Abstract
Background
Homegardens in Ethiopia are currently facing different threats mainly due genetic erosion, loss of traditional knowledge on their use and management and drought. On the other hand, research and documentation works on homegardens in the country are very limited. There is no previous report indicating conduct of ethnobotanical study on homegardens in selected study district. The present study thus attempted to document knowledge on uses and management practices of homegardens by people in study district.
Methods
The study was conducted in Sebeta-Awas District, Southwestern Shewa Zone of Oromia Region, Ethiopia, between March and September 2009 to assess use, species diversity and conservation status of homegardens in the District. Data were collected using semi-structured interviews as well as through homegarden visits, market surveys and different ranking exercises. For the semi-structured interviews, 42 homegarden owners were selected randomly from seven sampled kebeles (smallest administrative units in Ethiopia), six from each kebele. For different ranking exercises, 14 informants (10 males and 4 females) were sampled using convenient sampling method from among homegarden owners that already participated in semi-structured interviews.
Results
In total, 113 plant species belonging to 46 families were recorded from the study area, of which 45 (39.8 %) were herbs, 34 (30.1 %) were trees, 26 (23.0 %) were shrubs and 8 (7.1 %) were climbers. Fabaceae had the highest number of species, followed by the families Asteraceae, Lamiaceae and Solanaceae. The cash crops Catha edulis, Rhamnus prinoides and Ruta chalepensis were the most frequently encountered homegarden plants. Cupressus lusitanica, Eucalyptus camaldulensis and Faidherbia albida were the most abundant tree species that had the highest densities of occurrence. Of the recorded plant species, 25 % were used as sources of food, 13 % as medicine and 10 % as household tools.
Conclusion
It can be concluded that homegardens in the study area are rich in crops and, therefore, significantly contribute to the agrobiodiversity of the study District, in particular, and Ethiopia, in general.
Keywords: Homegarden, Agrobiodiversity, Local knowledge, Sebeta-Awas, Ethiopia
Background
Homegarden is commonly defined as a piece of land with a definite boundary surrounding a homestead, being cultivated with diverse mixture of perennial and annual plant species, arranged in a multilayered vertical structure, often in combination with raising livestock, and managed mainly by household members for subsistence production [1–4]. Homegardens are complex ecosystems close to the house where plants can be closely observed and managed and are convenient place for traditional plant experimentation [5].
Homegardens are important in the conservation of useful plant species since they contain very large numbers of species which are often absent or disappearing from other production systems [6]. Homegardens also provide a wide range of ecological benefits and services and a valuable set of products for the rural poor [6]. Homegardens provide people with supplementary food, fuel and fodder [7]. They are used to grow medicinal, spice, ornamental and stimulant plants [8]. Homegardens are widely spread in the tropical and subtropical regions of Asia [9], Africa [10] and Central and South America [11].
Although there is no direct evidence as to when homegardening started in Ethiopia, based on the antiquity of agriculture, crop composition, oral literature and rich vernacular designations in different local languages, it is assumed to have long history [12]. Homegardening in Ethiopia is estimated to have started as early as 5000 to 7000 years ago, around the time when agriculture started in the country [13, 14]. In relation to the house, Ethiopian homegardens may occupy different positions such as the backyards, frontyards, side yards and yards that almost encircle the house, and have variable shapes and sizes and composition of plant species [12]. In Ethiopia, homegardens are prevalent in the highland areas and mainly accommodate supplementary fruits and vegetables as a principal means of livelihood for households [15–18]. A study [16] indicated that more than 170 crop species belonging to 121 genera and 50 families have been recorded in Ethiopia, of which, the families Fabaceae, Lamiaceae, Poaceae, Rubiaceae, Asteraceae, and Rubiaceae contributed more than 10 species each.
Ethiopia is one of the eight world centers of origin and diversity of agricultural products [19] which is partly the result of in situ conservation of plants traditionally grown in homegardens [12, 17]. However, homegardens are currently threatened mainly due to genetic erosion, loss of traditional knowledge of different management practices, man-made habitat changes, and drought [4, 20]. On the other hand, research and documentation works done on homegardens in Ethiopia are very limited [21–26] and most of them have been conducted in the south and southwestern parts of the country. There is no report indicating the conduct of ethnobotanical study on homegardens of the selected district. The present study thus attempted to gather and document information on the use of plant species and management practices of homegardens by people in Sebeta-Awas District, Southwestern Shewa Zone of Oromia Region, Ethiopia.
Methods
The study area
This study was conducted in Sebeta-Awas District (Fig. 1), Oromia Region, Ethiopia, which is located at a distance of 24 km to 45 km southwest of the capital Addis Ababa. The District has an area of 87,532 ha. It shares borders with Akaki District in the East, Kerssa and Tole districts in the south, Welmera District in the North and Ilu and Ejere districts in the West. The land feature of Sebeta-Awas is characterized by mountains and hills (Wachacha and Hoche mountains) and marshy plains (Furi-Gara-Bello, Gejja Ballachis and Jammo), and is surrounded by Awash water shade in the west [27]. Altitude in the District ranges between 1800 and 3385 m a.s.l (Sabata Awas District Rural and Agricultural Office, unpublished data of 2001).
Fig. 1.
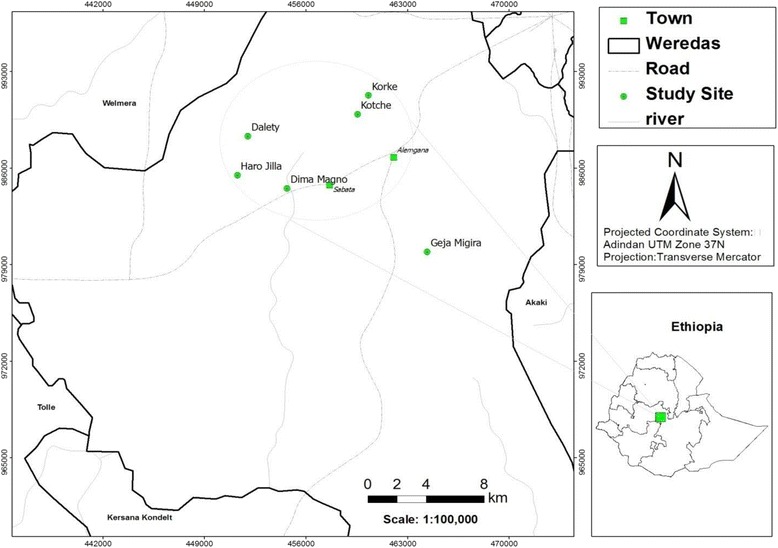
Map of Sebeta-Awas District locating the selected study kebeles (drawn based on Ethio GIS Data)
Agricultural activity is the dominant means of livelihood in Sebeta-Awas District. People in the District use functional categorization to classify their lands, e.g., grazing land, agricultural land, homestead land and forestland. According to annual report of Sebeta-Awas District, Rural and Agricultural Development Office, out of 87,532 ha of land, 73,838 ha (84.4 %) are used for agriculture to cultivate different crops for household consumption and sale in local market, and 3.689 ha (4.2 %) of land is used as grazing area (Sabata Awas District Rural and Agricultural Office, unpublished data of 2006).
