Abstract
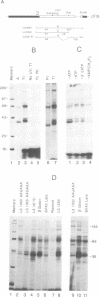
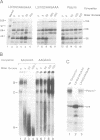
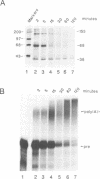
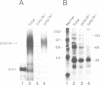
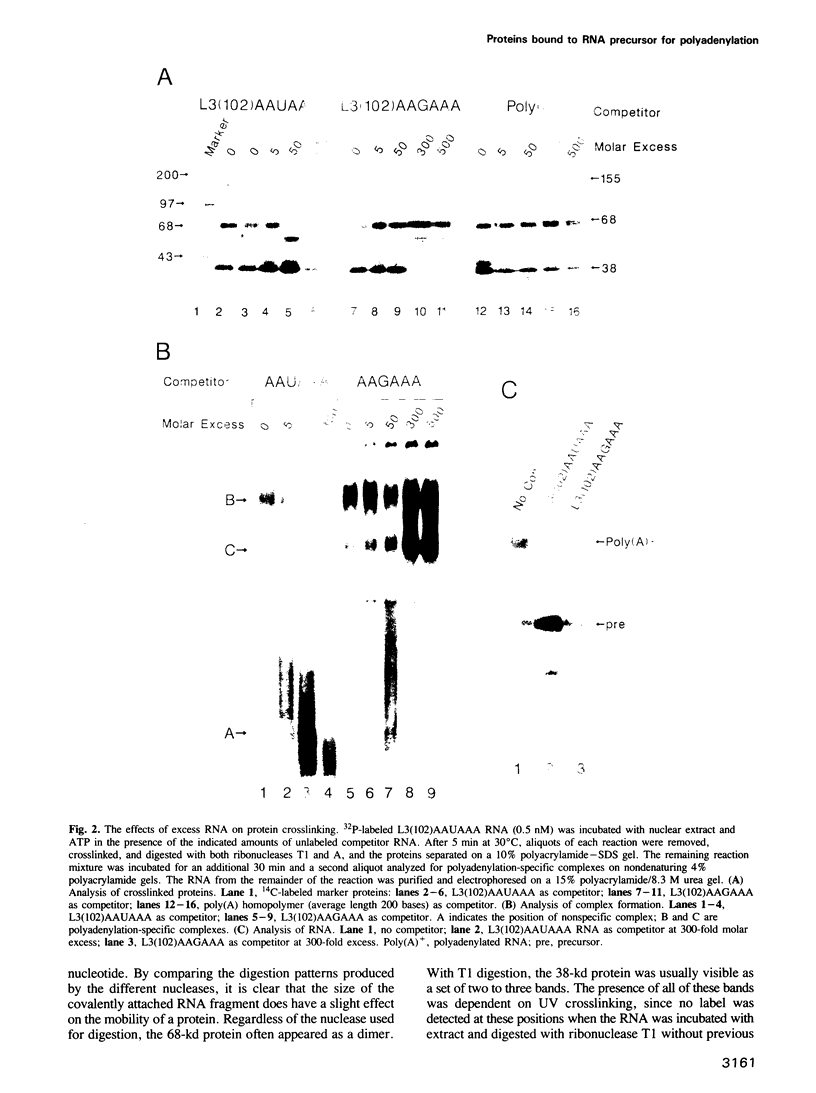
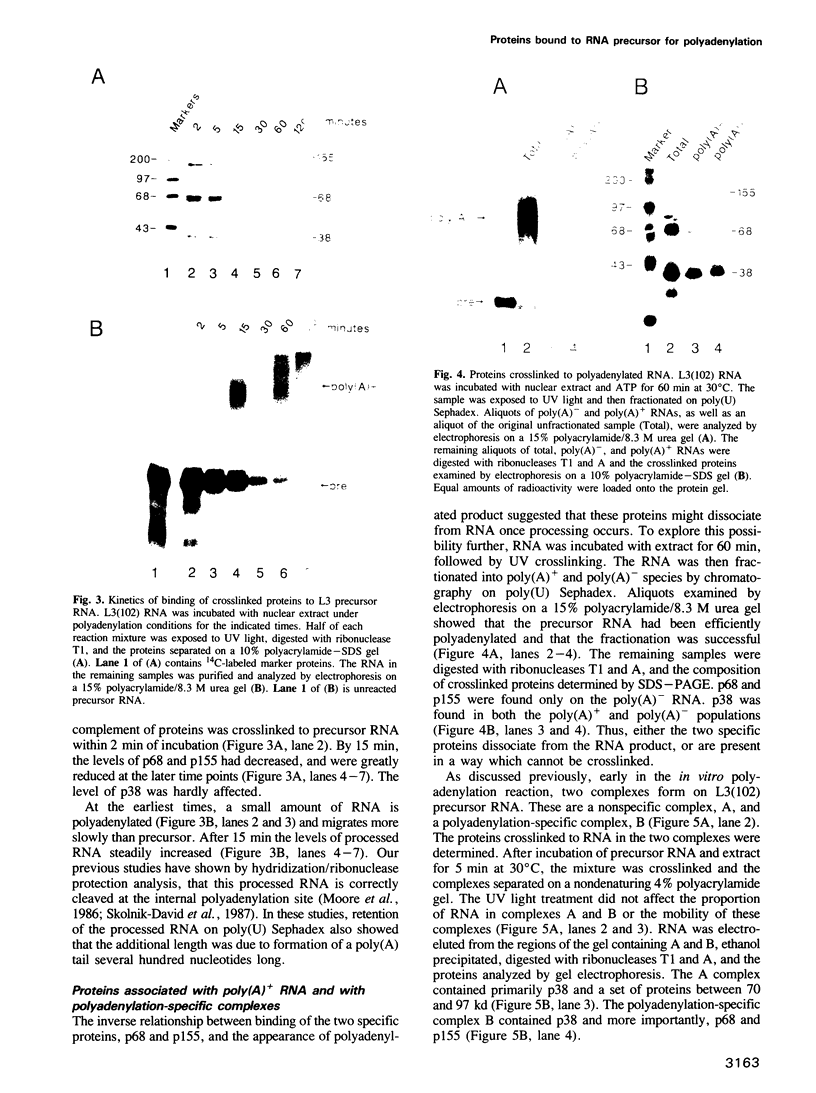
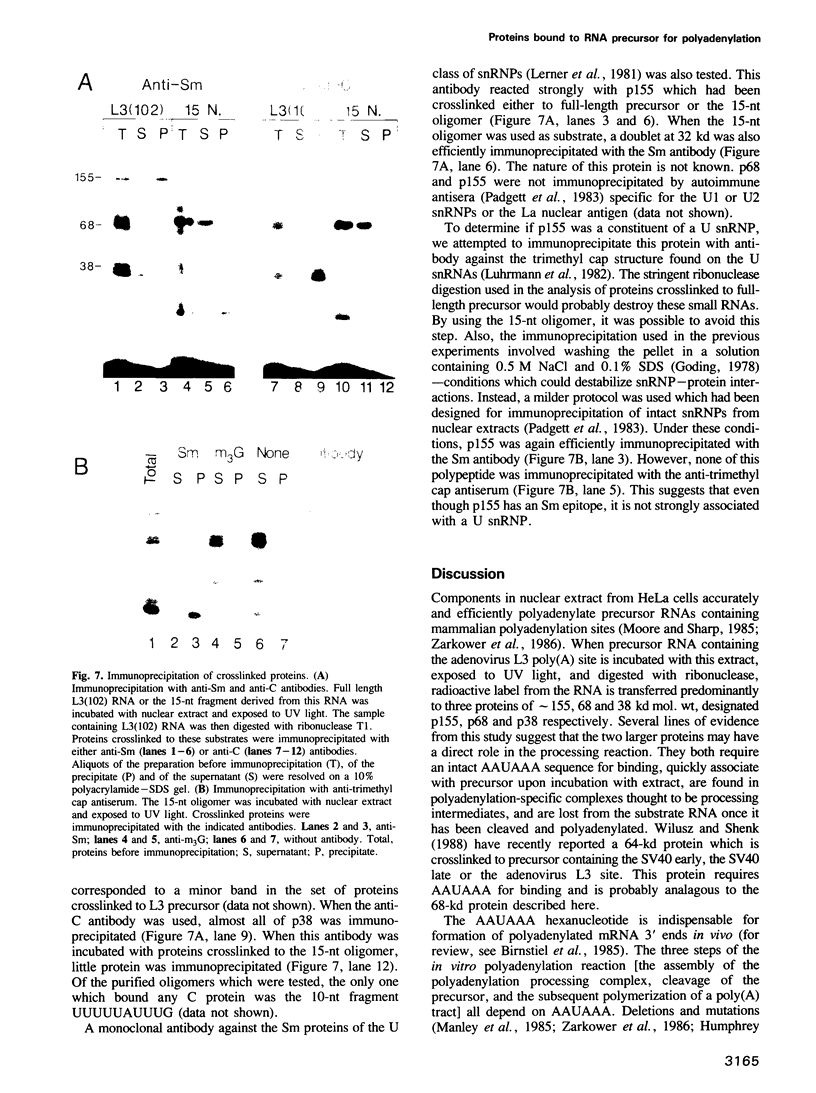
The major proteins crosslinked by UV light to RNA containing the adenovirus-2 L3 poly(A) site are species of 155, 68 and 38 kd mol. wt (p155, p68 and p38). Mutation of AAUAAA to AAGAAA prevented cross-linking of the two larger proteins and destroyed the ability of the RNA to compete for binding of these proteins. However, association of p155 and p68 with precursor was unaffected by deletion of sequences downstream of the poly(A) site critical for in vitro polyadenylation. These two proteins are in the polyadenylation-specific, but not the nonspecific complexes detected by electrophoresis in nondenaturing gels. In addition, p155 and p68 are not found on RNA which has been processed. p155 bound a 15-nt oligomer containing AAUAAA, and thus does not require extended RNA sequence for interaction with RNA. Identified by immunoprecipitation with specific antibody, p38 is the C protein of heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles (hmRNPs). While p155 has an Sm epitope, it is not associated with snRNPs containing trimethylated guanosine caps.
Full text
PDF
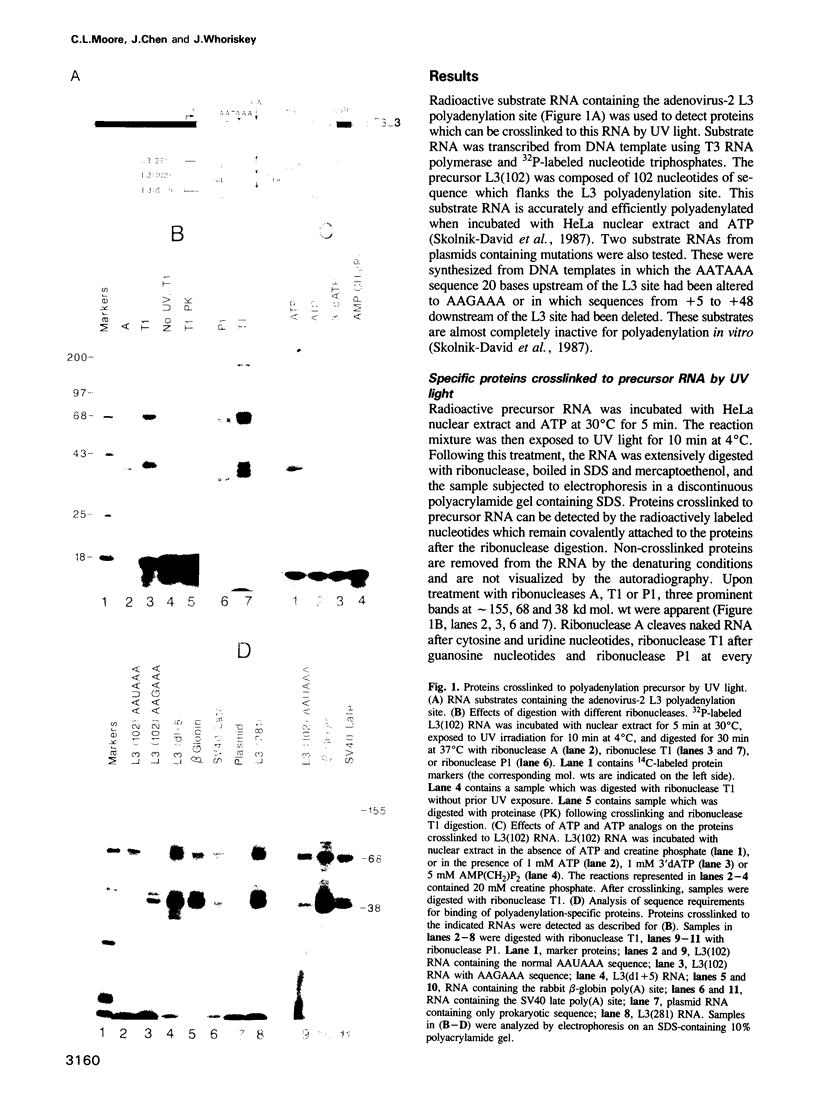






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berget S. M. Are U4 small nuclear ribonucleoproteins involved in polyadenylation? Nature. 1984 May 10;309(5964):179–182. doi: 10.1038/309179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer A. L., Christensen M. E., Walker B. W., LeStourgeon W. M. Identification and characterization of the packaging proteins of core 40S hnRNP particles. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):127–138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90323-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnstiel M. L., Busslinger M., Strub K. Transcription termination and 3' processing: the end is in site! Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):349–359. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80007-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi Y. D., Grabowski P. J., Sharp P. A., Dreyfuss G. Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins: role in RNA splicing. Science. 1986 Mar 28;231(4745):1534–1539. doi: 10.1126/science.3952495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung S. Y., Wooley J. Set of novel, conserved proteins fold pre-messenger RNA into ribonucleosomes. Proteins. 1986 Nov;1(3):195–210. doi: 10.1002/prot.340010302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conway L., Wickens M. Analysis of mRNA 3' end formation by modification interference: the only modifications which prevent processing lie in AAUAAA and the poly(A) site. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4177–4184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02764.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G., Choi Y. D., Adam S. A. Characterization of heterogeneous nuclear RNA-protein complexes in vivo with monoclonal antibodies. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;4(6):1104–1114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.6.1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfuss G. Structure and function of nuclear and cytoplasmic ribonucleoprotein particles. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:459–498. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Economidis I. V., Pederson T. Structure of nuclear ribonucleoprotein: heterogeneous nuclear RNA is complexed with a major sextet of proteins in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1599–1602. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehresmann B., Backendorf C., Ehresmann C., Ebel J. P. Characterization of the regions from E. coli 16 S RNA covalently linked to ribosomal proteins S4 and S20 after ultraviolet irradiation. FEBS Lett. 1977 Jun 15;78(2):261–266. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerke V., Steitz J. A. A protein associated with small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles recognizes the 3' splice site of premessenger RNA. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):973–984. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90812-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil A., Proudfoot N. J. Position-dependent sequence elements downstream of AAUAAA are required for efficient rabbit beta-globin mRNA 3' end formation. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):399–406. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90292-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Use of staphylococcal protein A as an immunological reagent. J Immunol Methods. 1978;20:241–253. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(78)90259-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green T. L., Hart R. P. Mutations in poly(A) site downstream elements affect in vitro cleavage activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1839–1841. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamm J., Kazmaier M., Mattaj I. W. In vitro assembly of U1 snRNPs. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3479–3485. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02672.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Ali H., Nevins J. R. Definition of essential sequences and functional equivalence of elements downstream of the adenovirus E2A and the early simian virus 40 polyadenylation sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2975–2983. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart R. P., McDevitt M. A., Nevins J. R. Poly(A) site cleavage in a HeLa nuclear extract is dependent on downstream sequences. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):677–683. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90240-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto C., Steitz J. A. A small nuclear ribonucleoprotein associates with the AAUAAA polyadenylation signal in vitro. Cell. 1986 May 23;45(4):581–591. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90290-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey T., Christofori G., Lucijanic V., Keller W. Cleavage and polyadenylation of messenger RNA precursors in vitro occurs within large and specific 3' processing complexes. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4159–4168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02762.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmich G. A., Randles J., Brand J. S. Assay of picomole amounts of ATP, ADP, and AMP using the luciferase enzyme system. Anal Biochem. 1975 Nov;69(1):187–206. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Moullec J. M., Akusjärvi G., Stålhandske P., Pettersson U., Chambraud B., Gilardi P., Nasri M., Perricaudet M. Polyadenylic acid addition sites in the adenovirus type 2 major late transcription unit. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):127–134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.127-134.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner E. A., Lerner M. R., Janeway C. A., Jr, Steitz J. A. Monoclonal antibodies to nucleic acid-containing cellular constituents: probes for molecular biology and autoimmune disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2737–2741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J., Falck-Pedersen E., Darnell J. E., Jr, Shenk T. A poly(A) addition site and a downstream termination region are required for efficient cessation of transcription by RNA polymerase II in the mouse beta maj-globin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8306–8310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luhrmann R., Appel B., Bringmann P., Rinke J., Reuter R., Rothe S., Bald R. Isolation and characterization of rabbit anti-m3 2,2,7G antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7103–7113. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Yu H., Ryner L. RNA sequence containing hexanucleotide AAUAAA directs efficient mRNA polyadenylation in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):373–379. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Gaffney D., Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. The consensus sequence YGTGTTYY located downstream from the AATAAA signal is required for efficient formation of mRNA 3' termini. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 25;13(4):1347–1368. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.4.1347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Accurate cleavage and polyadenylation of exogenous RNA substrate. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):845–855. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80065-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Skolnik-David H., Sharp P. A. Analysis of RNA cleavage at the adenovirus-2 L3 polyadenylation site. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1929–1938. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04446.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore C. L., Skolnik-David H., Sharp P. A. Sedimentation analysis of polyadenylation-specific complexes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):226–233. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.226. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mowry K. L., Steitz J. A. Identification of the human U7 snRNP as one of several factors involved in the 3' end maturation of histone premessenger RNA's. Science. 1987 Dec 18;238(4834):1682–1687. doi: 10.1126/science.2825355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller K., Brimacombe R. Specific cross-linking of proteins S7 and L4 to ribosomal RNA, by UV irradiation of Escherichia coli ribosomal subunits. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 9;141(4):343–355. doi: 10.1007/BF00331455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett R. A., Mount S. M., Steitz J. A., Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors is inhibited by antisera to small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90212-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker R., Siliciano P. G., Guthrie C. Recognition of the TACTAAC box during mRNA splicing in yeast involves base pairing to the U2-like snRNA. Cell. 1987 Apr 24;49(2):229–239. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90564-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Photochemical cross-linking of cap binding proteins to eucaryotic mRNAs: effect of mRNA 5' secondary structure. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):3222–3230. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.3222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinke J., Yuki A., Brimacombe R. Studies on the environment of protein S7 within the 30-S subunit Escherichia coli ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):77–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Sonenberg N. Identification of nuclear cap specific proteins in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6489–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Requirements for accurate and efficient mRNA 3' end cleavage and polyadenylation of a simian virus 40 early pre-RNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):495–503. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaufele F., Gilmartin G. M., Bannwarth W., Birnstiel M. L. Compensatory mutations suggest that base-pairing with a small nuclear RNA is required to form the 3' end of H3 messenger RNA. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):777–781. doi: 10.1038/323777a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoemaker H. J., Schimmel P. R. Photo-induced joining of a transfer RNA with its cognate aminoacyl-transfer RNA synthetase. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 25;84(4):503–513. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90112-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Todaro G. J. The genome-associated, specific RNA binding proteins of avian and mammalian type C viruses. Cell. 1977 Jan;10(1):91–99. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90143-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setyono B., Greenberg J. R. Proteins associated with poly(A) and other regions of mRNA and hnRNA molecules as investigated by crosslinking. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):775–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skolnik-David H., Moore C. L., Sharp P. A. Electrophoretic separation of polyadenylation-specific complexes. Genes Dev. 1987 Sep;1(7):672–682. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.7.672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry A. O., Berget S. M. In vitro cleavage of the simian virus 40 early polyadenylation site adjacent to a required downstream TG sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4734–4741. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefano J. E., Adams D. E. Assembly of a polyadenylation-specific 25S ribonucleoprotein complex in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2052–2062. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takagaki Y., Ryner L. C., Manley J. L. Separation and characterization of a poly(A) polymerase and a cleavage/specificity factor required for pre-mRNA polyadenylation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):731–742. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90411-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tazi J., Alibert C., Temsamani J., Reveillaud I., Cathala G., Brunel C., Jeanteur P. A protein that specifically recognizes the 3' splice site of mammalian pre-mRNA introns is associated with a small nuclear ribonucleoprotein. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):755–766. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90518-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilusz J., Shenk T. A 64 kd nuclear protein binds to RNA segments that include the AAUAAA polyadenylation motif. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90510-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Stephenson P., Sheets M., Wickens M. The AAUAAA sequence is required both for cleavage and for polyadenylation of simian virus 40 pre-mRNA in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2317–2323. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Wickens M. A functionally redundant downstream sequence in SV40 late pre-mRNA is required for mRNA 3'-end formation and for assembly of a precleavage complex in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5780–5788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Wickens M. Formation of mRNA 3' termini: stability and dissociation of a complex involving the AAUAAA sequence. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):177–186. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04736.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zarkower D., Wickens M. Specific pre-cleavage and post-cleavage complexes involved in the formation of SV40 late mRNA 3' termini in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4185–4192. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02765.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F., Cole C. N. Identification of a complex associated with processing and polyadenylation in vitro of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase precursor RNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3277–3286. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhuang Y., Weiner A. M. A compensatory base change in U1 snRNA suppresses a 5' splice site mutation. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]