Abstract
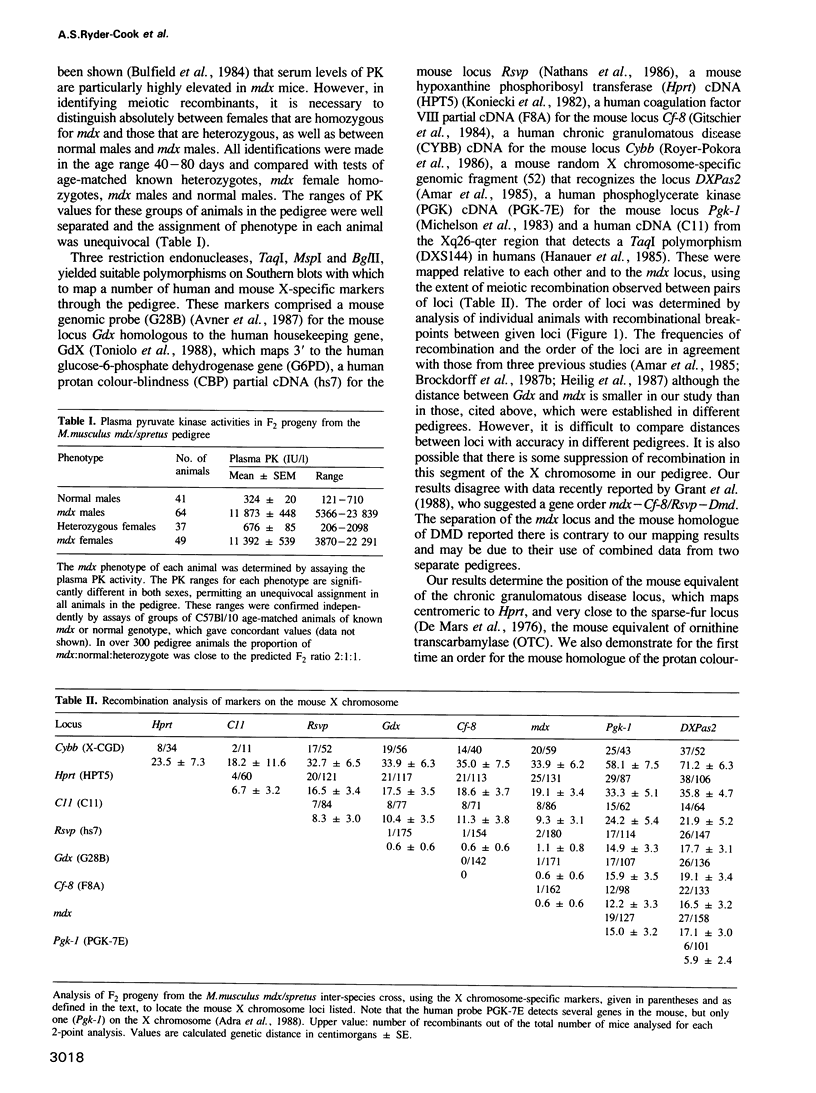
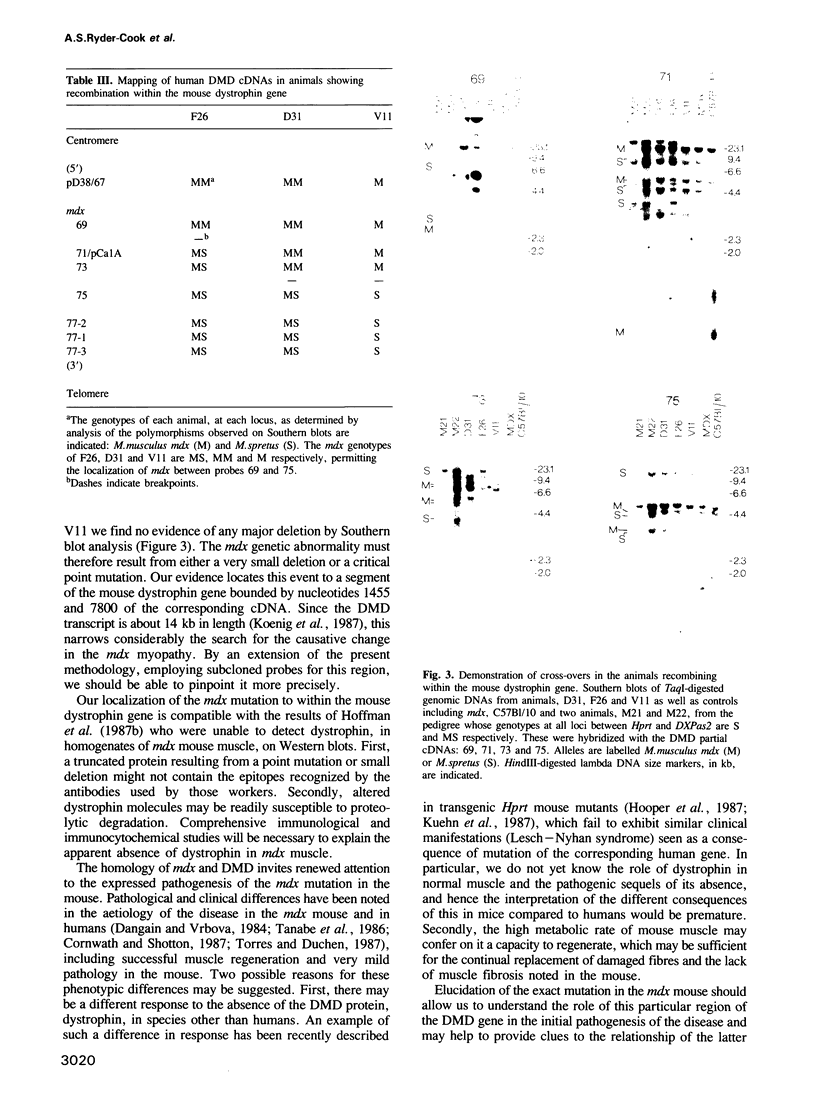
We have mapped human and mouse X chromosome-specific genomic and cDNA probes through an interspecies Mus musculus/spretus pedigree which contains the mdx mutation. The positions of these markers relative to one another and to the mdx mutation were delineated. Using probes corresponding to segments of the human Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) gene transcript, the position of a cross-hybridizing mouse equivalent gene (mDMD) was located. In more than 200 animals mapped, three were identified which show recombination within this mDMD gene. Analysis of these three animals shows that the mDMD gene is oriented with its 5' end centromeric and its 3' end telomeric on the mouse X chromosome. Furthermore, their recombinational breakpoints are on either side of the mdx mutation, thus providing the first unequivocal demonstration that the mdx mutation is located within the mDMD gene and defining limits within that gene between which the mutation must lie. Within that segment the evidence indicates that there is no major deletion of an exon as detectable by Southern blot analysis in mdx animals. The mdx mouse becomes important as an animal model for the study of the expression of the DMD gene and its developmental consequences, for transgenic and other corrective manipulations.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adra C. N., Ellis N. A., McBurney M. W. The family of mouse phosphoglycerate kinase genes and pseudogenes. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Jan;14(1):69–81. doi: 10.1007/BF01535050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amar L. C., Arnaud D., Cambrou J., Guenet J. L., Avner P. R. Mapping of the mouse X chromosome using random genomic probes and an interspecific mouse cross. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 30;4(13B):3695–3700. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04137.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avner P., Amar L., Arnaud D., Hanauer A., Cambrou J. Detailed ordering of markers localizing to the Xq26-Xqter region of the human X chromosome by the use of an interspecific Mus spretus mouse cross. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1629–1633. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockdorff N., Cross G. S., Cavanna J. S., Fisher E. M., Lyon M. F., Davies K. E., Brown S. D. The mapping of a cDNA from the human X-linked Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene to the mouse X chromosome. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):166–168. doi: 10.1038/328166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockdorff N., Fisher E. M., Cavanna J. S., Lyon M. F., Brown S. D. Construction of a detailed molecular map of the mouse X chromosome by microcloning and interspecific crosses. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3291–3297. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02648.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulfield G., Siller W. G., Wight P. A., Moore K. J. X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) in the mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1189–1192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burmeister M., Lehrach H. Long-range restriction map around the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene. Nature. 