The District is divided into two agro-ecological zones locally called Baddaa (12 %) and Badda daree (88 %), which means highland and midland areas, respectively (Sabata Awas District Rural and Agricultural Office, unpublished data of 2006). The study area experiences alternating wet and dry seasons. The main rainy season is between June and September and is locally called rooba gaanaa. Light rain occurs between January and March and is locally called rooba arfassa. There is no temperature data for Sebeta-Awas District. Thus temperature data of Alemtena, a nearby district having similar altitude as that of Sebeta-Awas District, was used to compute 10 years (1995 to 2006) annual mean temperature for the study area. The annual mean maximum and minimum temperatures are 25.4 °C and 13.9 °C, respectively. The annual mean maximum and the minimum temperatures were recorded in the months of May and July, respectively. The total mean annual rainfall from 1995 to 2006 is 1054.7 mm and the highest rainfall recorded is for July (National Metrological Service of Ethiopia, unpublished data of 2009).
Selection of study kebeles and homegardens
Reconnaissance survey was conducted in Sebeta-Awas District in January 2009 to select study kebeles (smallest administrative units in Ethiopia) and conduct homegarden surveys. During the reconnaissance survey, seven kebeles (from a total of 42 kebeles in the District) including Dima Guranda, Dalety, Dima Magno, Geja Migra, Haro Jilla, Korke and Kotche were randomly selected. In each selected kebele, visits were made to 50 households that were sampled during random walks to check for the presence or absence of homegardens and assess their sizes, shapes and locations with respect to houses.
Selection of informants and ethnobotanical data collection
Ethnobotanical data were collected between March and August 2009 mainly through homegarden tours, market surveys and semi-structured interviews. Interviews were conducted using pre-prepared questions with 42 randomly selected homegarden owners (32 males and 10 females with ages ranging from 35 to 72 years) from the randomly selected seven kebeles, six from each kebele, after receiving their full consent. The homegarden owners involved in the interviews were sampled from the list of households that were found to own homegardens during survey of 350 households (50 from each sampled kebele) to check for the presence or absence of homegardens. All interviews were conducted in Oromo language. During interviews with the informants, attempts were made to document information on the use of homegarden plants for different purposes (household food supply, medicine, shade, aesthetics and ornament, fuel wood production and for income generation) and management practices. Additional data were also gathered through, simple preference ranking, direct matrix ranking and paired comparison exercises [28–30] by involving 14 informants (two from each kebele) between the ages of 40 and 65 (10 males and 4 females). The informants were sampled using convenient sampling method from among homegarden owners that already participated in the semi-structured interviews. The study was conducted in accordance with the Code of Ethics of the International Society of Ethnobiology [31].
Simple preference ranking
During preference ranking exercise, 14 informants were asked to rank seven marketable homegarden plants in Sebeta-Awas District that were found to have the highest frequencies and relative frequencies of occurrence and rank them according to their perceived values or desirability following the method of Martin [30]. The integer values 1, 2, 3 and 4 were used whereby the most important plant was given the highest value, while the least important one was assigned with the smallest value. The numbers were then summed for all respondents to come up with an overall ranking.
Direct matrix ranking
Direct matrix ranking exercises were conducted by the same 14 informants on six multipurpose tree species as reported during interviews using the approach of Martin [30] to rank them based on their uses as construction material, fertilizer, household tools, charcoal/firewood, shade, live fence and medicine. Informants were asked to assign value to each attribute (5 = best, 4 = very good, 3 = good, 2 = less used, 1 = least used and 0 = not used).
Paired comparison
Paired comparison exercises were conducted by the 14 informants following the methods of Martin [30] on five nutraceutical plants (plants used as sources of both food and medicine) as reported during interviews with informants.
Market survey
Market survey was conducted in one open market found in Sebeta, an administrative town of the Sebeta-Awas District, to check for availability of marketable homegarden plants. Data were gathered through observation and interaction with sellers and buyers of homegarden products.
Plant specimen collections and identification
Specimens of plants recorded as homegarden species were collected, numbered, pressed and dried. They were later identified using taxonomic keys of the Flora of Ethiopia and Eritrea and by comparison with already identified specimens that were deposited at National Herbarium (ETH), Addis Ababa University. The identities of the specimens were authenticated by taxonomists at ETH.
Data analysis
Descriptive statistical methods were employed to determine frequencies, relative frequencies, densities and relative densities. Shannon and Wiener index and Sorensen’s Index were used to estimate species diversity and similarity, respectively, in sample plots of 15 m x 15 m (225 m2) in homegardens of the 42 randomly selected informants, six from each of the seven selected kebeles.
Frequency and relative frequency
Frequencies and relative frequencies were calculated for plants in the sampled homegardens. Frequency describes the distribution of a species throughout the stands. It is determined by calculating the percentage of plots/quadrants in a sample area on which a given species occurs [30].
Relative frequency is the number of occurrences of a species as a percentage of the total occurrences of all species [30].
Density and relative density
Density is the average number of individuals of a species on a unit area basis. It is closely related to abundance but more useful in estimating the importance of a species [30].
Relative density is the number of individuals of a species as a percentage of the total number of individuals of all species in that area [30].
Multipurpose trees species occurring in home gardens of the study area were considered in the computation of densities and relative densities.
Similarity and diversity indices
Sorenson’s Index of Similarity was used to compare the degree of similarity of species in the 42 homegardens randomly selected from the seven study kebeles (6 homegardens in each kebele) based on the species composition of quadrats [32]. It was calculated using the formula Ss = 2a/2a + b + c, where SS = Sorensen’s similarity coefficient, a = number of species common to quadrat, b = number of species in quadrat 1 and c = number of species in quadrats 2. The coefficient values range from 0 (complete dissimilarity) to 1 (total similarity). This method was applied in all the 42 homegardens in the selected kebeles.
The Shannon-Weiner Index [33] was used to calculate and compare species diversity in the 42 homegardens in the seven study kebeles. It was calculated using the formula H = ∑ − (Pi ln Pi), where H = the Shannon diversity index, Pi = fraction of the entire population made up of species I, S = numbers of species encountered, ∑ = sum from species 1 to species S and ‘ln’ is the natural logarithm to the base e (log e).
Results and discussion
Distribution, location and plant composition of homegardens
Out of the 350 houses surveyed in the seven selected kebeles in the study District, 248 (70.9 %) had homegardens, of which 126 (36 %), were located in the backyard (Table 1). Homegardens had different sizes and shapes, and served as animal houses, grain stores and land for growing different plant species. The size of homegardens sampled ranged from 300 m2 to 1200 m2. Distinct variation in size, diversity and composition of species was observed among homegardens. With increasing size of homegardens, more richness of species composition was observed. A similar study conducted in southern Ethiopia [24] revealed that as the size of homegarden increases, so does the diversity of plant species. Concerning distance, some homegardens were located very close to houses, where as others were found at places a bit far from houses (at a walking distance of 5–7 min).
