Significance
The mechanisms that the “dormant microbial majority” use to remain energized in nutrient-starved soil ecosystems have long remained elusive. In this work, we used an isolate of the highly abundant but poorly understood soil phylum Acidobacteria as a model for understanding microbial persistence mechanisms. When the bacterium entered a persistent state due to nutrient-exhaustion, we showed it could scavenge the trace concentrations of molecular hydrogen gas (H2) found in ambient air using a specialized high-affinity enzyme. These findings demonstrate that Acidobacteria can consume H2 and contribute to global hydrogen cycling. We propose that consumption of trace gases such as H2 provides a dependable general mechanism for dominant soil phyla to generate the maintenance energy required for long-term survival.
Keywords: hydrogenase, hydrogen, dormancy, rare biosphere, extremophile
Abstract
The majority of microbial cells in global soils exist in a spectrum of dormant states. However, the metabolic processes that enable them to survive environmental challenges, such as nutrient-limitation, remain to be elucidated. In this work, we demonstrate that energy-starved cultures of Pyrinomonas methylaliphatogenes, an aerobic heterotrophic acidobacterium isolated from New Zealand volcanic soils, persist by scavenging the picomolar concentrations of H2 distributed throughout the atmosphere. Following the transition from exponential to stationary phase due to glucose limitation, the bacterium up-regulates by fourfold the expression of an eight-gene operon encoding an actinobacteria-type H2-uptake [NiFe]-hydrogenase. Whole-cells of the organism consume atmospheric H2 in a first-order kinetic process. Hydrogen oxidation occurred most rapidly under oxic conditions and was weakly associated with the cell membrane. We propose that atmospheric H2 scavenging serves as a mechanism to sustain the respiratory chain of P. methylaliphatogenes when organic electron donors are scarce. As the first observation of H2 oxidation to our knowledge in the Acidobacteria, the second most dominant soil phylum, this work identifies new sinks in the biogeochemical H2 cycle and suggests that trace gas oxidation may be a general mechanism for microbial persistence.
Field surveys over the last two decades have revealed that the majority of bacteria in soil ecosystems exist in a range of nonreplicative persistent states (1). The ability of bacteria to establish and maintain dormancy has been correlated with their capacity to resist environmental changes. Indeed, multiple studies show that the structures of bacterial soil communities are stable following exposure to both short-term and long-term physical, chemical, and biological pressures (1, 2). One of the primary drivers that induces bacteria to transition from growth to persistence is starvation for electron donors (e.g., organic carbon sources) required for energy-generation (1). The maintenance energy for persistent cells is predicted to be three orders of magnitude lower than for growing cells (3). However, although such cells have reduced metabolic activity, they inevitably require some energy input for cell maintenance, macromolecule repair, morphological changes, and environmental sensing, among other processes (1, 4). Several processes have been linked to energy-maintenance in dormant states, ranging from triacylglycerol storage in nonreplicative persistent mycobacteria (5), to predation and cannibalism by sporulating bacilli (6). More recently, it has been proposed that consumption of atmospheric trace gases such as molecular hydrogen (H2) serves as a dependable mechanism to generate maintenance energy in several organisms during persistence (4, 7–9).
Most of our understanding of the physiology of soil microorganisms, including their persistence mechanisms, has come from studying fast-growing organisms. We have generally relied on extending findings about fast-growers from four bacterial phyla, the Proteobacteria, Firmicutes, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria, to soil ecosystems as a whole. However, 16S rRNA gene surveys of soil ecosystems show that five rarely cultivated, poorly characterized taxa, the Acidobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, Chloroflexi, Planctomycetes, and Gemmatimonadetes, are also among the most dominant soil phyla (10, 11), with Acidobacteria alone comprising an average of 20% of the global soil bacteria (11–13). Physiological characterization of the few representative species within these dominant phyla shows slow-growth and a propensity toward dormancy (14–16). So the question arises, how have such slow-growing phyla become abundant members within microbial communities? The current belief is that abundant fast-growing species use energy sources within ecosystems to grow competitively, whereas dominant slow-growing species use anabiosis-type strategies to outcompete other strains by persisting during periods of starvation (2, 17). Resolving the mechanisms used by these bacteria for persistence has implications for understanding the wider composition and behavior of soil microbial ecosystems.
We recently undertook a study of the acidobacterial strain Pyrinomonas methylaliphatogenes K22T to understand its ecological role within soil environments. This strain was isolated from heated soils adjacent to a fumarole on the outer crater rim of the stratovolcano Mt. Ngauruhoe in the Taupō Volcanic Zone, New Zealand (14, 18). Bacteriological analysis revealed that the bacterium exclusively grows aerobically using simple carbohydrates (18). This apparent limited respiratory flexibility is surprising given the bacterium is able to remain energized in an environment as physically demanding and chemically deprived as a volcanic fumarole. To resolve this contradiction, we took a genome-guided approach to identify alternative energy sources capable of supporting persistence of this bacterium. We identified a [NiFe]-hydrogenase similar to those involved with sporulation of streptomycetes (19–21) and nonreplicative persistence of mycobacteria (22–24). Here, we show that the [NiFe]-hydrogenase is expressed and activated during persistence, following exhaustion of metabolizable carbon sources and entry into stationary phase. This high-affinity hydrogenase enables P. methylaliphatogenes to consume the picomolar concentrations of H2 ubiquitously distributed in the atmosphere. We propose this serves as a dependable anabiosis mechanism for this bacterium–and persisters in general–to remain energized in otherwise physically challenging and chemically deprived environments.
Results
P. methylaliphatogenes Encodes and Expresses an Actinobacteria-Type [NiFe]-Hydrogenase.
We analyzed the recently sequenced genome of P. methylaliphatogenes (GI = 746989994) to identify enzymes involved in energy-generation. Consistent with an obligately aerobic heterotrophic lifestyle (18), the organism encodes several primary dehydrogenases (nuo complex, succinate dehydrogenase), a terminal oxidase (cytochrome bd complex), and an F1F0-ATPase. The genome does not encode enzymes capable of using most alternative electron donors (e.g., hydrocarbons, hydrogen sulfide) and acceptors (e.g., nitrate, sulfate, fumarate). However, we did identify multiple genes predicted to encode a [NiFe]-hydrogenase and associated maturation and accessory factors (PYK22_03060 to PYK22_03082) (Table S1).
Table S1.