1986 Dec 11;324(6097):582–585. doi: 10.1038/324582a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnwath J. W., Shotton D. M. Muscular dystrophy in the mdx mouse: histopathology of the soleus and extensor digitorum longus muscles. J Neurol Sci. 1987 Aug;80(1):39–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(87)90219-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Grant S. G., Reeves A. A., Mullins L. J., Stephenson D. A., Hoffman E. P., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M., Caskey C. T., Chapman V. M. Regional localization of the murine Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene on the mouse X chromosome. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Nov;13(6):671–678. doi: 10.1007/BF01534487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chamberlain J. S., Pearlman J. A., Muzny D. M., Gibbs R. A., Ranier J. E., Caskey C. T., Reeves A. A. Expression of the murine Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in muscle and brain. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1416–1418. doi: 10.1126/science.3347839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. S., Speer A., Rosenthal A., Forrest S. M., Smith T. J., Edwards Y., Flint T., Hill D., Davies K. E. Deletions of fetal and adult muscle cDNA in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3277–3283. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02646.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dangain J., Vrbova G. Muscle development in mdx mutant mice. Muscle Nerve. 1984 Nov-Dec;7(9):700–704. doi: 10.1002/mus.880070903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeMars R., LeVan S. L., Trend B. L., Russell L. B. Abnormal ornithine carbamoyltransferase in mice having the sparse-fur mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1693–1697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest S. M., Cross G. S., Speer A., Gardner-Medwin D., Burn J., Davies K. E. Preferential deletion of exons in Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophies. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):638–640. doi: 10.1038/329638a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitschier J., Wood W. I., Goralka T. M., Wion K. L., Chen E. Y., Eaton D. H., Vehar G. A., Capon D. J., Lawn R. M. Characterization of the human factor VIII gene. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):326–330. doi: 10.1038/312326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Weaver D., Baltimore D., Costantini F. Introduction of a mu immunoglobulin gene into the mouse germ line: specific expression in lymphoid cells and synthesis of functional antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heilig R., Lemaire C., Mandel J. L., Dandolo L., Amar L., Avner P. Localization of the region homologous to the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus on the mouse X chromosome. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):168–170. doi: 10.1038/328168a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Brown R. H., Jr, Kunkel L. M. Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):919–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90579-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Monaco A. P., Feener C. C., Kunkel L. M. Conservation of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy gene in mice and humans. Science. 