Table 1.
Distribution and location of homegardens in the selected seven study kebeles of Sebeta-Awas District
| Kebeles | No. of surveyed houses | No. of houses with homegardens | Position of homegardens | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| front yard gardens | backyard gardens | side yard gardens | front yard & backyard gardens | front yard & side yard gardens | backyard & side yard gardens | round yard gardens | |||
| Dima Guranda | 50 | 39 | 5 | 12 | - | 3 | - | 4 | 1 5 |
| Dima Magno | 50 | 35 | - | 18 | 5 | - | - | 12 | |
| Haro Jila | 50 | 38 | 22 | 4 | 10 | 2 | |||
| Dalati | 50 | 34 | 6 | 18 | 2 | - | 7 | 1 | - |
| Geja Migra | 50 | 33 | 4 | 14 | - | 3 | 3 | 8 | 1 |
| Koche | 50 | 37 | 14 | 22 | - | - | - | - | 1 |
| Korke | 50 | 32 | - | 20 | - | 7 | - | 5 | - |
| Total | 350 | 248 | 29 | 126 | 11 | 23 | 10 | 18 | 31 |
| % | 70.9 | 8.3 | 36 | 3.1 | 6.6 | 2.9 | 5.1 | 8.9 | |
Homegarden plants in the study area were composed of trees, shrubs, herbs and climbers in different strata. They consisted of trees approximately 10 to 15 m tall on the upper strata (e.g., Cordia Africana), fruit crops 1 to 10 m tall in the middle strata (e.g., Citrus sinensis) and herbaceous plants up to 1 m tall on the ground strata (e.g., Brassica carinata and Cymbopogon citratus).
Management of homegardens
People in the study area have developed homegardens (locally called eddo) with considerable diversity and flexibility that support production of major livelihood crops. They have managed to select crops that co-adapt the local environment and that give multiple benefits. Some homegarden owners reported that they grew vegetables during the rainy season as well as the dry season by fetching water from where it is available. Some homegarden owners stated that they continuously manage plants for economic as well as ecological benefits. Crop residues, weeds, ashes and manures were reported to be used as fertilizers in homegardens. Few homegarden owners reported efforts made to reduce soil depletion in erosion-prone areas by planting shrubs (e.g., Rosmarinus officinalis) near the homestead.
Homegardens in the study area were open plots, or fenced or semi-fenced areas. Trees and shrubs were used as live fences to protect homegarden plants from predators. Management of homegardens was done through division of labor among family members. Observation and conversation with informants revealed that females played more roles than males in managing homegardens. Females were more involved in weeding, watering and planting, whereas, males’ activity was limited to fencing. Dominance of females in hoeing, weeding, and harvesting has been indicated in works conducted in Tanzania [34] and Ghana [35]. Selection of crops or vegetables for homegardening has been done in consultation with household members although the final decision was left to women. Despite the fact that management of homegardens in the study area was mainly the responsibility of females, as explained by women homegarden owners, access to or control over its benefits depends on the type of production. Men had more control on major income crops (e.g., Chata edulis). Minor income generated from crops such as vegetables is controlled by women. In homegardens dominated by subsistence crops, females did most of the work. However, in homegardens dominated by cash crop fruit trees, women’s participation was very minimal. Such a clear gender division in homegarden responsibilities is frequently recorded in the literature, e.g., Vietnam [36] and Mexico [37] and Peru [38].
Exchange of seeds of selected varieties and knowledge among homegarden owners was reported to be common practices in the study area. Exchange of information regarding homegardens among relatives, friends, and neighbors played a role in maintaining local cultural knowledge and practices in the study area. Exchange of plant resources and information among local communities is essential for agrobiodiversity conservation [30].
Richness and diversity of homegarden plant species
Out of 350 houses visited in the seven selected kebeles, 248 (70.9 %) had homegardens, of which 42 (6 from each kebele) were selected for detailed interview surveys. The interview survey revealed 113 homegarden plant species belonging to 46 families (Table 2) which supports the assertion that homegardens are valuable sources of plant agrobiodiversity [39]. It was found out that the family Fabaceae had the highest number of species (15 spp.), followed by Asteraceae (10 spp.), Lamiaceae (7 spp.), Solanaceae (6 spp.), Poaceae and Rosaceae (5 spp. each), and Myrtaceae and Rutaceae (4 species each). Five families had three species each. Other nine families had 2 species each and 24 families had one species each. A study conducted in Loma and Gena Bosa districts of Ethiopia also reported the high number of homegarden plants belonging to the families of Fabaceae, Asteraceae and Poaceae [8]. Of the total species, 45 (39.8 %), were herbs, 34 (30.1 %) were trees, 26 (23.0 %) were shrubs and 8 (7.1 %) were climbers. Cupressus lusitanica, Eucalyptus camaldulensis Eucalyptus globules and Grevellea robusta were the canopy tree species. Among shrub species, Catha edulis, Rosmarinus officinalis and Rhamnus prinoides were the most prominent ones.
Table 2.