Genes associated with the hydrogenase-encoding locus of P. methylaliphatogenes strain K22T
| Locus | Gene name | Proposed function |
| Structural operon | ||
| PYK22_03064 | hhyS | Hydrogenase small subunit |
| PYK22_03065 | hhyL | Hydrogenase large subunit |
| PYK22_03066 | hhyE | Putative [2Fe2S] electron transfer protein |
| PYK22_03067 | hhaA | Conserved hypothetical protein |
| PYK22_03068 | hhaB | Conserved hypothetical protein |
| PYK22_03069 | hhaC | Conserved hypothetical protein |
| PYK22_03070 | Unconserved hypothetical protein | |
| PYK22_03071 | hupD | Hydrogenase apoprotein endopeptidase |
| Upstream genes | ||
| PYK22_03060 | Homologous to hhyS, possibly sensory or nonfunctional | |
| PYK22_03061 | PAS domain-containing histidine kinase | |
| PYK22_03062 | LuxR-like response regulator | |
| PYK22_03063 | Putative transmembrane protein | |
| Downstream genes | ||
| PYK22_03072 | Predicted nonconserved 43-residue peptide | |
| PYK22_03073 | YceI-like transmembrane protein | |
| PYK22_03074 | hypA | Ni2+ insertion into hydrogenase large subunit |
| PYK22_03075 | hypB | Ni2+ insertion into hydrogenase large subunit |
| PYK22_03076 | hypC | Transfer of Fe-(CN−)2-(CO) Moiety to Large Subunit |
| PYK22_03077 | Conserved hypothetical protein | |
| PYK22_03078 | hypD | Transfer of Fe-(CN−)2-(CO) Moiety to Large Subunit |
| PYK22_03079 | hypE | Biosynthesis of CN− Ligands |
| PYK22_03080 | gmhA | Phosphoheptose Isomerase |
| PYK22_03081 | Conserved hypothetical protein | |
| PYK22_03082 | hypF | Biosynthesis of CN− Ligands |
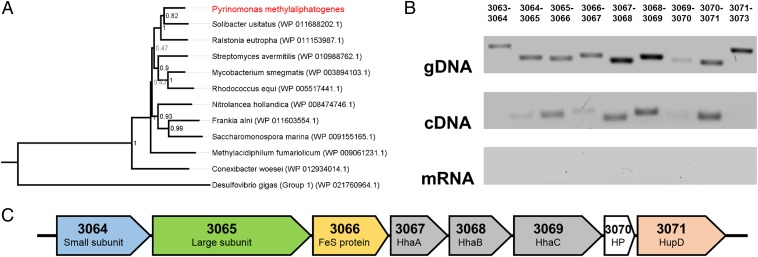
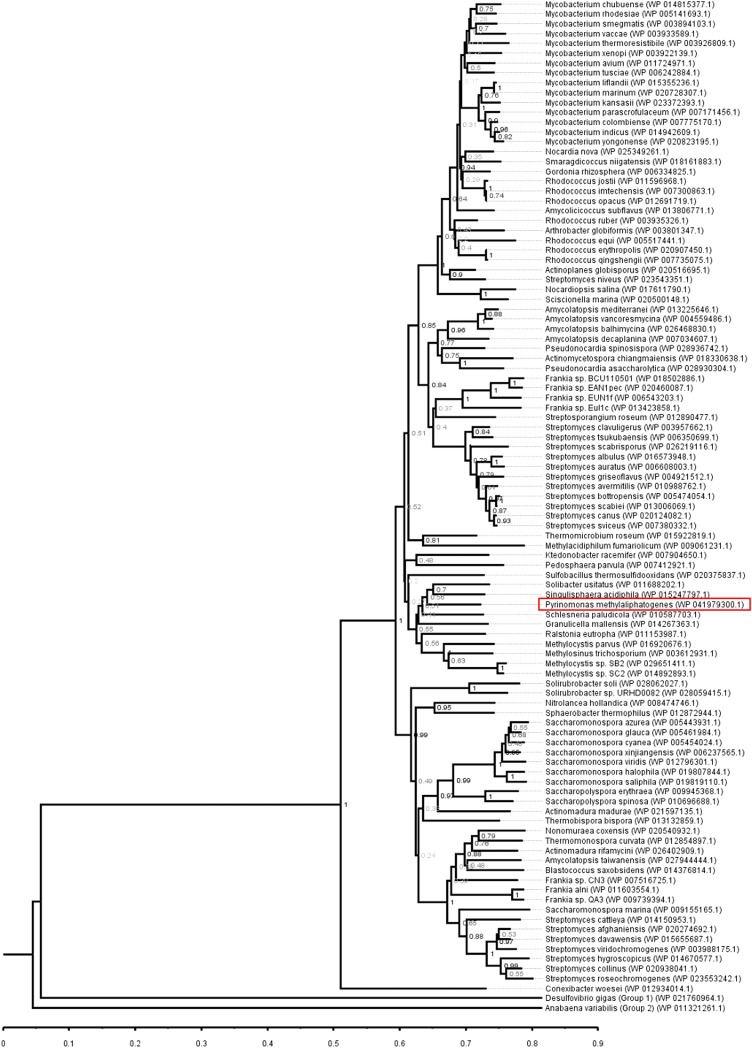
To gain insight into possible function, we classified the enzyme into one of five presently recognized [NiFe]-hydrogenase groups (19, 25) by analyzing the phylogeny of its large subunit sequence. This analysis confirmed that the hydrogenase is a member of the Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases (Fig. 1A), a recently discovered class of enzymes known to catalyze high-affinity H2 oxidation during persistence of certain Actinobacteria (7). The structural subunits of the enzyme were homologous to the recently characterized Hyd2 of Mycobacterium smegmatis (23, 24), sharing 77% (large subunit) and 72% (small subunit) amino acid sequence identity. Multiple sequence alignments confirmed that the structural subunits encode sufficient residues to bind the [NiFe]-center for H2 cleavage (large subunit) (Fig. S1) and three [4Fe4S]-clusters for electron transfer (small subunit) (Fig. S2).
Fig. 1.
Hydrogenase determinants in P. methylaliphatogenes strain K22T. (A) Phylogenetic tree showing the phylogeny of the P. methylaliphatogenes hydrogenase large subunit sequence compared with those of Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases. The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method, bootstrapped with 500 replicates, and rooted using representatives of the Group 1 and Group 2 [NiFe]-hydrogenases. (B) RT-PCR analysis determining the structure of the operon encoding the hydrogenase structural components. The structure was determined by detecting the presence of intergenic PCR products for cDNA samples against positive controls (gDNA) and negative controls (mRNA). Primers were designed to amplify the start, end, and intergenic regions of adjacent genes (loci numbers shown above the lane). (C) To-scale structure of the elucidated operon showing locus numbers and functional annotations of the genes.