1987 Oct 16;238(4825):347–350. doi: 10.1126/science.3659917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper M., Hardy K., Handyside A., Hunter S., Monk M. HPRT-deficient (Lesch-Nyhan) mouse embryos derived from germline colonization by cultured cells. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):292–295. doi: 10.1038/326292a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Hoffman E. P., Bertelson C. J., Monaco A. P., Feener C., Kunkel L. M. Complete cloning of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) cDNA and preliminary genomic organization of the DMD gene in normal and affected individuals. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):509–517. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90504-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konecki D. S., Brennand J., Fuscoe J. C., Caskey C. T., Chinault A. C. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase genes of mouse and Chinese hamster: construction and sequence analysis of cDNA recombinants. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6763–6775. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuehn M. R., Bradley A., Robertson E. J., Evans M. J. A potential animal model for Lesch-Nyhan syndrome through introduction of HPRT mutations into mice. Nature. 1987 Mar 19;326(6110):295–298. doi: 10.1038/326295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu P. K., Barnard E. A., Barnard P. J. Blood plasma pyruvate kinase as a marker of muscular dystrophy. Properties in dystrophic chickens and hamsters. Exp Neurol. 1980 Mar;67(3):581–600. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(80)90128-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Markham A. F., Orkin S. H. Isolation and DNA sequence of a full-length cDNA clone for human X chromosome-encoded phosphoglycerate kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):472–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nathans J., Thomas D., Hogness D. S. Molecular genetics of human color vision: the genes encoding blue, green, and red pigments. Science. 1986 Apr 11;232(4747):193–202. doi: 10.1126/science.2937147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Royer-Pokora B., Kunkel L. M., Monaco A. P., Goff S. C., Newburger P. E., Baehner R. L., Cole F. S., Curnutte J. T., Orkin S. H. Cloning the gene for an inherited human disorder--chronic granulomatous disease--on the basis of its chromosomal location. Nature. 1986 Jul 3;322(6074):32–38. doi: 10.1038/322032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe Y., Esaki K., Nomura T. Skeletal muscle pathology in X chromosome-linked muscular dystrophy (mdx) mouse. Acta Neuropathol. 1986;69(1-2):91–95. doi: 10.1007/BF00687043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toniolo D., Persico M., Alcalay M. A "housekeeping" gene on the X chromosome encodes a protein similar to ubiquitin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):851–855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres L. F., Duchen L. W. The mutant mdx: inherited myopathy in the mouse. Morphological studies of nerves, muscles and end-plates. Brain. 1987 Apr;110(Pt 2):269–299. doi: 10.1093/brain/110.2.269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]