Homegarden plants documented from Sebeta-Awas District
| Family | Scientific name | Local name | Habit | Indigenous/exotic | Use | Coll. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acanthaceae | Justicia schimperiana (Hochst. ex Nees) T.Anders. | Dhummugaa (O) | Shrub | Indigenous | Live fence | TM75 |
| Alliaceae | Allium cepa L. | Qullubii-diimaa (O) | Herb | Exotic | Vegetable | TM105 |
| Allium sativum L. | Quulubii-adii (O) | Herb | Exotic | Vegetable, medicine | TM76 | |
| Amaranthaceae | Amaranthus hybridus L. | Oromee (O) | Herb | Exotic | Vegetable, weed | TM32 |
| Achyranthes aspera L. | - | Herb | Indigenous | Medicine, weed | TM92 | |
| Iresine herbstii Hook. ex. Lindl. | - | Herb | Exotic | Ornament | TM16 | |
| Anacardiaceae | Rhus glutinosa A. Rich | Xaxeecha (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Fuel wood | TM104 |
| Schinus molle L. | Alaaltu (O) | Tree | Exotic | Shade, household tool | TM63 | |
| Mangifera indica L. | Mango (O, A, G) | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM45 | |
| Annonaceae | Annona cherimola Mill. | Gishta (A) | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM87 |
| Apiaceae | Anethum graveolens L. | - | Herb | Exotic | Weed | TM10 |
| Daucus carota L. | Carorot (A) | Herb | Indigenous | Vegetable | TM57 | |
| Apocynaceae | Carissa spinarum L. | Hagamsa (O) | Liana | Indigenous | Live fence | TM70 |
| Asparagaceae | Agave americana L. | Argissa (O) | Herb | Exotic | Household tool | TM47 |
| Agave sisalana Perrine ex. Engler | Argissa (O) | Herb | Exotic | Household tool | TM79 | |
| Asteraceae | Artemisia absinthum L. | Arrity | Herb | Exotic | Medicine | TM24 |
| Conyza pyrrhopappa Sch. Bip ex A. Rich. | - | Herb | Indigenous | Ornament | TM109 | |
| Guizotia schimperi Sch.Bip ex. Walp | - | Herb | Indigenous | Weed | TM39 | |
| Lactuca sativa L. | Selata (A) | Herb | Exotic | Vegetable | TM108 | |
| Parthenium hysterophorous L. | Faramsiisa (O) | Herb | Exotic | Weed | TM107 | |
| Silybum marianum (L.) Gaertn. | Sokooruu (O) | Herb | Exotic | Weed | TM99 | |
| Sonchus oleraceus L. | Sokooruu (O) | Herb | Exotic | Weed | TM58 | |
| Spathodea campanulata P. Beauv. | - | Tree | Exotic | Shade | TM65 | |
| Tagetes patula L. | - | Herb | Exotic | Ornament | TM89 | |
| Vernonia amygdalina Del. | Ebichaa (O) | Shrub | Indigenous | Household tool, medicine | TM19 | |
| Boraginaceae | Cordia africana Lam. | Wadeecha (O | Tree | Indigenous | Household tool, shade, medicine | TM15 |
| Brassicaceae | Brassica carinata A. Br. | Yeguragiegomen (A) | Herb | Indigenous | Vegetable | TM111 |
| Brassica oleracea L. | Goommana (O), Tql-gomen (A) | Herb | Exotic | Vegetable | TM93, TM101 | |
| Cactaceae | Opuntia cylindrica (Lam.) DC. | Qulqal (A) | Shrub | Exotic | Live fence | TM30 |
| Caricaceae | Carica papaya L. | Papay (A) | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop, medicine | TM7 |
| Celastraceae | Catha edulis (Vahl) Forssk. ex Endl. | Caatii (O) | Shrub | Indigenous | Stimulant | TM6 |
| Chenopodiaceae | Beta vulgaris L. | Qosta (A) | Herb | Exotic | Vegetable | TM20 |
| Cucurbitaceae | Cucurbita pepo L. | Dabaaqula (O) | Liana | Exotic | Vegetable, medicine | TM46 |
| Lagenaria abyssinica (Hook. f.) C. Jeffery | Hadoftu (O) | Liana | Indigenous | Household tool | TM59 | |
| Cupresaceae | Cupressus lusitanica Mill. | Gaattiraa–faraanjii (O) | Tree | Exotic | Live fence | TM48 |
| Juniperus procera Hochst. ex Endl. | Gatira Habasha (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Construction, household tool | TM44 | |
| Cyperaceae | Cyperus rotundus L. | - | Herb | Indigenous | Household tool | TM13 |
| Euphorbiacaeae | Croton macrostachyus Del. | Bakkanisa (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Fuel wood, shade, household tool | TM60 |
| Euphorbia ampliphylla Pax. | Adamee (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Weed | TM36 | |
| Ricinus communis L. | Qobboo (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Household tool | TM78 | |
| Fabaceae | Acacia abyssinica Hochst. ex Benth. | Laaftto (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Fuel wood, shade, household tool | TM9 |
| Faidherbia albida (Delile) A. Chev. | Laftto (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Shade, household tool | TM1 | |
| Acacia mearnsii De Willd. | Yetemenja–zaf (O) | Tree | Exotic | Fuel wood | TM18 | |
| Acacia saligna (Labill.) Wendl. | - | Tree | Exotic | Shade | TM4 | |
| Albizia schimperiana Oliv. | Hambabessa (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Shade, household tool | TM8 | |
| Caesalpinia decapetala (Roth) Alston | Arangamaa (O) | Liana | Exotic | Live fence | TM3 | |
| Calpurnia aurea (Ait.) Benth. | Ceekaa (O) | Shrub | Indigenous | Medicine | TM68 | |
| Erythrina brucei Schweinf. | Wolensuu (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Shade | TM52 | |
| Millettia ferruginea (Hochst.) Bak. | Sotoollo (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Shade, household tool | TM77 | |
| Phaseolus lunatus L. | Adengware (A) | Liana | Exotic | Pulse | TM49 | |
| Phaseolus vulgaris L. | Boloqqie (A) | Liana | Exotic | Pulse | TM71 | |
| Senna septemtrionalis (Viv.) Irwin & Barnby | Akayi-warabessa (O) | Tree | Exotic | Fuel wood | TM17 | |
| Sesbania sesban (L.) Merr. | - | Shrub | Exotic | Live fence | TM35 | |
| Trifolium tembense Fresen. | - | Herb | Indigenous | Weed | TM112 | |
| Vicia faba L. | Baqeella (O) | Herb | Exotic | Pulse | TM110 | |
| Flacourtiaceae | Dovyalis caffra (Hook. f. & Harv.) Hook. f. | Koshomii (O) | Shrub | Exotic | Live fence | TM80 |
| Lamiaceae | Mentha longifolia (L.) Hudson | - | Herb | Indigenous | fragrant | TM40 |
| Mentha puegium L. | Nana (A) | Herb | Indigenous | Spice | TM94 | |
| Ocimum basilicum L. | Besobilla (A) | Herb | Exotic | Spice | TM74 | |
| Ocimum lamiifolium Hochst. ex Benth. | Koricha–Michii (O) | Shrub | Indigenous | Medicine | TM66 | |
| Ocimum urticifolium Roth | Koricha-alkani (O) | Shrub | Indigenous | Medicine | TM100 | |
| Otostegia integrifolia Benth. | Tungit (A) | Shrub | Indigenous | Medicine | TM106 | |
| Rosmarinus officinalis L. | Siga-metibesha (A) | Shrub | Exotic | Fragrant | TM31 | |
| Lauraceae | Persea americana Mill. | Abukado (O, A, G) | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM2 |
| Loganiaceae | Buddleja davidii Franch. | Amfar (O) | Shrub | Exotic | Live fence | TM82 |
| Lythraceaee | Punica granatum L. | Roman (A) | Shrub | Exotic | Fruit crop, medicine | TM85 |
| Malvaceae | Hibiscus sp. | - | Shrub | Indigenous | Ornament | TM25 |
| Malva verticillata L. | Litii (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Medicine | TM64 | |
| Sida schimperiana Hochst. ex. A. Rich. | Guute (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Household tool | TM103 | |
| Moraceae | Ficus elastica Roxb. | Yegoma-zaf (A) | Tree | Exotic | Shade | TM95 |
| Ficus sur Forssk. | Harbuu (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Shade | TM29 | |
| Morus alba L. | Enjorie (O) | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM28 | |