Fig. S1.
Multiple sequence alignments (Clustal) of the genes encoding the large subunits of the Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases in P. methylaliphatogenes (PYK22_03065), Solibacter usitatus (Acid_6556), Mycobacterium smegmatis (MSMEG_2719), Streptomyces avermitilis (SAV_7367), and Ralstonia eutropha (PHG065). The four cysteine residues highlighted in yellow ligate the [NiFe] center that serves as the catalytic center. Sequences in red are predicted to be cleaved by the HupD endopeptidase during hydrogenase maturation.
Fig. S2.
Multiple sequence alignments (Clustal) of the genes encoding the small subunits of the Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases in P. methylaliphatogenes (PYK22_03064), Solibacter usitatus (Acid_6555), Mycobacterium smegmatis (MSMEG_2720), Streptomyces avermitilis (SAV_7367), and Ralstonia eutropha (PHG064). The subunit ligates a 3Cys1Asp[4Fe4S]proximal (ligands highlighted in green), 4Cys[4Fe4S]medial cluster (ligands highlighted in blue), and a 3Cys1His[4Fe4S]distal cluster (ligands highlighted in pink).
Reverse transcriptase PCR was used to confirm P. methylaliphatogenes expressed this hydrogenase. Intergenic RT-PCRs (Fig. 1B) confirmed that the hydrogenase is expressed as part of an eight-gene operon, PYK22_03064-3071 (Fig. 1C), that includes the small and large structural subunits (HhySL), a putative iron-sulfur protein (HhyE), conserved hypothetical proteins (HhaA, HhaB, HhaC), and an endopeptidase (HupD) (Fig. 1C). These subunits are all typically associated with Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases (7). The operon interposed upstream genes encoding a possible two-component sensory system (PYK22_03060-3063) and downstream gene clusters encoding standard [NiFe]-hydrogenase maturation factors (PYK22_03072-3082) (Table S1). RT-PCR indicates that these genes are not cotranscribed with the hydrogenase (Fig. 1B).
Hydrogenase Expression Is Up-Regulated During Nonreplicative Persistence.
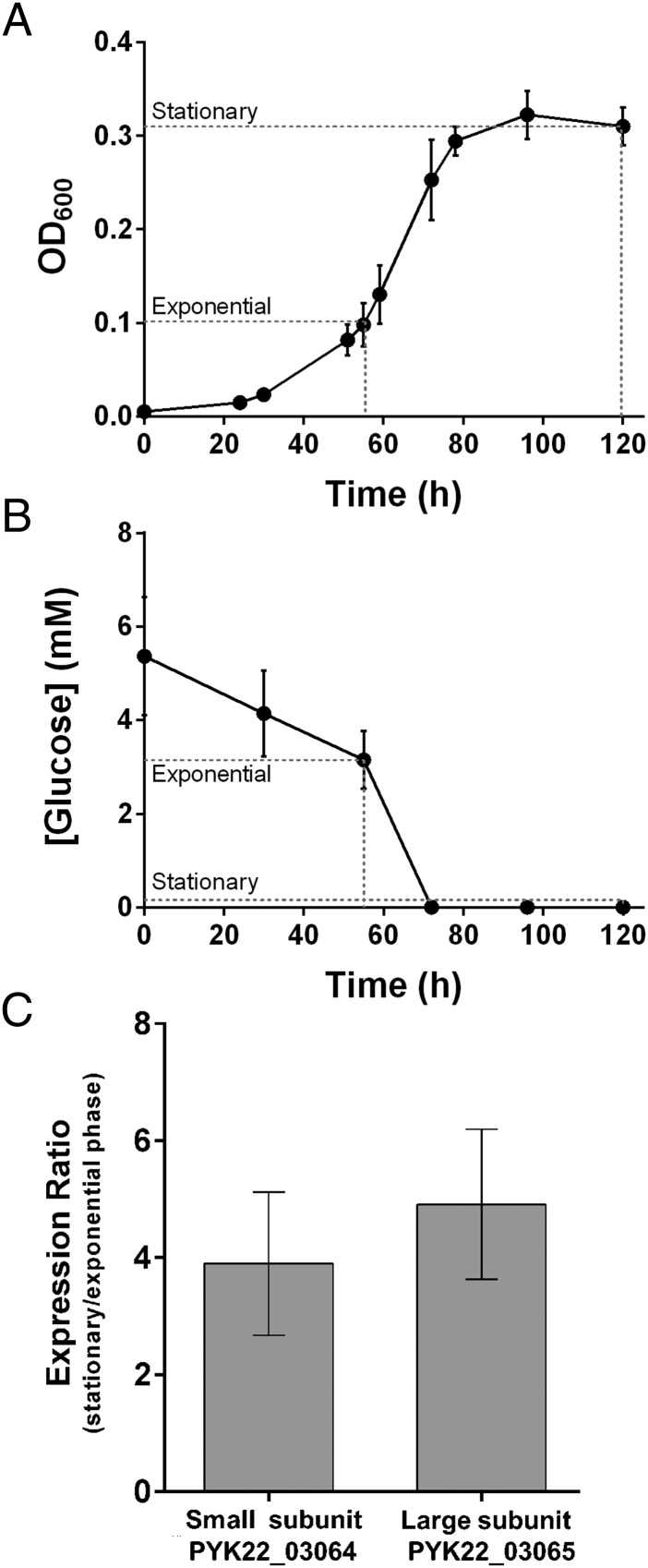
Given Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases are linked to dormancy in Actinobacteria (19, 23, 26, 27), we investigated whether the hydrogenase also contributed to persistence in cultures of P. methylaliphatogenes. We used quantitative RT-PCR (qRT-PCR) to compare the expression of the hydrogenase structural genes using RNA extracted from exponential-phase and stationary-phase cultures (Fig. 2A); it was confirmed that the bacteria entered stationary-phase after exhausting their supply of the energy source glucose (Fig. 2B). There was a low- to midlevel hydrogenase expression under exponential phase (CT PYK22_03064 = 24.6 for exponential-phase cultures, 32.5 for no template controls). However, the expression of both the small subunit and large subunit genes increased four- to fivefold in stationary compared with exponential-phase cultures (Fig. 2C); the hydrogenase operon is up-regulated during nonreplicative persistence. Consistent with a physiological role in survival rather than growth, P. methylaliphatogenes was unable to support autotrophic growth or enhance mixotrophic growth using an exogenous supply of H2.
