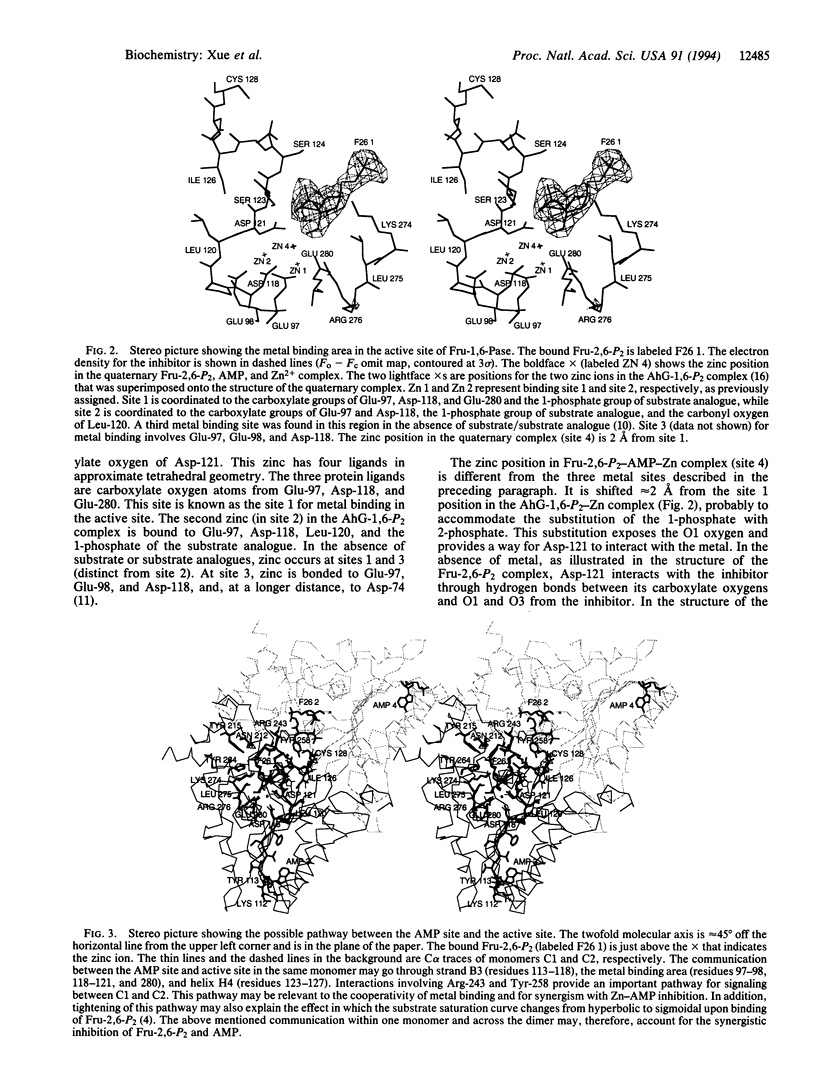
The crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (Fru-1,6-Pase; EC 3.1.3.11) complexed with Zn2+ and two allosteric regulators, AMP and fructose 2,6-bisphosphate (Fru-2,6-P2) has been determined at 2.0-A resolution. In the refined model, the crystallographic R factor is 0.189 with rms deviations of 0.014 A and 2.8 degrees from ideal geometries for bond lengths and bond angles, respectively. A 15 degrees rotation is observed between the upper dimer C1C2 and the lower dimer C3C4 relative to the R-form structure (fructose 6-phosphate complex), consistent with that expected from a T-form structure. The major difference between the structure of the previously determined Fru-2,6-P2 complex (R form) and that of the current quaternary T-form complex lies in the active site domain. A zinc binding site distinct from the three binding sites established earlier was identified within each monomer. Helix H4 (residues 123-127) was found to be better defined than in previously studied ligated Fru-1,6-Pase structures. Interactions between monomers in the active site domain were found involving H4 residues from one monomer and residues Tyr-258 and Arg-243 from the adjacent monomer. Cooperativity between AMP and Fru-2,6-P2 in signal transmission probably involves the following features: an AMP site, the adjacent B3 strand (residues 113-118), the metal site, the immediate active site, the short helix H4 (residues 123-127), and Tyr-258 and Arg-243 from the adjacent monomer within the upper (or lower) dimer. The closest distance between the immediate active site and that on the adjacent monomer is only 5 A. Thus, the involvement of H4 in signal transmission adds another important pathway to the scheme of the allosteric mechanism of Fru-1,6-Pase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benkovic S. J., deMaine M. M. Mechanism of action of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1982;53:45–82. doi: 10.1002/9780470122983.ch2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brünger A. T., Kuriyan J., Karplus M. Crystallographic R factor refinement by molecular dynamics. Science. 1987 Jan 23;235(4787):458–460. doi: 10.1126/science.235.4787.458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- François J., Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. On the mechanism of inhibition of neutral liver fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Aug 1;134(2):269–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07561.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. A., Zou J. Y., Cowan S. W., Kjeldgaard M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr A. 1991 Mar 1;47(Pt 2):110–119. doi: 10.1107/s0108767390010224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke H. M., Liang J. Y., Zhang Y. P., Lipscomb W. N. Conformational transition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase: structure comparison between the AMP complex (T form) and the fructose 6-phosphate complex (R form). Biochemistry. 1991 May 7;30(18):4412–4420. doi: 10.1021/bi00232a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke H. M., Thorpe C. M., Seaton B. a., Lipscomb W. N., Marcus F. Structure refinement of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase and its fructose 2,6-bisphosphate complex at 2.8 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1990 Apr 5;212(3):513–539. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90329-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke H. M., Zhang Y. P., Liang J. Y., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal structure of the neutral form of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase complexed with the product fructose 6-phosphate at 2.1-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):2989–2993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ke H. M., Zhang Y. P., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal structure of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase complexed with fructose 6-phosphate, AMP, and magnesium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5243–5247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liang J. Y., Huang S., Zhang Y., Ke H., Lipscomb W. N. Crystal structure of the neutral form of fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase complexed with regulatory inhibitor fructose 2,6-bisphosphate at 2.6-A resolution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2404–2408. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2404. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilkis S. J., El-Maghrabi M. R., Pilkis J., Claus T. Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 25;256(8):3619–3622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHIMASSEK H., MITZKAT H. J. UBER EINE SPEZIFISCHE WIRKUNG DES GLUCAGON AUF DIE EMBDEN-MEYERHOF-KETTE IN DER LEBER. VERSUCHE AN DER ISOLIERT PERFUNDIERTEN RATTENLEBER. Biochem Z. 1963 Aug 14;337:510–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tejwani G. A. Regulation of fructose-bisphosphatase activity. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1983;54:121–194. doi: 10.1002/9780470122990.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E. Fructose 2,6-bisphosphate. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1987;59:315–395. doi: 10.1002/9780470123058.ch7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Schaftingen E., Hers H. G. Inhibition of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase by fructose 2,6-biphosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2861–2863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Liang J. Y., Huang S., Ke H., Lipscomb W. N. Crystallographic studies of the catalytic mechanism of the neutral form of fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 23;32(7):1844–1857. doi: 10.1021/bi00058a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]