| Musaceae | Ensete ventricosum (Welw.) Cheesman. | Qoccoo (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Medicine, household tool | TM41 |
| Myrtaceae | Eucalyptus camaldulensis Dehnh. | Bargamo-diimaa (O) | Tree | Exotic | Construction, fuel wood, live fence | TM5 |
| Eucalyptus globulus Labill. | Bargamo-adii (O) | Tree | Exotic | Construction, medicine | TM27 | |
| Myrtus communis L. | Ades (A, G) | Herb | Exotic | Fragrant | TM86 | |
| Psidium guajava L. | Zeytunaa (O) | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM53 | |
| Nyctaginaceae | Bougainvillea glabra Choisy | Bugambe (A) | Liana | Exotic | Ornament | TM51 |
| Oleaceae | Jasminum abyssinicum Hochest. ex DC. | Qamaxxee (O) | Liana | Indigenous | Medicine | TM91 |
| Olea europaea L. subsp. cuspidata (Wall. ex G. Don) Cif. | Ejeersa (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Fragrant | TM22 | |
| Phytolaccaceae | Phytolacca dodecandra L’ Herit. | Endod (A) | Shrub | Indigenous | Household tool | TM81 |
| Pinaceae | Pinus patula Schiede ex. Schltdl. Cham. | Arzelibanose (A) | Tree | Exotic | Live fence | TM33 |
| Poaceae | Arundo donax L. | Shambako (O) | Herb | Exotic | Household tool, live fence | TM97 |
| Cynodon dactylon (L.) Pers. | Coqoorsa (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Household tool | TM90 | |
| Cymbopogon citratus (DC.) Stapf | Tej-sar (A) | Herb | Exotic | Fragrant, medicine | TM21 | |
| Saccharum officinarum L. | Shenkor-ageda (A) | Herb | Exotic | Sugar crop | TM54 | |
| Zea mays L. | Boqqolloo (O) | Herb | Exotic | Cereal crop | TM113 | |
| Poygonaceae | Rumex nepalensis Spreng. | Shultii (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Medicine | TM88 |
| Proteaceae | Grevillea robusta R. Br. | - | Tree | Exotic | Live fence, shade | TM50 |
| Rhamnaceae | Rhamnus prinoides L’ Herit. | Geeeshoo (O, A) | Shrub | Indigenous | Household tool | TM14 |
| Rosaceae | Hagenia abyssinica (Bruce) J. F. Gmel. | Heexoo (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Medicine | TM61 |
| Malus sylvestris Miller | Apple | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM98 | |
| Prunus x domestica L. | Prim (A) | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM69 | |
| Rosa abyssinica Lindley | Qega (A) | Shrub | Indigenous | Live fence | TM42 | |
| Rosa hybrida L. | Tsigereda (A) | Shrub | Exotic | Ornament | TM12 | |
| Rubiaceae | Coffea arabica L. | Buna (O, A, G) | Shrub | Indigenous | Stimulant | TM11 |
| Galium aparinoides Forssk. | Maxaanee (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Weed | TM114 | |
| Rutaceae | Casimiroa edulis La Llave | Shasho (A) | Tree | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM43 |
| Citrus aurantifolia (Christm.) Swingle | Lomii (O) | Shrub | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM37 | |
| Citrus sinensis (L.) Osb. | Burtukaana (O) | Shrub | Exotic | Fruit crop | TM83 | |
| Ruta chalepensis L. | Chiracot (O, G) | Herb | Exotic | Spice, medicine | TM67 | |
| Salicaceae | Populus sp. | Ye-kibrit enchet (A) | Tree | Exotic | Household tool | TM23 |
| Santalaceae | Osyris quandripartita Decn. | Watoo (O) | Tree | Indigenous | Construction | TM62 |
| Scrophulariaceae | Verbascum sinaiticum Benth. | Guraa haree | Shrub | Indigenous | Weed | TM56 |
| Simarobaceae | Brucea antidysenterica J. F Mill. | Qomeenyo (O) | Shrub | Indigenous | Medicine | TM38 |
| Solanaceae | Capsicum annuum L. | Brbare (O) | Herb | Exotic | Vegetable | TM34 |
| Datura stramonium L. | Asangiraa (O) | Herb | Indigenous | Medicine | TM102 | |
| Lycopersicon esculentum Mill. | Timatimi (O) | Herb | Exotic | Vegetable | TM73 | |
| Nicotiana tabacum L. | Tamboo (O) | Herb | Exotic | Stimulant | TM55 | |
| Solanum tuberosum L. | Dinichaa (O) | Herb | Exotic | Tuber crop | TM84 | |
| Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal | Gizawa (A) | Herb | Indigenous | Medicine | TM72 | |
| Verbenaceae | Lantana camara L. | Ye- wof kolo (A) | Shrub | Exotic | Ornament | TM26 |
| Lippia abyssinica (Otto & A. Dietr.) Cufod. | Kusaaye (O) | Shrub | Indigenous | Spice, fragrant | TM96 |
A Amharic Language, O Oromo language
Of the total reported homegarden plants, 63 (58 %) were found to be exotic species and 51 (48 %) were indigenous species (Table 2). The fact that the majority of homegarden plants were exotic might be attributed to their management suitability. Of the exotic plants, relatively higher number of species (24) was used as food plants and eight species were used as live fence. Relatively higher number of the indigenous plants (13 species) was used as source of medicine and nine species were used as household tools.
Of the study kebeles, Dima Guranda had the highest species diversity (H’ = 3.555), followed by Haro Jilla (H’ = 3.497). The lowest diversity index (H’ = 3.348) was computed for Dalety (H’ = 2.890) (Table 3). Homegarden owners reported that homegarden species diversity could be related to factors such as access to water, size of homegarden and infestation of plants by pests and weeds. Elsewhere, it was reported that low species diversity could be a result of the shifting from polycultural gardening practices to cultivating few income generating food crops [26].
Table 3.
Shannon-Wiener Diversity Index (H’) and Evenness (J) for the seven study sites in Sebeta-Awas District
| Study sites | Species richness | Shannon’s index (H’) | Evenness (H’/H’ max) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dima Guranda | 35 | 3.555 | 1.000 |
| Dima Magno | 29 | 3.367 | 0.947 |
| Haro Jilla | 33 | 3.497 | 0.984 |
| Dalety | 18 | 2.89 | 0.813 |
| Geja Migira | 19 | 2.994 | 0.842 |
| Kotche | 32 | 3.446 | 0.969 |
| Korke | 25 | 3.219 | 0.905 |
Diversity of uses of homegarden species
It was found that food plants (fruits, vegetables, legumes and pulses) constituted 25 %, of the recorded homegarden species (Fig. 2), which is in agreement with findings of studies conducted in Sabata town of Ethiopia [26] and in Loma and Gena Bosa districts of Ethiopia [8] where the most frequently maintained crops in the homegardens of Sabata town were reported to be those that serve as source of food. In the study area, medicinal and household tool plants comprised 13 and 10 % of the total reported plants, respectively.
Fig. 2.
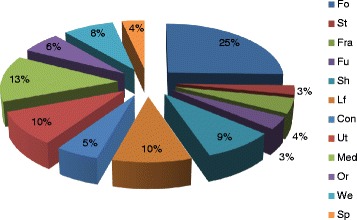
Use category of homegarden plant species in Sebeta-Awas District with their percentage occurrence: Fo = food crop, St = stimulant, Fra = fragrant, Fu = fuel wood, Sh = shade, Lf = Life fence, Con = construction, Ut = household tools, Med = medicine, Om = ornamental, Wd = weed, Sp = spice
Food plants
Food plants are cultivated in homegardens year round in the study area although most of these plants are available in adequate amount only during the main rainy season (June and September). Five nutraceutical plants were recorded from homegardens in the study area (Table 4). Paired comparison exercise conducted on all the five nutraceutical plants revealed Allium sativum and Ensete ventricosum as the most important nutraceutical plants (Table 5). The two species are the ones that are commonly used as nutraceuticals in Ethiopia as revealed in studies conducted elsewhere in the country [26, 40].