Fig. 2.
Hydrogenase expression in P. methylaliphatogenes strain K22T. (A) Growth of P. methylaliphatogenes in FS1V minimal medium supplemented with 2.5 mM glucose. Cells were harvested for RNA extraction during exponential phase (OD600 = 0.1) and stationary phase (t = 120 h). (B) Glucose concentration of the external medium during cell growth. (C) Expression ratios of the genes encoding the hydrogenase small and large subunit during stationary vs. exponential phase as determined by qRT-PCR and normalized to 16S rRNA gene expression. In both cases, error bars represent SDs from three biological replicates.
P. methylaliphatogenes Oxidizes H2 Using a Weakly Membrane-Associated, Respiration-Linked Hydrogenase.
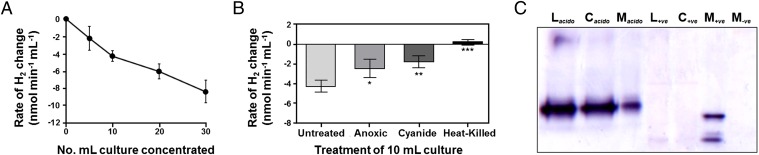
In whole-cell amperometric assays, stationary-phase cultures of P. methylaliphatogenes consumed H2 at a rate directly proportional to cell density (Fig. 3A). The rate of H2 oxidation decreased in cyanide-treated or anoxic (nitrogen-sparged) vessels by twofold (Fig. 3B), suggesting this activity is linked to the aerobic respiratory chain. Low levels of activity were also observed in long-term anoxic cultures (relative to controls).
Fig. 3.
Hydrogenase activity in carbon-limited stationary-phase cultures of P. methylaliphatogenes strain K22T. (A) Density-dependent whole-cell oxidation of H2. (B) Whole-cell oxidation of H2 following nitrogen-sparging (anoxic), cyanide-treatment, or heat-killing of the cells. For both A and B, H2 concentration was measured using a H2 microsensor. Positive values infer net H2 evolution, whereas negative values infer net H2 oxidation. Error bars represent SDs from three biological replicates; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (Student’s t test). (C) Zymographic detection of hydrogenase activity in concentration-normalized cell lysates (L), cytosols (C), and membranes (M) separated by native PAGE and anaerobically stained with the artificial electron acceptor nitroblue tetrazolium. Acidobacterial samples (labeled acido in subscript) were run against the M. smegmatis mc2155 as a positive control (+ve) and its hydrogenase triple mutant derivative as a negative control (−ve).
We verified zymographically that this activity emerges from the behavior of a Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenase. P. methylaliphatogenes lysates efficiently catalyzed electron transfer from H2 to the artificial electron acceptor nitroblue tetrazolium (E’o = −80 mV) in gel and cuvette assays (Fig. 3C). Consistent with the activity of other Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases (24), the enzyme was not capable of catalyzing electron transfer to lower-potential acceptors (such as methyl viologen; E’o = −360 mV). When cell fractions (normalized to protein concentration) were separated on native polyacrylamide gels, hydrogenase activity was observed in single bands within cell lysates, cytosols, and membranes alike (Fig. 3C); this suggests the hydrogenase is weakly membrane-associated, but largely dissociates from the membrane following lysis. Although the structural subunits lack predicted transmembrane regions or membrane-targeting motifs, it is notable that predicted membrane proteins (PYK22_03063, PYK22_3073) are encoded from the wider hydrogenase-associated genomic region (Table S1). The staining behavior significantly differed to that of the positive control M. smegmatis, where all hydrogenase activity is strongly membrane-associated (Fig. 3C).
P. methylaliphatogenes Consumes Atmospheric H2 in a High-Affinity, First-Order Kinetic Process.
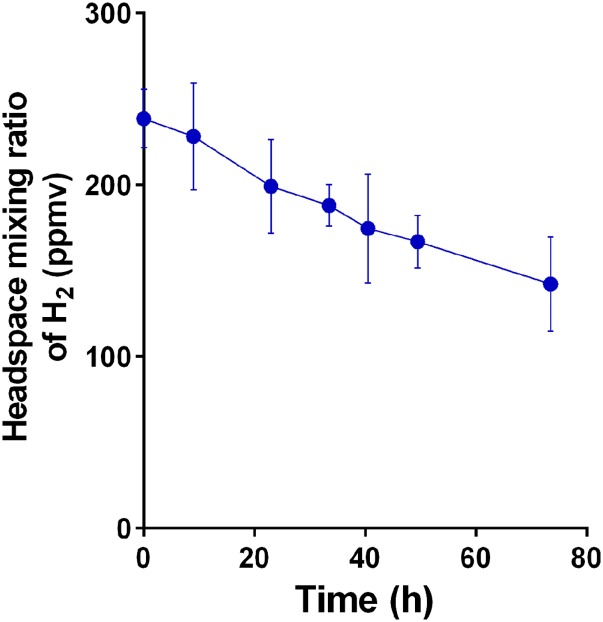
Given some Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases have a very high-affinity for H2 (19, 21, 24), we subsequently investigated the ability of P. methylaliphatogenes to consume atmospheric concentrations of H2 (530 ppbv; ref. 28). Gas chromatography measurements showed that the cultures oxidized exogenously added H2 (11.2 ± 0.2 ppmv) to below atmospheric concentrations (85 ± 13 ppbv) over 120 h (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
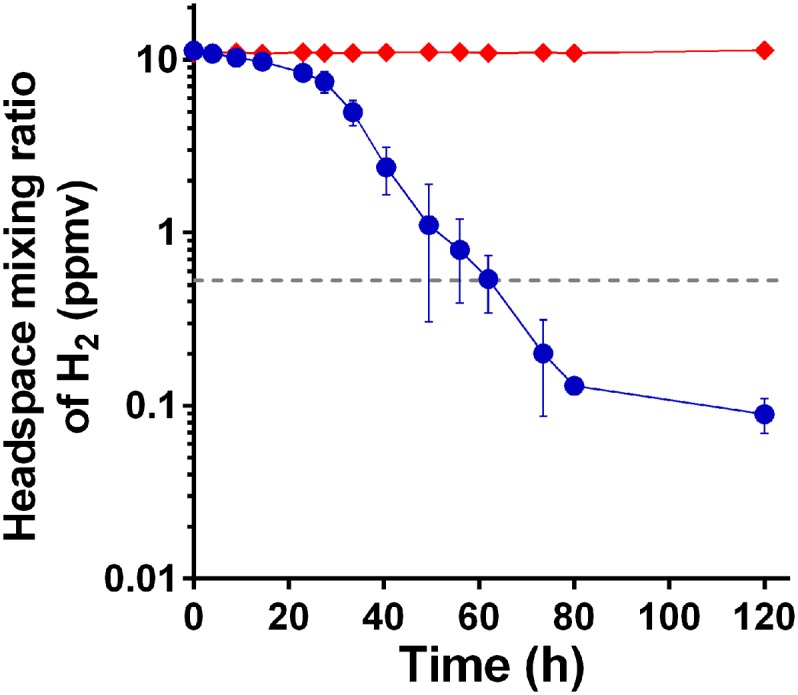
H2 uptake in carbon-limited stationary-phase cultures of P. methylaliphatogenes strain K22T. The depletion of a headspace of H2 was measured as a function of time in cultures inoculated with the bacterium (blue circles) against no-culture controls (red triangles). Mixing ratios are displayed on a logarithmic scale. Error bars represent SDs from three biological replicates. The gray dotted line shows the global mixing ratio of H2 in the lower atmosphere (0.53 ppmv).
