Abstract
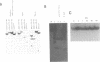
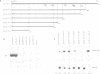
We have previously reported that c-myc protein may promote cellular DNA replication by binding to initiation sites of replication. Here we report that a putative origin of human cellular DNA replication (ori) is present at approximately 2 kb upstream of the coding region of the c-myc gene itself. The c-myc protein, or protein(s) complexed with c-myc protein, bind to the upstream region (approximately 200 bp in length) which has transcriptional enhancer activity as well as autonomously replicating activity in human cells, suggesting that the c-myc protein may be an enhancer binding protein as well as a DNA replication protein. Results with deletion mutants suggest that the sequence essential to the origin of DNA replication may be adjacent to, but cannot be clearly separated from, the sequence responsible for enhancer activity. Furthermore, when cloned DNA containing putative c-myc protein binding sequences was transfected as competitor into HL-60 cells, expression of c-myc was inhibited, suggesting that c-myc protein itself may be necessary for c-myc expression.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariga H., Itani T., Iguchi-Ariga S. M. Autonomous replicating sequences from mouse cells which can replicate in mouse cells in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):1–6. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ariga H., Sugano S. Initiation of simian virus 40 DNA replication in vitro. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):481–491. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.481-491.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brennand J., Chinault A. C., Konecki D. S., Melton D. W., Caskey C. T. Cloned cDNA sequences of the hypoxanthine/guanine phosphoribosyltransferase gene from a mouse neuroblastoma cell line found to have amplified genomic sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1950–1954. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung J., Sinn E., Reed R. R., Leder P. Trans-acting elements modulate expression of the human c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7918–7922. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Sheiness D. K., Bishop J. M. Transcripts from the cellular homologs of retroviral oncogenes: distribution among chicken tissues. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):617–624. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.617. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Bishop J. M., Levens D. Regulatory elements that modulate expression of human c-myc. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):659–671. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Itani T., Kiji Y., Ariga H. Possible function of the c-myc product: promotion of cellular DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2365–2371. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02513.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Itani T., Yamaguchi M., Ariga H. c-myc protein can be substituted for SV40 T antigen in SV40 DNA replication. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4889–4899. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itani T., Ariga H., Yamaguchi N., Tadakuma T., Yasuda T. A simple and efficient liposome method for transfection of DNA into mammalian cells grown in suspension. Gene. 1987;56(2-3):267–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90143-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto C., Chizzonite R., Crowl R., Rupprecht K., Kramer R., Schaber M., Kumar G., Poonian M., Ju G. Molecular cloning and regulated expression of the human c-myc gene in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae: comparison of the protein products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7232–7236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Gruss P. Specific interaction between enhancer-containing molecules and cellular components. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):403–411. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90233-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Bishop J. M. DNA and RNA from uninfected vertebrate cells contain nucleotide sequences related to the putative transforming gene of avian myelocytomatosis virus. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):514–521. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.514-521.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Yokota J., Ueyama Y. Amplification and expression of a cellular oncogene (c-myc) in human gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):414–418. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Villiers J., Schaffner W., Tyndall C., Lupton S., Kamen R. Polyoma virus DNA replication requires an enhancer. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):242–246. doi: 10.1038/312242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]