Table 4.
Homegarden nutraceutical plants recorded from the Sebeta-Awas District
| Botanical name | Part used | Ailment treated | Method of preparation and use |
|---|---|---|---|
| Allium sativum | Bulb | Headache, abdominal cramp and flue | The bulb is eaten alone and/or pounded together with Zingiber officinale |
| Carica papaya | Seed | Intestinal parasites | Fresh seeds are eaten |
| Cucurbita pepo | Seed | Tape worm infection | Roasted seeds are chewed and swallowed |
| Ensete ventricosum | Corm | Broken legs and arms | The underground part is boiled and eaten |
| Punica granatum | Leaf | Tape worm infection | Decoction of leaves is drunk |
Table 5.
Results of paired comparisons on five homegarden nutraceutical plants in Sebeta-Awas District
| Medicinal plant name | Informants (coded R1 to R12) | Total score | Ranking | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | |||
| Allium sativum | 3 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 41 | 1 |
| Carica papaya | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 18 | 4 |
| Cucurbita pepo | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 30 | 3 |
| Ensete ventricosum | 3 | 2 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 37 | 2 |
| Punica granatum | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 14 | 5 |
Medicinal plants
People of Sebeta-Awas District are dependent on medicinal plants grown in their homegardens in to partly fulfill their day-to-day health care needs. Twelve percent of the plants recorded from homegardens are medicinal plants. Of the medicinal plants, herbs were the most common used ones, followed by shrubs. Study conducted in homegardens of the Holeta town of Ethiopia also indicated the common use of herbs as sources of medicine [40].
Marketed plants
Homegardens support families in generating additional income although income varied with size of the homegardens. Farmers of Sebeta-Awas District who were in close vicinity to roads and local markets (Sebeta and Alemgana) gave priority to grow cash crops such as Catha edulis, Rhamnus prinoides and Rosmarinus officinalis in their homegardens. The role of home gardens in generating income to families in Ethiopia has also been reported by different authors [8, 26, 40, 41]. Focus to grow few cash crops by neglecting other beneficial crops could reduce the diversity of species managed in homegardens. Simple preference ranking exercise conducted on seven marketed homegarden plants in Sebeta-Awas District with the highest frequencies and relative frequencies of occurrence revealed Catha edulis as the most valued marketed homegarden plant, followed by Rosmarinus officinalis and Rhamnus prinoides (Table 6). The stimulant plant Catha edulis has been reported as one of three homegarden plants that generate the highest income in Holeta town of Ethiopia [40].
Table 6.
Simple Preference ranking exercise on seven marketable homegarden plants in Sebeta-Awas District with the highest frequencies and relative frequencies of occurrence
| Botanical name | Respondents (R) | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 | R2 | R3 | R4 | R5 | R6 | R7 | R8 | R9 | R10 | R11 | R12 | R13 | R14 | Total score | Rank | |
| Artemisia absinthium | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 22 | 7 |
| Catha edulis | 7 | 6 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 7 | 4 | 6 | 7 | 6 | 7 | 92 | 1 |
| Cymbopogon citratus | 2 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 26 | 6 |
| Myrtus communis | 1 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 3 | 3 | 37 | 5 |
| Rhamnus prinoides | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 7 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 72 | 3 |
| Ruta chalepensis | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 60 | 4 |
| Rosmarinus officinalis | 6 | 7 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 7 | 5 | 7 | 6 | 85 | 2 |
Value 7 was assigned to the most valuable plant while 1 to the least valuable plant
Similarity among homegardens
Sorenson’s Index of Similarity calculated for homegarden plants in the seven selected kebeles revealed that there is highest similarity between homegardens of Kotche and Geja Migira kebeles, followed by that of Dalety and Dima Guranda (Table 7).
Table 7.
Sorenson’s Index of similarity of homegarden species among seven selected kebeles of Sebeta-Awas District
| Study kebele | DG | DM | HJ | DA | GM | KO | KOC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DG | 1.00 | ||||||
| DM | 0.66 | 1.00 | |||||
| HJ | 0.60 | 0.66 | 1.00 | ||||
| DA | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.66 | 1.00 | |||
| GM | 0.58 | 0.50 | 0.57 | 0.66 | 1.00 | ||
| KO | 0.70 | 0.47 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.66 | 1.00 | |
| KOC | 0.63 | 0.66 | 0.80 | 0.27 | 0.81 | 0.66 | 1.0 |
DG Dima Guranda, HJ Haro Jila, DM Dima Magno, DA Dalety, GM Geja Migira, KO Korke, KOC Kotche
Multipurpose tree species
Local people in the study District grow in their homegardens plants having diverse uses. Direct matrix ranking exercise conducted on six multipurpose tree species selected during ethnobotanical survey showed Eucalyptus globulus as the most preferred multipurpose tree species, followed by Juniperus procera and Acacia abyssinica (Table 8). A direct matrix ranking exercise conducted by respondents in Holeta town of Ethiopia revealed Juniperus procera as the most preferred multipurpose tree species in homegardens [40].
Table 8.
Result of direct matrix ranking exercise conducted on six multipurpose homegarden tree species in Sebeta-Awas District
| Cordia africana | Croton macrostachyus | Acacia abyssinica | Acacia albida | Juniperus procera | Eucalyptus globulus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Construction | 40 | 21 | 32 | 36 | 64 | 74 |
| Soil fertility | 38 | 30 | 52 | 60 | 28 | - |
| Furniture/ Implements | 65 | 42 | 48 | 38 | 42 | 28 |
| Charcoal/ fire wood | 34 | 26 | 60 | 56 | 25 | 59 |
| Shade | 48 | 36 | 50 | 32 | 38 | 24 |
| Live fence | 31 | 22 | 32 | 24 | 66 | 59 |
| Medicine | 35 | 62 | 26 | 18 | 38 | 63 |
| Total score | 291 | 229 | 300 | 254 | 301 | 307 |
| Rank | 4 | 6 | 3 | 5 | 2 | 1 |
Homegarden plants with the highest frequency of occurrence
Marketed homegarden plants were assessed for their frequencies and relative frequencies of occurrence. It was found out that Catha edulis had the highest frequency and relative frequency of occurrence, followed by Rosmarinus officinalis and Rhamnus prinoides. Seven marketed homegarden plants with the highest frequencies and relative frequencies of occurrence are given in Table 9. Result of another study conducted in Jibithenan District, Ethiopia, showed Catha edulis as one of the top five most abundant woody species in homegardens [41].
Table 9.