The kinetic parameters of H2 oxidation in whole-cell cultures of P. methylaliphatogenes were also determined. At enzyme-saturating concentrations of H2 (250 ppmv) (Fig. S3), oxidation proceeded linearly with a Vmax (app) of 480 ± 20 pmol (g dw)-1 min−1. The rate of H2 oxidation was fivefold lower than observed for M. smegmatis (24) and more similar to that observed for Streptomyces sp. PCB7 (21). At lower concentrations (11 ppmv), P. methylaliphatogenes oxidized H2 in a first-order process that, following an initial lag, obeyed Michaelis-Menten kinetics (Fig. 4). The Michaelis constant (KM [app]) of the whole-cell hydrogenase activity was 35 ± 13 nM. The threshold H2 concentration for hydrogenase activity to occur was 64 ± 10 pM. These kinetic parameters are on the same order as calculated for whole-soil samples and the high-affinity hydrogenases of streptomycetes (19).
Fig. S3.
Hydrogen oxidation by stationary-phase cultures of P. methylaliphatogenes strain K22T at H2 partial pressures capable of saturating the [NiFe]-hydrogenase. The depletion of a headspace of H2 was measured as a function of time in cultures inoculated with the bacterium. Mixing ratios are displayed on a linear scale. Error bars show SDs from three biological replicates.
Discussion
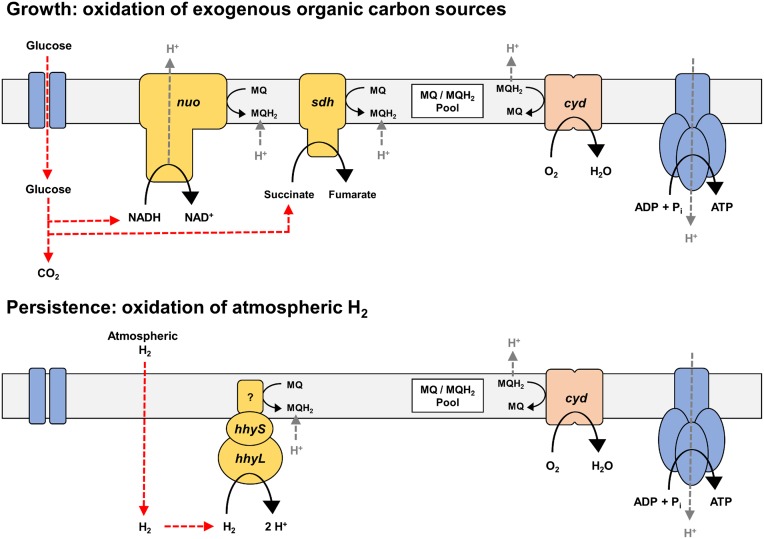
This study used P. methylaliphatogenes as a model organism to identify the mechanisms that energize persistent soil bacteria. We demonstrated that carbon-exhausted persistent cells of the organism scavenged atmospheric H2 in a membrane-associated, respiration-linked process. This activity correlated with the fourfold up-regulation of an actinobacteria-type [NiFe]-hydrogenase following the transition from growth to persistence due to energy-limitation. Our expression and biochemical studies demonstrated the hydrogenase is involved in persistence, likely harnessing atmospheric H2 as an energy source when preferred carbon substrates become exhausted. However, due to the absence of efficient genetic systems for Acidobacteria or specific inhibitors for [NiFe]-hydrogenases, we could not use phenotypic approaches to further explore the importance of H2 oxidation in this organism. Given the reduction in long-term viability of M. smegmatis strains lacking the Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenase (23, 26), we nevertheless infer that atmospheric H2 scavenging may enhance the survival of P. methyaliphatogenes. As atmospheric H2 is ubiquitous and diffusible, this gas acts as a highly dependable source of energy for bacterial persistence (7, 28). A model of the role of atmospheric H2 scavenging in energy-generation during persistence of P. methylaliphatogenes is shown in Fig. 5.
Fig. 5.
Model of the respiratory chain of P. methylaliphatogenes in carbon-replete (Upper) and carbon-limiting (Lower) conditions. The genome of P. methylaliphatogenes suggests its respiratory chain is highly minimalistic. It comprises three primary dehydrogenases (nuo: NADH dehydrogenase type I; sdh: succinate dehydrogenase; hhy: high-affinity [NiFe]-hydrogenase), a single terminal oxidase (cyd: cytochrome bd oxidase), and an F1Fo-ATP synthase. In carbon-replete conditions, import and oxidation of heterotrophic carbon sources such as glucose yields NADH and succinate that serve as an input into the respiratory chain via nuo and sdh. A large proton-motive force is generated, primarily through the action of the proton-translocating nuo, generating sufficient ATP for growth. In carbon-limiting conditions, the high-affinity hydrogenase hhy oxidizes the atmospheric H2 that diffuses into the cell. This may generate a small proton-motive force via a redox-loop mechanism dependent on menaquinone protonation and menaquinol deprotonation, providing sufficient ATP for maintenance.
