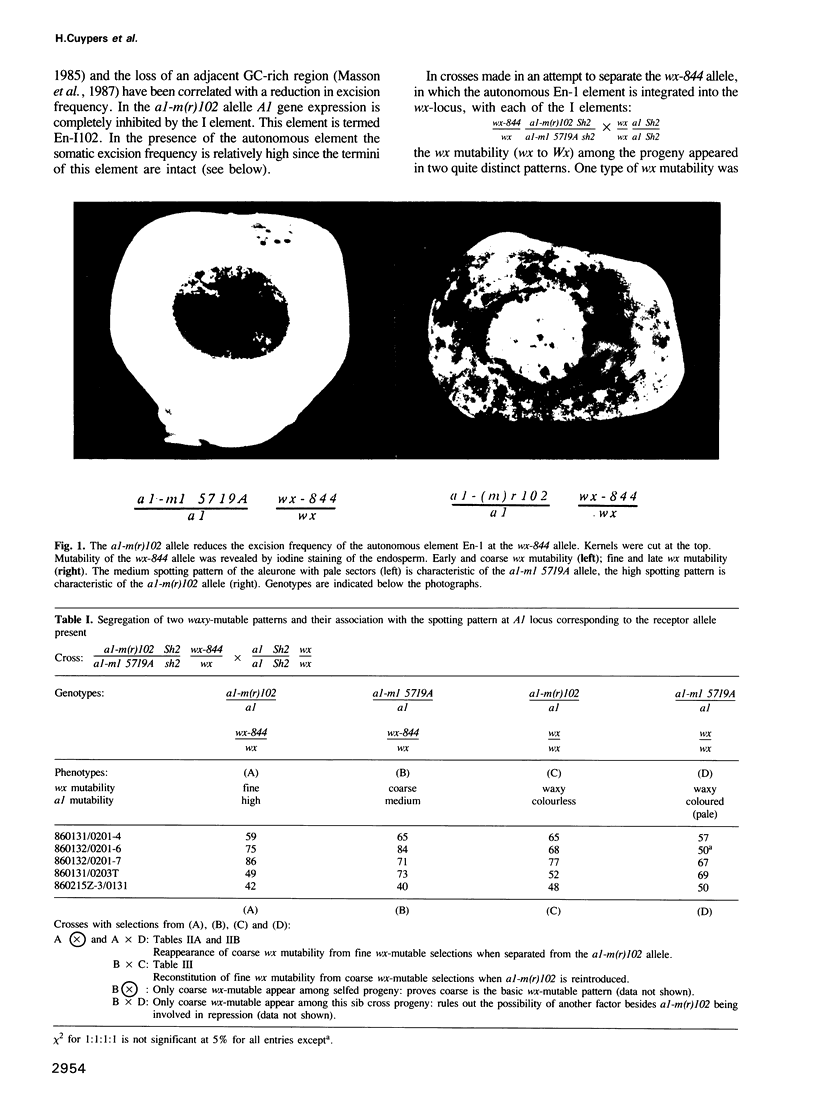
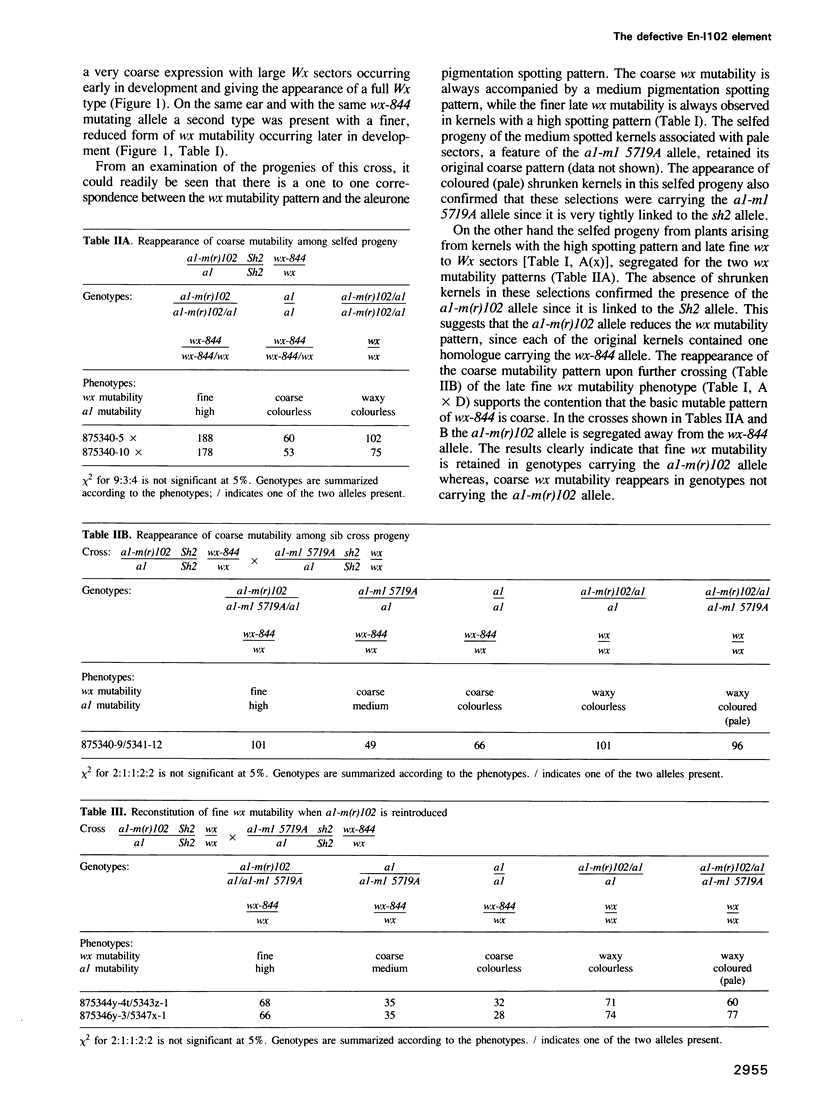
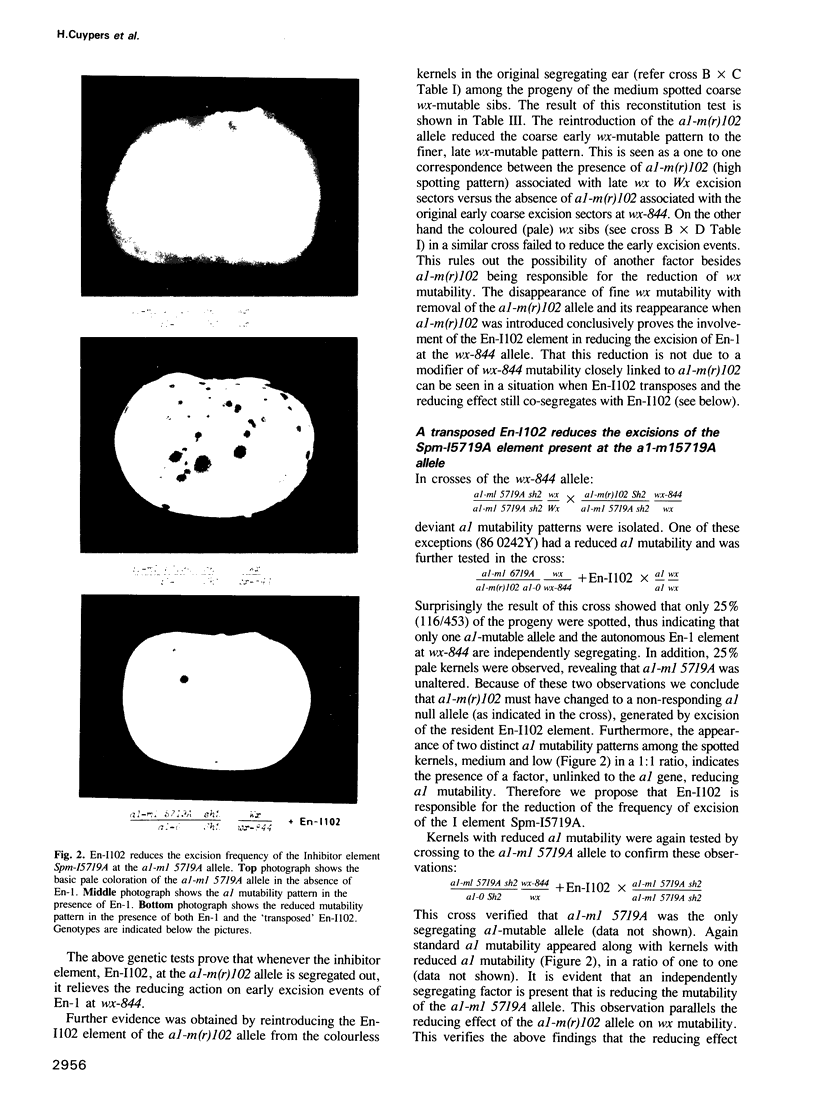
Abstract
Genetic and molecular analysis has revealed a specific En-element deletion derivative (En-I102) which reduces En/Spm-induced mutability. In the presence of En-I102 the excision frequency of both the autonomous En-1 element and the inhibitor element Spm-I5719A is reduced and excision occurs later in development. The 3697 bp long En-I102 element is derived from En-1 by an internal deletion of 4590 bp removing nucleotides 1862-6451. The promoter at the left end and sequences required for polyadenylation are retained in En-I102. It is transcribed to yield predominantly a 1.8 kb poly(A) RNA. cDNA analysis of this transcript indicated that it contains the coding capacity for a 386 amino acid polypeptide. This polypeptide shares homology with En/Spm encoded functions and we suggest that it interferes with transposition at the protein level.
Keywords: excision, gene structure, transposable element, Zea mays
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banks J., Kingsbury J., Raboy V., Schiefelbein J. W., Nelson O., Fedoroff N. The Ac and Spm controlling element families in maize. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1985;50:307–311. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1985.050.01.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black D. M., Jackson M. S., Kidwell M. G., Dover G. A. KP elements repress P-induced hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4125–4135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonas U., Sommer H., Saedler H. The 17-kb Tam1 element of Antirrhinum majus induces a 3-bp duplication upon integration into the chalcone synthase gene. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1015–1019. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone K. C., Burr F. A., Burr B. Molecular analysis of the maize anthocyanin regulatory locus C1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9631–9635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierl A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Saedler H. Molecular interactions between the components of the En-I transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):579–583. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03669.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isackson P. J., Bertrand K. P. Dominant negative mutations in the Tn10 tet repressor: evidence for use of the conserved helix-turn-helix motif in DNA binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6226–6230. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson P., Surosky R., Kingsbury J. A., Fedoroff N. V. Genetic and molecular analysis of the Spm-dependent a-m2 alleles of the maize a locus. Genetics. 1987 Sep;117(1):117–137. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.1.117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A., Cuypers H., Gierl A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Saedler H. Molecular analysis of the En/Spm transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):835–841. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira A., Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Bertram I., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Genetic and molecular analysis of the Enhancer (En) transposable element system of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):17–23. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02311.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P A. Mutable a(1) of the En System in Maize. Genetics. 1961 Jul;46(7):759–771. doi: 10.1093/genetics/46.7.759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiefelbein J. W., Raboy V., Fedoroff N. V., Nelson O. E., Jr Deletions within a defective suppressor-mutator element in maize affect the frequency and developmental timing of its excision from the bronze locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4783–4787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Berndtgen R., Saedler H. Sequence comparison of 'states' of a1-m1 suggests a model of Spm (En) action. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2439–2443. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03953.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Gierl A., Klösgen R. B., Wienand U., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. The Spm (En) transposable element controls the excision of a 2-kb DNA insert at the wx allele of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1021–1028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz-Sommer Z., Shepherd N., Tacke E., Gierl A., Rohde W., Leclercq L., Mattes M., Berndtgen R., Peterson P. A., Saedler H. Influence of transposable elements on the structure and function of the A1 gene of Zea mays. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):287–294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]