Lists of seven homegarden plants in Sebeta-Awas District with the highest frequencies and relative frequencies of occurrence
| Botanical name | Frequency in percent | Relative frequency in percent |
|---|---|---|
| Artemisia absinthium | 45.2 | 1.63 |
| Catha edulis | 80.9 | 2.94 |
| Cymbopogon citratus | 52.3 | 1.89 |
| Myrtus communis | 47.6 | 1.73 |
| Rhamnus prinoides | 73.8 | 2.68 |
| Ruta chalepensis | 71.4 | 2.59 |
| Rosmarinus officinalis | 78.5 | 2.85 |
Homegarden multipurpose tree species with highest density of occurrence
Among multipurpose tree species in the study area, Cupressus lusitanica was found to be the most abundant one with the highest relative density, followed by Eucalyptus camaldulensis and Eucalyptus globulus (Table 10). The reason for this may be due to the availability of seedlings at local market and nursery sites in the nearby Sabata town. A study [26] revealed Cupressus lusitanica as having the highest relative density among homegarden tree species in Sabata town of Ethiopia
Table 10.
Multipurpose tree species in Sebeta-Awas District having the highest densities and relative densities of occurrence
| Botanical name | Abundance/number | Density | Relative density % |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cupressus lusitania | 250 | 0.0264 | 0.0042 |
| Eucalyptus camaldulensis | 92 | 0.0097 | 0.0015 |
| Acacia albida | 23 | 0.0024 | 0.0002 |
| Eucalyptus globulus | 81 | 0.0085 | 0.0013 |
| Olea europaea subsp. cuspidata | 29 | 0.0030 | 0.0004 |
| Cordia africana | 21 | 0.0022 | 0.0003 |
| Juniperus procera | 28 | 0.0020 | 0.0003 |
| Grevillea robusta | 68 | 0.0071 | 0.0011 |
| Acacia abyssinica | 17 | 0.0017 | 0.0002 |
Factors affecting species diversity and productivity of homegarden plants
Main factors affecting the diversity and productivity of homegardens plants in Sebeta-Awas District have been reported by respondents. These, among others, include lack of access to water, size of the homegarden, and occurrence of pests and weeds. Shortage of water was mentioned as the main constraint in growing homegarden crops. According to the informants, homegardens in the study area were primarily dependent on rain and as a result diversity and productivity of plants was highly affected during the dry season. Water fetching from distant areas and use of irrigation have been reported to be laborious and time-consuming task. As explained by some informants, the effect of pests on some homegarden plants could not be undermined. Galium aparinoides and Parthenium hysterophorus were among the weeds that affect the diversity and productivity of homegarden plants. As noted by many authors, there are a number of factors affecting development of productive homegardens. These include socio-cultural and economic factors [2, 42–46], ecological factors and farmers’ knowledge and awareness [47], access to land [48, 49] and labour inputs [7].
Conclusions
Homegardens are still playing important role in the overall farming system in Sebeta-Awas District. The fact that the majority of households in the District have homegardens shows that gardening is considered important by farmers as it contributes towards ensuring household food security and income generation. The contribution of individual gardens to biodiversity conservation in the study District should also not be underestimated. In addition, homegardens provide important ecological, social, and cultural functions. Species diversity of homegarden plants in Sebeta-Awas District is affected by a number of factors. Water is the main factor limiting species richness and diversity as water is not always sufficiently available. Because of the need for large field crops as well as scarcity of land, there has been over time, decrease in homegarden plot size. People in the study area largely cultivate homegarden plants, which have better market values. Based on findings of the current research, it is recommended that farmers should be encouraged to manage their homegardens as homegardens play important role in ensuring food security and increasing household income. Community members in the study area should, therefore, be made aware of the role of homegarden plants in fulfilling their nutritional and other requirements as many seem to be not very much aware of such fact.
Acknowledgments
First, we would like to express our gratitude to the technical staffs of the National Herbarium, Addis Ababa University (AAU), who assisted in the drying, identification and storage of voucher specimens. We also thank AAU for the financial support to conduct this study.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
The three authors had significant intellectual contribution towards the design of the study, data collection and analysis and write-up of the manuscript. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Tefera Mekonen, Email: teferamek@yahoo.com.
Mirutse Giday, Email: mirutseg@yahoo.com.
Ensermu Kelbessa, Email: ensermu.kelbessa@aau.edu.et.
References
- 1.Christanty L. Homegardens in tropical Asia with special references to Indonesia. In: Ladue K, Brazil M, editors. Tropical homegardens. Tokyo: The United Nations University Press; 1990. pp. 9–20. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fernandes ECM, Nair PKR. An evolution of the structure and function of tropical homegardens. Agric Syst. 1986;21:279–310. doi: 10.1016/0308-521X(86)90104-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hoogerbrugge ID, Fresco LO. Homegarden system: agricultural characteristics and challenges. Gatekeeper series no. 39. London: International Institute for Environment and Development; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kumar BM, Nair PKR. The enigma of tropical homegardens. Agrofor Syst. 2004;61:135–52. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Agbogidi OM, Adolor EB. Home gardens in the maintenance of biological diversity. Appl Sci Rep. 2013;1:19–25. [Google Scholar]
- 6.Hodgkin T. Home gardens and the maintenance of genetic diversity. In: Watson JW, Eyzaguirre PB, editors. Proceedings of the second international home gardens workshop: contribution of home gardens to in situ conservation of plant genetic resources in farming systems: 17–19 July 2001. Rome: International Plant Genetic Resources Institute; 2002. pp. 14–8. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Brownrigg L. Homegardening in international development: What the literature shows. League for International Food Education: Washington; 1985. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Agize M, Demissew S, Asfaw Z. Indigenous knowledge on management of home gardens and plants in Loma and Gena Bosa districts (weredas) of Dawro Zone, Southern Ethiopia: plant biodiversity conservation, sustainable utilization and environmental protection. Int J Sci: Basic Appl Res (IJSBAR) 2013;10:63–99. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Godbole A. Maintenance of biodiversity. In: Rastogi A, Godbole A, Shengii P, editors. Applied ethnobotany in natural resources management. Nepal: International Center for Integrated Mountain Development; 1998. pp. 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Okigbo NB. Homegardens in tropical Africa. In: Landauer K, Brazil M, editors. Tropical homegardens. Tokyo: UNU; 1990. pp. 21–40. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Padoch C, Jong W. The house gardens of Santa Rosa: diversity and variability in an Amazonian agricultural system. Econ Bot. 1991;45:166–75. doi: 10.1007/BF02862045. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Asfaw Z. Home gardens in Ethiopia: some observations and generalizations. In: Watson JW, Eyzaguirre PB, editors. Proceedings of the second international home gardens workshop: contribution of home gardens to in situ conservation of plant genetic resources in farming systems, 17–19 July 2001. Rome: International Plant Genetic Resources Institute; 2002. p. 128139. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ehret C. On the antiquity of agriculture in Ethiopia. J Afr Hist. 1979;20:161–77. doi: 10.1017/S002185370001700X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brandt SA. New perspectives on the origins of food production in Ethiopia. In: Clark JD, Brandt SA, editors. From hunters to farmers: the causes and consequences of food production in Africa. Berkeley: University of California Press; 1984. pp. 173–90. [Google Scholar]
