Abstract
A novel factor IX gene mutation (factor IX London 2) has been characterized. This causes severe crm+ haemophilia B as the patient's plasma shows normal factor IX antigen level and less than 1% clotting activity. Sequence analysis of the entire cloned coding and promoter regions revealed a single point mutation: a G----A transition at position 31,119. This region of the patient's DNA was amplified in vitro by the polymerase chain reaction and the nucleotide change was confirmed by direct sequencing of the amplified products. The mutation results in the substitution of the arginine at position 333 by glutamine. This arginine residue is absolutely conserved in the catalytic domain of normal human and bovine factor IX, X and prothrombin. The substitution by glutamine causes the loss of a positive charge from the surface of the factor IX London 2 protein. This mutation pinpoints a previously unknown, functionally critical feature of factor IX which may be involved in substrate or co-factor binding.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
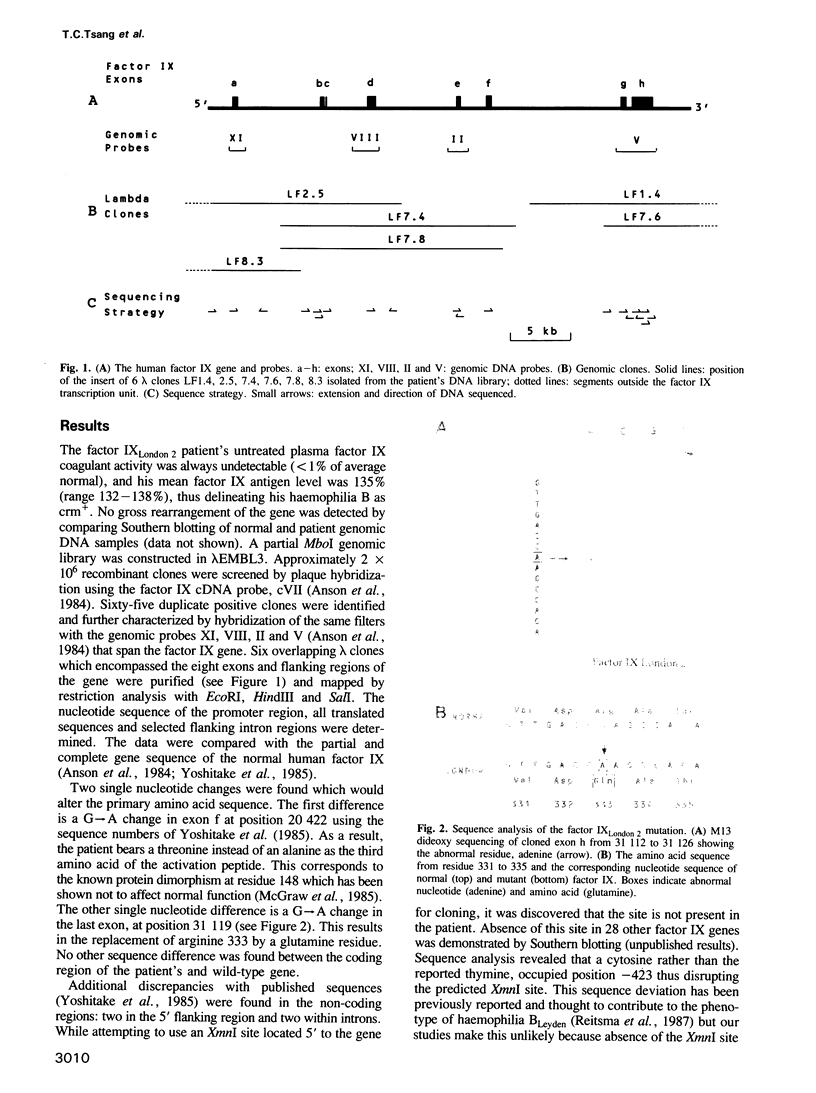
- Anson D. S., Choo K. H., Rees D. J., Giannelli F., Gould K., Huddleston J. A., Brownlee G. G. The gene structure of human anti-haemophilic factor IX. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):1053–1060. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlaud G. J., Gagnon J. Complete amino acid sequence of the catalytic chain of human complement subcomponent C1-r. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 12;22(8):1758–1764. doi: 10.1021/bi00277a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker D., Schafer M., White R. Restriction sites containing CpG show a higher frequency of polymorphism in human DNA. Cell. 1984 Jan;36(1):131–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90081-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley A. K., Rees D. J., Rizza C., Brownlee G. G. Defective propeptide processing of blood clotting factor IX caused by mutation of arginine to glutamine at position -4. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):343–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90319-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. R. Primary structure of human complement component C2. Homology to two unrelated protein families. Biochem J. 1986 Oct 15;239(2):339–345. doi: 10.1042/bj2390339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birktoft J. J., Blow D. M. Structure of crystalline -chymotrypsin. V. The atomic structure of tosyl- -chymotrypsin at 2 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 21;68(2):187–240. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90210-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Hartley B. S. Location of disulphide bridges by diagonal paper electrophoresis. The disulphide bridges of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):214–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1010214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter P. E., Dunbar B., Fothergill J. E. The serine proteinase chain of human complement component C1s. Cyanogen bromide cleavage and N-terminal sequences of the fragments. Biochem J. 1983 Dec 1;215(3):565–571. doi: 10.1042/bj2150565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chehab F. F., Doherty M., Cai S. P., Kan Y. W., Cooper S., Rubin E. M. Detection of sickle cell anaemia and thalassaemias. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):293–294. doi: 10.1038/329293b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christie D. L., Gagnon J. Amino acid sequence of the Bb fragment from complement Factor B. Sequence of the major cyanogen bromide-cleavage peptide (CB-II) and completion of the sequence of the Bb fragment. Biochem J. 1983 Jan 1;209(1):61–70. doi: 10.1042/bj2090061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. W., Fujikawa K., McMullen B. A., Davie E. W. Human plasma prekallikrein, a zymogen to a serine protease that contains four tandem repeats. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2410–2417. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cool D. E., Edgell C. J., Louie G. V., Zoller M. J., Brayer G. D., MacGillivray R. T. Characterization of human blood coagulation factor XII cDNA. Prediction of the primary structure of factor XII and the tertiary structure of beta-factor XIIa. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13666–13676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulondre C., Miller J. H., Farabaugh P. J., Gilbert W. Molecular basis of base substitution hotspots in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):775–780. doi: 10.1038/274775a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis L. M., McGraw R. A., Ware J. L., Roberts H. R., Stafford D. W. Factor IXAlabama: a point mutation in a clotting protein results in hemophilia B. Blood. 1987 Jan;69(1):140–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degen S. J., MacGillivray R. T., Davie E. W. Characterization of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid and gene coding for human prothrombin. Biochemistry. 1983 Apr 26;22(9):2087–2097. doi: 10.1021/bi00278a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diuguid D. L., Rabiet M. J., Furie B. C., Liebman H. A., Furie B. Molecular basis of hemophilia B: a defective enzyme due to an unprocessed propeptide is caused by a point mutation in the factor IX precursor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5803–5807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embury S. H., Scharf S. J., Saiki R. K., Gholson M. A., Golbus M., Arnheim N., Erlich H. A. Rapid prenatal diagnosis of sickle cell anemia by a new method of DNA analysis. N Engl J Med. 1987 Mar 12;316(11):656–661. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198703123161103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. C., Yoshitake S., Davie E. W. The nucleotide sequence of the gene for human protein C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4673–4677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujikawa K., Chung D. W., Hendrickson L. E., Davie E. W. Amino acid sequence of human factor XI, a blood coagulation factor with four tandem repeats that are highly homologous with plasma prekallikrein. Biochemistry. 1986 May 6;25(9):2417–2424. doi: 10.1021/bi00357a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Campbell R. M., MacGillivray R. T. Blood coagulation factor X mRNA encodes a single polypeptide chain containing a prepro leader sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4481–4492. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung M. R., Hay C. W., MacGillivray R. T. Characterization of an almost full-length cDNA coding for human blood coagulation factor X. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3591–3595. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green P. M., Bentley D. R., Mibashan R. S., Giannelli F. Partial deletion by illegitimate recombination of the factor IX gene in a haemophilia B family with two inhibitor patients. Mol Biol Med. 1988 Apr;5(2):95–106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Gray C. L., O'Hara P., Grant F. J., Saari G. C., Woodbury R. G., Hart C. E., Insley M., Kisiel W., Kurachi K. Characterization of a cDNA coding for human factor VII. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helms C., Graham M. Y., Dutchik J. E., Olson M. V. A new method for purifying lambda DNA from phage lysates. DNA. 1985 Feb;4(1):39–49. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Murray K. Packaging recombinant DNA molecules into bacteriophage particles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopp T. P., Woods K. R. Prediction of protein antigenic determinants from amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3824–3828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3824. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson C. M., Nemerson Y. Blood coagulation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:765–811. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.004001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katayama K., Ericsson L. H., Enfield D. L., Walsh K. A., Neurath H., Davie E. W., Titani K. Comparison of amino acid sequence of bovine coagulation Factor IX (Christmas Factor) with that of other vitamin K-dependent plasma proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4990–4994. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kogan S. C., Doherty M., Gitschier J. An improved method for prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases by analysis of amplified DNA sequences. Application to hemophilia A. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 15;317(16):985–990. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710153171603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson B., Janco R., Phillips J., 3rd, Gitschier J. A novel missense mutation in the factor VIII gene identified by analysis of amplified hemophilia DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9797–9805. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGillivray R. T., Davie E. W. Characterization of bovine prothrombin mRNA and its translation product. Biochemistry. 1984 Apr 10;23(8):1626–1634. doi: 10.1021/bi00303a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGraw R. A., Davis L. M., Noyes C. M., Lundblad R. L., Roberts H. R., Graham J. B., Stafford D. W. Evidence for a prevalent dimorphism in the activation peptide of human coagulation factor IX. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2847–2851. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noyes C. M., Griffith M. J., Roberts H. R., Lundblad R. L. Identification of the molecular defect in factor IX Chapel Hill: substitution of histidine for arginine at position 145. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4200–4202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. J., Rizza C. R., Brownlee G. G. Haemophilia B caused by a point mutation in a donor splice junction of the human factor IX gene. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):643–645. doi: 10.1038/316643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A. Direct cloning and sequence analysis of enzymatically amplified genomic sequences. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1076–1078. doi: 10.1126/science.3461561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smillie L. B., Furka A., Nagabhushan N., Stevenson K. J., Parkes C. O. Structure of chymotrypsinogen B compared with chymotrypsinogen A and trypsinogen. Nature. 1968 Apr 27;218(5139):343–346. doi: 10.1038/218343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoflet E. S., Koeberl D. D., Sarkar G., Sommer S. S. Genomic amplification with transcript sequencing. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.3340835. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stroud R. M., Kay L. M., Dickerson R. E. The structure of bovine trypsin: electron density maps of the inhibited enzyme at 5 Angstrom and at 2-7 Angstron resolution. J Mol Biol. 1974 Feb 25;83(2):185–208. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90387-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. R. Structure, function, and molecular defects of factor IX. Blood. 1986 Mar;67(3):565–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Titani K., Ericsson L. H., Neurath H., Walsh K. A. Amino acid sequence of dogfish trypsin. Biochemistry. 1975 Apr 8;14(7):1358–1366. doi: 10.1021/bi00678a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsang T. C., Bentley D. R. An improved sequencing method using Sequenase that is independent of template concentration. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 11;16(13):6238–6238. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.13.6238. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vidaud M., Chabret C., Gazengel C., Grunebaum L., Cazenave J. P., Goossens M. A de novo intragenic deletion of the potential EGF domain of the factor IX gene in a family with severe hemophilia B. Blood. 1986 Oct;68(4):961–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong C., Dowling C. E., Saiki R. K., Higuchi R. G., Erlich H. A., Kazazian H. H., Jr Characterization of beta-thalassaemia mutations using direct genomic sequencing of amplified single copy DNA. 1987 Nov 26-Dec 2Nature. 330(6146):384–386. doi: 10.1038/330384a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrischnik L. A., Higuchi R. G., Stoneking M., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N., Wilson A. C. Length mutations in human mitochondrial DNA: direct sequencing of enzymatically amplified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 26;15(2):529–542. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshitake S., Schach B. G., Foster D. C., Davie E. W., Kurachi K. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for human factor IX (antihemophilic factor B). Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 2;24(14):3736–3750. doi: 10.1021/bi00335a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





