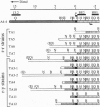
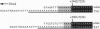Abstract
TART, a telomere-associated DNA element from Drosophila, is shown in this paper to have structural homology to LINE (long interspersed element)-like retrotransposons and to transpose to broken chromosome ends. TART DNA was detected by in situ hybridization in 7 of 10 independent additions of DNA to a chromosome end. We found evidence that a TART element had transposed to the chromosome end in each of two additions that were examined in detail. From the DNA sequence of a TART element that recently transposed, we infer that TART encodes two proteins having significant sequence similarity to the putative proteins of many LINEs. These results support the hypothesis that TART elements preferentially retrotranspose to the termini of chromosomes as part of the essential process by which Drosophila telomeres are maintained.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berg J. M. Zinc fingers and other metal-binding domains. Elements for interactions between macromolecules. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6513–6516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Champion L. E., O'Hair M., Ikenaga K., Kasravi B., Mason J. M. Frequent transpositions of Drosophila melanogaster HeT-A transposable elements to receding chromosome ends. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(12):4459–4469. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Kasravi B., Bui T., Fujiwara G., Champion L. E., Mason J. M. Comparison of two active HeT-A retroposons of Drosophila melanogaster. Chromosoma. 1994 Apr;103(2):90–98. doi: 10.1007/BF00352317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M., Ferry K., d'Hulst M., Valgeirsdottir K., Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. Addition of telomere-associated HeT DNA sequences "heals" broken chromosome ends in Drosophila. Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):663–673. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90478-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biessmann H., Mason J. M. Genetics and molecular biology of telomeres. Adv Genet. 1992;30:185–249. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilevskaya O. N., Petrov D. A., Pavlova M. N., Koga A., Kurenova E. V., Hartl D. L. A repetitive DNA element, associated with telomeric sequences in Drosophila melanogaster, contains open reading frames. Chromosoma. 1992 Dec;102(1):32–40. doi: 10.1007/BF00352288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danilevskaya O., Slot F., Pavlova M., Pardue M. L. Structure of the Drosophila HeT-A transposon: a retrotransposon-like element forming telomeres. Chromosoma. 1994 Jun;103(3):215–224. doi: 10.1007/BF00368015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eickbush T. H. Transposing without ends: the non-LTR retrotransposable elements. New Biol. 1992 May;4(5):430–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazelrigg T., Levis R., Rubin G. M. Transformation of white locus DNA in drosophila: dosage compensation, zeste interaction, and position effects. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90240-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karpen G. H., Spradling A. C. Analysis of subtelomeric heterochromatin in the Drosophila minichromosome Dp1187 by single P element insertional mutagenesis. Genetics. 1992 Nov;132(3):737–753. doi: 10.1093/genetics/132.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R. W., Ganesan R., Houtchens K., Tolar L. A., Sheen F. M. Transposons in place of telomeric repeats at a Drosophila telomere. Cell. 1993 Dec 17;75(6):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90318-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R. W. Viable deletions of a telomere from a Drosophila chromosome. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):791–801. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis R., Hazelrigg T., Rubin G. M. Effects of genomic position on the expression of transduced copies of the white gene of Drosophila. Science. 1985 Aug 9;229(4713):558–561. doi: 10.1126/science.2992080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louis E. J., Naumova E. S., Lee A., Naumov G., Haber J. E. The chromosome end in yeast: its mosaic nature and influence on recombinational dynamics. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):789–802. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luan D. D., Korman M. H., Jakubczak J. L., Eickbush T. H. Reverse transcription of R2Bm RNA is primed by a nick at the chromosomal target site: a mechanism for non-LTR retrotransposition. Cell. 1993 Feb 26;72(4):595–605. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90078-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumov G. I., Naumova E. S., Michels C. A. Genetic variation of the repeated MAL loci in natural populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Saccharomyces paradoxus. Genetics. 1994 Mar;136(3):803–812. doi: 10.1093/genetics/136.3.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare K., Murphy C., Levis R., Rubin G. M. DNA sequence of the white locus of Drosophila melanogaster. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 15;180(3):437–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pirrotta V., Hadfield C., Pretorius G. H. Microdissection and cloning of the white locus and the 3B1-3C2 region of the Drosophila X chromosome. EMBO J. 1983;2(6):927–934. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01523.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priimägi A. F., Mizrokhi L. J., Ilyin Y. V. The Drosophila mobile element jockey belongs to LINEs and contains coding sequences homologous to some retroviral proteins. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):253–262. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90197-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smoller D. A., Petrov D., Hartl D. L. Characterization of bacteriophage P1 library containing inserts of Drosophila DNA of 75-100 kilobase pairs. Chromosoma. 1991 Sep;100(8):487–494. doi: 10.1007/BF00352199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugawara N., Haber J. E. Characterization of double-strand break-induced recombination: homology requirements and single-stranded DNA formation. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):563–575. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traverse K. L., Pardue M. L. A spontaneously opened ring chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster has acquired He-T DNA sequences at both new telomeres. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):8116–8120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.8116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiong Y., Eickbush T. H. Origin and evolution of retroelements based upon their reverse transcriptase sequences. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3353–3362. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07536.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]