- 15.Asfaw Z, Nigatu A. Homegardens in Ethiopia: characteristics and plant diversity. SINET: Ethiop J Sci. 1995;18:235–66. [Google Scholar]
- 16.Asfaw Z. Survey of indigenous food plants, their preparations and home gardens in Ethiopia. In: Okigbo BN, editor. Indigenous food crops and useful plants. 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Asfaw Z. The role of homegardens in the production and conservation of medicinal plants. In: Zewdu M, Demissie A, editors. Proceedings of the National workshop on biodiversity conservation and sustainable use of medicinal plants in Ethiopia: 28 April - 01 May 1998. Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: Institute of Biodiversity Conservation and Research; 2001. pp. 76–91. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Asfaw Z. Origin and evolution of rural homegardens in Ethiopia. In: Friis I, Ryding O, editors. Proceedings of the third International symposium on the Flora of Ethiopia and Eritrea: biodiversity research in the horn of Africa region, August 25–27, 1999. Copenhagen: Carlsberg Academy; 2001. pp. 273–86. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Vavilov NI. The origin, variation, immunity and breeding of cultivated plants: selected writings. Translated from the Russian by Chester S K. New York: The Ronald Company; 1951. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Asfaw Z. Homegarden and agrobiodiversity. In: Eyzaguirre PB, Linares OF, editors. The enset based homegardens of Ethiopia. Washington: Smithsonian Institution; 2004. pp. 123–147. [Google Scholar]
- 21.Asfaw Z, Woldu Z. Crop association of homegardens in Walayta and Gurage in Southern Ethiopia. SINET: Ethiop J Sci. 1997;20:73–90. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Woldeyes F. A study on Biodiversity Management in Daddegoyo (Tradition Homegardens) by Kaficho People of Bonga area (Southwestern Ethiopia): an ethnobotanical approach. MSc thesis: Addis Ababa University; 2000. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wassihun B, Asfaw Z, Demissew S. Ethnobotanical study of useful plants in Daniio Gade (homegardens) in southern Ethiopia. Ethiop J Biol Sci. 2003;2:119–41. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Abebe T. Diversity in homegarden agroforestry systems of Southern Ethiopia. PhD dissertation. Netherlands: Wageningen University; 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Seta T. Diversity in ensete-based homegardens and its significance to household supply in Welayta (Southern Ethiopia): an ethnobotanical approach. MSc thesis: Addis Ababa University; 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Hailu H, Asfaw Z. Homegardens and agrobiodiversity conservation in Sabata town, Oromia Regional State, Ethiopia. SINET: Ethiop J Sci. 2011;34:1–16. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gutema T. Agricultural land use in Alamganaa Woreda. BA Senior Essay: Addis Ababa University; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Alexiades M. Collecting ethnobotanical data: an introduction to basic concepts and techniques. In: Alexiades MN, editor. Selected guideline for ethnobotanical research: a field manual. New York: The New York Botanical Garden; 1996. pp. 52–94. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cotton CM. Ethnobotany: principle and applications. John Wiley Sons Ltd: Chichester; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Martin GJ. Ethnobotany: a method manual. London: Chapman and Hall; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 31.ISE. International Society of Ethnobiology Code of Ethics. [http://ethnobiology.net/code-of-ethics]
- 32.Kent M, Coker P. Vegetation description and analysis: a practical approach. New York: John Wiley and Sons; 1992. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Krebs C. Ecological methodology. Menlo Park, California: Addison-Wesley Educational Publishers; 1999. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Rugalema GH, Okting’ati A, Johnson FH. The homegarden agroforestry systems of Bukoba district, North-Western Tanzania. Agrofor Syst. 1994;26:53–64. doi: 10.1007/BF00705152. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bennett-Lartey SO, Ayernor GS, Markwei CM, Asante IK, Abbiw DK, Boateng SK, et al. Aspects of home-garden cultivation in Ghana: regional differences in ecology and society. In: Eyzaguirre PB, Linares OF, et al., editors. Homegardens and agrobiodiversity. Washington: Smithsonian Institution; 2004. pp. 148–67. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Trinh LN, Watson JM, Hue NN, De NN, Minh MV, Chu P, et al. Agrobiodiversity conservation and development in Vietnamese homegardens. Agric Ecosyst Environ. 2003;2033:1–28. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Alvarez-Buylla Roches ME, Lazos Chavero E, Garcia-Barrios JR. Homegardens of a humid tropical region in Southeast Mexico: an example of an agroforestry cropping system in a recently established community. Agrofor Syst. 1989;8:133–56. doi: 10.1007/BF00123117. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Niñez V. Working at half-potential: constructive analysis of home garden programmes in the Lima slums with suggestions for an alternative approach. Food Nutr Bull. 1985;7:6–14. [Google Scholar]
- 39.Brookfield H. Exploring of agrobiodiverity. New York: Columbia University; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Amberber M, Argaw M, Asfaw Z. The role of homegardens for in situ conservation of plant biodiversity in Holeta Town, Oromia National Regional State, Ethiopia. Int J Biodivers Conserv. 2014;6:8–16. doi: 10.5897/IJBC2013.0583. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Mekonnen EL, Asfaw Z, Zewdie S. Plant species diversity of homegarden agroforestry in Jabithenan District, north-west Ethiopia. Int J Biodivers Conserv. 2014;6:301–7. doi: 10.5897/IJBC2013.0583. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Arnold JEM, Dewees PA. Tree management in farmer strategies: responses to agricultural intensification. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 1995. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mergen F. Research opportunities to improve the production of homegardens. Agrofor Syst. 1987;5:57–67. doi: 10.1007/BF00046413. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Michon G, Bompard J, Ducatilion C. Tropical forest architectural analysis as applied to agroforests in the humid tropics: the example of traditional village agroforests in West Java. Agrofor Syst. 1983;1:117–29. doi: 10.1007/BF00596353. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Soemarwoto O. Homegardens: a traditional agroforestry system with promising future. In: Steppler HA, Nair PKR, editors. Agroforestery: a decade of development. Nairobi, Kenya: ICRAF; 1987. pp. 157–72. [Google Scholar]
- 46.Wiersum KF. Fuelwood in Indonesia: future prospects for a traditional energy source. Mimeograph. Bandung, Indonesia: Institute of Ecology, Padjadjaran University; 1982. [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gautam R, Sthapit BR, Shrestha PK. Home gardens in Nepal: Proceeding of a workshop on enhancing the contribution of home garden to on-farm management of plant genetic resources and to improve the livelihoods of Nepalese farmers: lessons learned and policy implications, 6–7 August 2004. Pokhara, Nepal: LI-BIRD, Biodiversity International and SDC; 2006. [Google Scholar]
- 48.Marsh R. Building on traditional gardening to improve household food security. Food nutrition and agriculture no. 20. Rome: Food and Agriculture Organization; 1998. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Vasey DE. Household gardens and their niche in Port Moresby, Papua New Guinea. Food Nutr Bull. 1985;7:37–43. [Google Scholar]