The physiological role of atmospheric hydrogen scavenging appears to be broadly conserved between P. methylaliphatogenes and M. smegmatis. However, the interactions of their Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases with the respiratory chain appear to significantly differ. Although H2 appears to be primarily aerobically respired in P. methyaliphatogenes, we also observed low-level oxygen-independent activity of the hydrogenase, suggesting H2 can be oxidized in a respiration-independent manner or in an anaerobic respiratory process coupling to an unidentified endogenous electron acceptor in this organism. This behavior significantly differs from that of M. smegmatis, which strictly depends on the presence exogenous O2 for H2 oxidation to be detectable (22, 24). Furthermore, the P. methylaliphatogenes hydrogenase has a weaker membrane-association than the M. smegmatis hydrogenase (7, 24) and runs as a single band rather than triplet of bands during native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Although the reasons for these behaviors are not yet understood, these results suggest that there are substantial differences in the oligomerisation or interactions of Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases in Acidobacteria compared with Actinobacteria. Significantly more work is needed in both model organisms to determine how Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases input electrons into the respiratory chain, including the nature of their immediate electron acceptor (HhyE or otherwise) (7).
A prevailing opinion is that trace gas oxidation is a “niche” process: Genome surveys restrict Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases almost exclusively to Actinobacteria (19, 24), with the notable exception of a low-affinity homolog within the proteobacterium Ralstonia eutropha (29). Concurrent with an analysis of newly available genomes (7), this study suggests that Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases are present in a greater proportion of bacteria than previously anticipated (Fig. S4). As a moderate-acidophile and thermophile, P. methylaliphatogenes has become adapted to geothermal soils (18). However, the phylogeny of the acidobacterial Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenase indicates that an ancestral form was acquired before the phylum diversified to occupy different ecological niches (12, 18). Hydrogenases sharing >75% amino acid sequence identity have now been identified in seven species and three subdivisions of Acidobacteria, including isolates from mesophilic agricultural soils (Solibacter usitatus; refs. 30 and 31), forest soils (Edaphobacter aggregans; ref. 32), and tundra soils (Granulicella mallensis; ref. 33). Furthermore, with the release of multiple new genomes for the phyla, genes encoding Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases have been sequenced in seven Chloroflexi, three Verrucomicrobia, and two Planctomycetes (7) (Fig. S4). Experimentally, atmospheric H2 oxidation has now been observed to support the persistence of organisms with very different life cycles: the relatively fast-growers M. smegmatis (24) and R. equi (27), the sporulators Streptomyces sp. PCB7 (21) and S. avermilitis (19), and, in this work, the slow-grower P. methylaliphatogenes. These findings, in combination with the taxonomic distribution of Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases, suggest that trace H2 gas oxidation may be a relatively conserved persistence mechanism among dominant soil phyla.
Fig. S4.
Distribution of Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases. The phylogenetic tree shows the phylogeny of the P. methylaliphatogenes hydrogenase large subunit sequence compared with those of Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases. The tree was constructed using the neighbor-joining method, bootstrapped with 500 replicates, and rooted using representatives of the Group 1 and Group 2 [NiFe]-hydrogenases. Over 100 Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases have been identified in the genomes of the dominant soil phyla Actinobacteria, Acidobacteria, Chloroflexi, Verrucomicrobia, Planctomycetes, and Proteobacteria.
This work also expands the biological participants involved in the global biogeochemical cycle of molecular hydrogen. A range of studies have shown that, whereas the main sources of atmospheric H2 are abiotic (i.e., geochemical and anthropogenic) (28), the primary sink of the gas is high-affinity soil bacteria (7, 28, 34). The soil sink appears to be ubiquitous and highly active (7, 34), as reflected by the high uptake (56–88 Tg yr−1) and short lifetime (1.4–2.1 y) of atmospheric H2 (28). Following the first description of a high-affinity H2-oxidizer in 2008 (21), it has been shown that three genera of Actinobacteria are capable of atmospheric H2 consumption using Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases (19, 24, 27). Our research now demonstrates that a second phylum outside that of Actinobacteria also consumes atmospheric H2. Supported by the ubiquitous occurrence of atmospheric H2 consumption within soil ecosystems (7, 28), it now seems likely that more than one dominant soil phyla makes a quantitatively important contribution to global atmospheric H2 consumption.
There is also significant evidence that atmospheric H2 scavenging contributes to the persistence of bacteria on the ecosystem scale (7). Field surveys show that genes encoding Group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenases are abundant in soils (106 to 108 copies per gram dry weight; ref. 19) and are expressed at a level inversely proportional to organic carbon content (35). In addition, theoretical calculations predict that atmospheric H2 can provide the maintenance energy for the survival of 107 bacteria per gram of soil (7, 19). Hence, atmospheric H2 may be sufficient to sustain populations of several of the most dominant phyla in nutrient-deprived soil ecosystems. It is also notable that soil ecosystems serve as sinks for other trace gases in addition to H2. Oxidation of trace concentrations of methane (CH4) and carbon monoxide (CO) (36) by high-affinity methanotrophs and carboxydotrophs has been previously reported (8, 37–39). Although the physiological role of these processes have yet to be explored, it is possible that these trace gases also serve as a fuel to support the persistence of microbial soil communities. In conclusion, we propose that trace gas-scavenging is an under-recognized general mechanism for bacterial persistence and is likely to provide the maintenance energy to sustain a significant proportion of the bacterial communities in soils.
Materials and Methods
Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions.
P. methylaliphatogenes strain K22T (18) was maintained on 50% R2A solidified medium (Phytagel, Sigma) (14). For liquid culture, the strain was grown on low-nutrient FS1V minimal medium (14) supplemented with 5 mM glucose. Liquid cultures were grown in 120-mL sealed serum vials containing 30 mL cultures. For fractionation experiments, growth was upscaled in 1,000-mL capped Schott bottles filled with 300 mL of culture. In all cases, vials/bottles contained a headspace of ambient air and were sealed after sterilization (121 °C, 100 kpa, 15 min). Cultures were incubated with agitation (120 rpm) at 60 °C. M. smegmatis mc2155 (40), and its triple hydrogenase mutant derivative (Δhyd123) (22) were maintained on LBT plates and grown on modified Hartmans de Bont (HdB) minimal medium with agitation (200 rpm) at 37 °C as described (24). All cultures were inoculated to an initial optical density of 0.005. Optical densities to assess growth were measured at 600 nm (OD600) in a Jenway 6300 spectrometer. To remove clumping, P. methylaliphatogenes cultures were vortexed for 30 seconds before OD measurement. Protein concentrations of lysed cells and fractions were measured using the BCA Protein Assay Kit (Pierce) against BSA standards. Glucose concentrations in the medium were determined by detecting NADH oxidation using a modified hexokinase/glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase assay as described (41).
Nucleic Acid Extraction.
