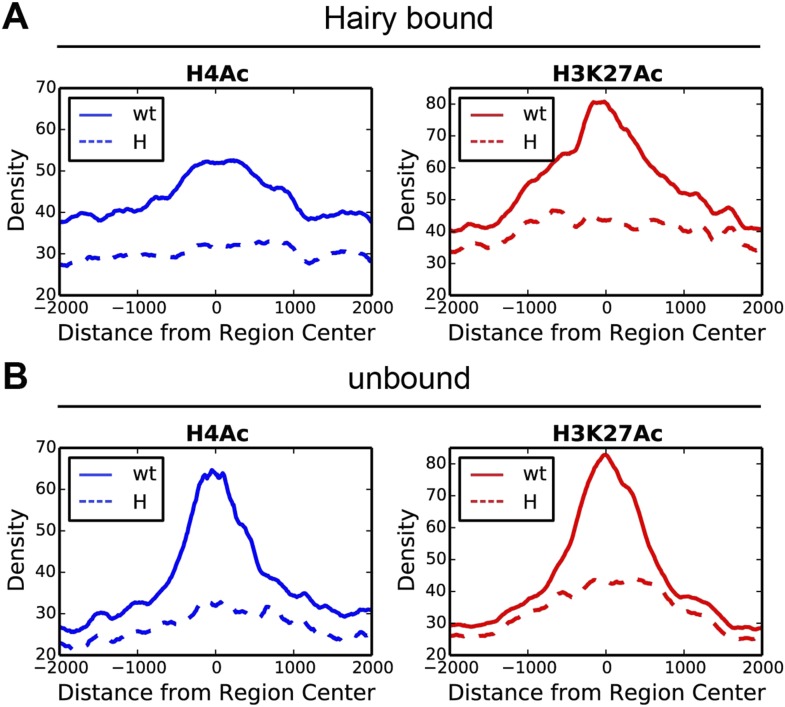
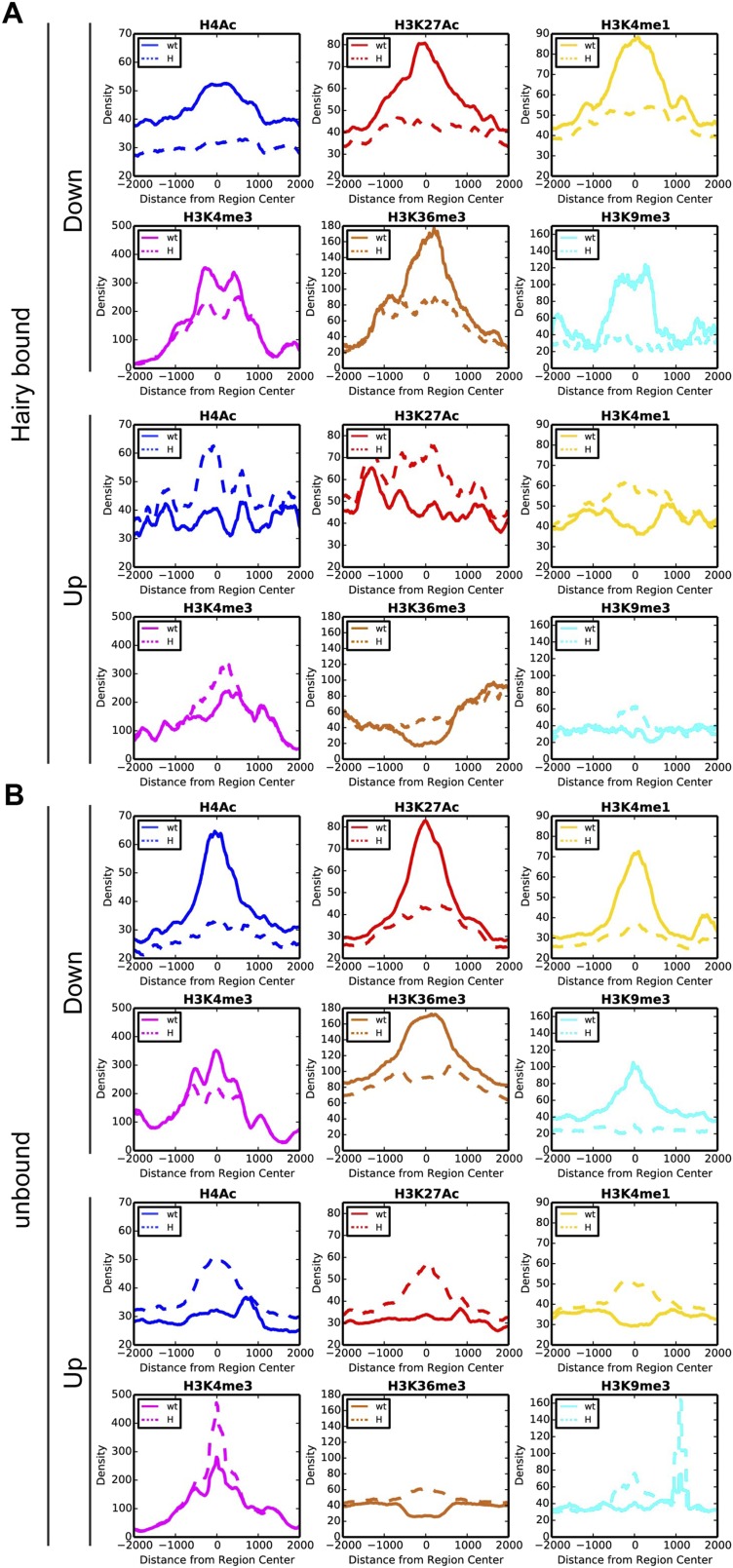
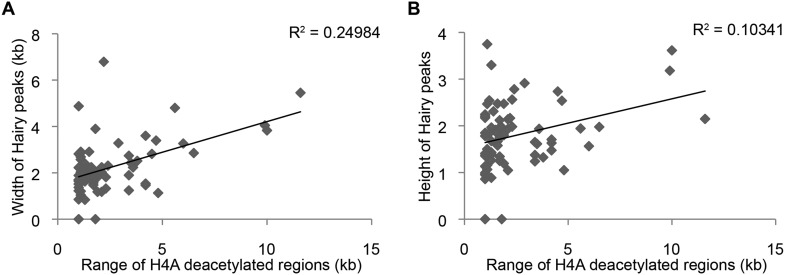
Figure 3. Direct Hairy target genes exhibit broad domains of chromatin effects.
Distribution of genome-averaged ChIP-seq signals before (straight line) and after (dashed line) Hairy induction, showing 4 kb window around affected regions. (A) Distributions of histone H4Ac and H3K27Ac marks of direct Hairy targets were significantly broader than for regions (B) not bound by Hairy (p = 2.55e-92 and p = 5.63e-70 respectively; KM test).