Genomic DNA from P. methylaliphatogenes was extracted from 10 mL using the cetyltrimethylammonium bromide (CTAB) method as described (42). For RNA isolation from P. methylaliphatogenes, exponential phase (OD600 = 0.1, 100-mL cultures) and stationary phase (t = 120 h, 30-mL cultures) cells were quenched with cold glycerol-saline solution (3:2 vol/vol, −20 °C), harvested by centrifugation (27,000 × g, 20 min, −20 °C), and resuspended in 1 mL of glycerol saline (1:1 vol/vol, −20 °C). Cell lysis was achieved by three cycles of bead-beating in a Mini-Beadbeater (Biospec) at 5,000 rpm for 30 s Total RNA was extracted using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA was treated with 2 U of RNase-free DNase using the TURBO DNA-free kit (Ambion), according to the manufacturer’s instructions. RNA concentration and purity were confirmed using a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer, whereas integrity was confirmed through electrophoresis on a 1% (wt/vol) agarose gel.
RT-PCR and Quantitative RT-PCR.
cDNA was synthesized from 1 µg of RNA for each sample with the SuperScript III Reverse Transcriptase Kit (Invitrogen). To determine operon structure, gene-specific primers (Integrated DNA Technologies) were designed to amplify the end and start of adjacent genes spanning the hydrogenase-encoding region (Table S2). PCRs were run using the Phusion High-Fidelity PCR Polymerase kit (Invitrogen) with 20 ng of gDNA, cDNA, or mRNA as template. Quantitative RT-PCR was performed using Platinum SYBR Green qPCR SuperMix-UDG with ROX (Invitrogen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Primer pairs were designed and optimized to amplify 300-bp regions of the hydrogenase large subunit, hydrogenase small subunit, and 16S rRNA genes (Table S2). The real-time PCR reactions were optimized and conducted in ABI Prism 7500 (Applied Biosystems). Relative gene expression was determined from calculated threshold cycle (CT) values that were normalized to 16S rRNA gene as an internal normalization standard.
Table S2.
Primers used in this study
| Name | Sequence (5′–3′) |
| RT-PCR | |
| 3063–3064FW | TCCGGGTTCGCGGCGGC |
| 3063–3064RV | CACATCTTCGATGCTCGGTT |
| 3064–3065FW | GGAGCGCGCGCTTCGAC |
| 3064–3065RV | GTAGCATTCGGCGACTTCG |
| 3065–3066FW | AACGGGCCGGACAAGTTCA |
| 3065–3066RV | GAGCAGCCGCTCAAGCGC |
| 3066–3067FW | TTCGAAGACGTGATGCTCGT |
| 3066–3067RV | ACCGGTTGCCATCTCGATC |
| 3067–3068FW | ATCGCTCCCATCGATGAATG |
| 3067–3068RV | GGTTCGATCATGATCTGGCA |
| 3068–3069FW | CGGCGCTACAAGGCTCGG |
| 3068–3069RV | CCGATTGCATCGCGCAGTA |
| 3069–3070FW | ATGAAGAGAAGCGCGAGGC |
| 3069–3070RV | TTTCCGGCGAGCGCTAGAT |
| 3070–3071FW | GTGTTGGTCGCTGTCGTCA |
| 3070–3071RV | CGCATAGGCCAGATCGAAG |
| 3071–3073FW | TTCGACGGCATGGGGCTG |
| 3071–3073FRV | CGCGAGATCGCGGAAGGT |
| qRT-PCR | |
| PyrinoSmallFW | TCCCCAACGAAGAGATCAAGC |
| PyrinoSmallRV | GCAGGTAAAGGACCGTCTCCA |
| PyrinoLargeFW | TACACCTACGAGCGCATGACC |
| PyrinoLargeRV | CACCTGTGTCGAGCGCTAAAT |
| Pyrino16SFW | CGGCGGATTAGCTAGTTGGTG |
| Pyrino16SRV | GTTAGCCGGGGCTTACAAAGG |
Hydrogenase Activity Measurements.
Hydrogenase activity was measured using carbon-exhausted stationary-phase cultures of P. methylaliphatogenes. For amperometric measurements, whole cells of the culture were concentrated 5-, 10-, 20-, and 30-fold by centrifugation. Rate of H2 oxidation was measured at 55 °C using a H2-MR hydrogen microsensor (Unisense) as described (22, 24). For zymographic measurements, 3-L cultures were harvested by centrifugation (15 min, 5,000 × g, 4 °C), resuspended and incubated in 20 mL of lysis buffer (23), and lysed by passage through a cell disruptor (Constant Systems) (35,000 psi, four times). After removal of unbroken cells by centrifugation (10 min, 10,000 × g, 4 °C), the crude cell lysate was fractionated by ultracentrifugation (1 h, 150,000 × g, 4 °C) to yield cytosols (supernatant) and membranes (pellets). To stain for hydrogenase activity, samples (5 µg protein) from each cell fraction were separated on native 7.5% (wt/vol) polyacrylamide gels (43) and incubated overnight in 50 mM potassium phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) supplemented with 0.5 mM nitroblue tetrazolium chloride in an anaerobic chamber [5% H2, 10% CO2, 85% N2 (vol/vol)] (Coy Laboratory Products).
Gas Chromatography Measurements.
H2 gas was added to stationary-phase cultures of P. methylaliphatogenes (in biological triplicate) to achieve final headspace concentrations of 11 ppmv and 250 ppmv. Culture vessels were agitated (100 rpm) throughout incubation (60 °C) to enhance transfer of H2 into the liquid phase. Headspaces (4 mL) were routinely sampled using a gas-tight syringe (VICI Precision Sampling) and loaded onto a PP1 Gas Analyzer (Peak Performer) equipped with a reducing compound photometer, Unibeads 1S 60/80 column, and Molecular Sieve 13× 60/80 column. Headspace pressure was measured with a syringe-fitted XP2i digital test gauge (Crystal Pressure) before sampling. Samples were calibrated against H2 standards prepared before experimentation. The reproducibility of the measurements was assessed throughout experimentation by comparison against manually prepared H2 gas standards. The KM of H2 oxidation was estimated by dividing the Vmax by the first-order rate constant k as described (44).
Taxonomic analysis
The large subunit protein sequences of the P. methylaliphatogenes hydrogenase were aligned with those of representatives of the Group 5, Group 2, and Group 1 using Clustal. The relationships between the sequenced were visualized on neighbor-joining phylogenetic trees constructed using MEGA6 (45).
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Peter Janssen for valuable comments that helped to establish this project. This work was supported by a CSIRO Office of the Chief Executive Postdoctoral Fellowship (to C.G.), an Otago School of Medical Sciences Summer Scholarship (to R.R.), and a University of Otago Postgraduate Scholarship (to K.H.). M.S. and C.C. acknowledge the support of the GNS Science’s DCF Geothermal Research programme funded by the Government of New Zealand.
Footnotes
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.1508385112/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Lennon JT, Jones SE. Microbial seed banks: The ecological and evolutionary implications of dormancy. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2011;9(2):119–130. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Jones SE, Lennon JT. Dormancy contributes to the maintenance of microbial diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(13):5881–5886. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0912765107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Price PB, Sowers T. Temperature dependence of metabolic rates for microbial growth, maintenance, and survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101(13):4631–4636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400522101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Morita RY. Is H2 the universal energy source for long-term survival? Microb Ecol. 1999;38(4):307–320. doi: 10.1007/s002489901002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alvarez HM, Steinbüchel A. Triacylglycerols in prokaryotic microorganisms. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2002;60(4):367–376. doi: 10.1007/s00253-002-1135-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.González-Pastor JE, Hobbs EC, Losick R. Cannibalism by sporulating bacteria. Science. 2003;301(5632):510–513. doi: 10.1126/science.1086462. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Greening C, et al. Atmospheric hydrogen scavenging: From enzymes to ecosystems. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2015;81(4):1190–1199. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03364-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Quiza L, Lalonde I, Guertin C, Constant P. Land-use influences the distribution and activity of high affinity CO-oxidizing bacteria associated to type I-coxL genotype in soil. Front Microbiol. 2014;5:271. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Greening C, Cook GM. Integration of hydrogenase expression and hydrogen sensing in bacterial cell physiology. Curr Opin Microbiol. 2014;18:30–38. doi: 10.1016/j.mib.2014.02.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bergmann GT, et al. The under-recognized dominance of Verrucomicrobia in soil bacterial communities. Soil Biol Biochem. 2011;43(7):1450–1455. doi: 10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.03.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Janssen PH. Identifying the dominant soil bacterial taxa in libraries of 16S rRNA and 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006;72(3):1719–1728. doi: 10.1128/AEM.72.3.1719-1728.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Quaiser A, et al. Acidobacteria form a coherent but highly diverse group within the bacterial domain: Evidence from environmental genomics. Mol Microbiol. 2003;50(2):563–575. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.2003.03707.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Barns SM, Takala SL, Kuske CR. Wide distribution and diversity of members of the bacterial kingdom Acidobacterium in the environment. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65(4):1731–1737. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.4.1731-1737.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Stott MB, et al. Isolation of novel bacteria, including a candidate division, from geothermal soils in New Zealand. Environ Microbiol. 2008;10(8):2030–2041. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01621.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Sait M, Hugenholtz P, Janssen PH. Cultivation of globally distributed soil bacteria from phylogenetic lineages previously only detected in cultivation-independent surveys. Environ Microbiol. 2002;4(11):654–666. doi: 10.1046/j.1462-2920.2002.00352.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Janssen PH, Yates PS, Grinton BE, Taylor PM, Sait M. Improved culturability of soil bacteria and isolation in pure culture of novel members of the divisions Acidobacteria, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Verrucomicrobia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2002;68(5):2391–2396. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.5.2391-2396.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Rappé MS, Giovannoni SJ. The uncultured microbial majority. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2003;57(1):369–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.micro.57.030502.090759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Crowe MA, et al. Pyrinomonas methylaliphatogenes gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel group 4 thermophilic member of the phylum Acidobacteria from geothermal soils. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2014;64(Pt 1):220–227. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.055079-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Constant P, Chowdhury SP, Pratscher J, Conrad R. Streptomycetes contributing to atmospheric molecular hydrogen soil uptake are widespread and encode a putative high-affinity [NiFe]-hydrogenase. Environ Microbiol. 2010;12(3):821–829. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.02130.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Constant P, Chowdhury SP, Hesse L, Pratscher J, Conrad R. Genome data mining and soil survey for the novel group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenase to explore the diversity and ecological importance of presumptive high-affinity H(2)-oxidizing bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(17):6027–6035. doi: 10.1128/AEM.00673-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Constant P, Poissant L, Villemur R. Isolation of Streptomyces sp. PCB7, the first microorganism demonstrating high-affinity uptake of tropospheric H2. ISME J. 2008;2(10):1066–1076. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2008.59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Berney M, Greening C, Hards K, Collins D, Cook GM. Three different [NiFe] hydrogenases confer metabolic flexibility in the obligate aerobe Mycobacterium smegmatis. Environ Microbiol. 2014;16(1):318–330. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.12320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Greening C, Villas-Bôas SG, Robson JR, Berney M, Cook GM. The growth and survival of Mycobacterium smegmatis is enhanced by co-metabolism of atmospheric H2. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e103034. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0103034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Greening C, Berney M, Hards K, Cook GM, Conrad R. A soil actinobacterium scavenges atmospheric H2 using two membrane-associated, oxygen-dependent [NiFe] hydrogenases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2014;111(11):4257–4261. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1320586111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Vignais PM, Billoud B. Occurrence, classification, and biological function of hydrogenases: An overview. Chem Rev. 2007;107(10):4206–4272. doi: 10.1021/cr050196r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Berney M, Cook GM. Unique flexibility in energy metabolism allows mycobacteria to combat starvation and hypoxia. PLoS One. 2010;5(1):e8614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0008614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Meredith LK, et al. Consumption of atmospheric hydrogen during the life cycle of soil-dwelling actinobacteria. Environ Microbiol Rep. 2014;6(3):226–238. doi: 10.1111/1758-2229.12116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ehhalt DH, Rohrer F. The tropospheric cycle of H2: A critical review. Tellus B Chem Phys Meterol. 2009;61(3):500–535. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Schäfer C, Friedrich B, Lenz O. Novel, oxygen-insensitive group 5 [NiFe]-hydrogenase in Ralstonia eutropha. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2013;79(17):5137–5145. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01576-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ward NL, et al. Three genomes from the phylum Acidobacteria provide insight into the lifestyles of these microorganisms in soils. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2009;75(7):2046–2056. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02294-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Eichorst SA, Kuske CR, Schmidt TM. Influence of plant polymers on the distribution and cultivation of bacteria in the phylum Acidobacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2011;77(2):586–596. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01080-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Koch IH, Gich F, Dunfield PF, Overmann J. Edaphobacter modestus gen. nov., sp. nov., and Edaphobacter aggregans sp. nov., acidobacteria isolated from alpine and forest soils. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2008;58(Pt 5):1114–1122. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.65303-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Männistö MK, Rawat S, Starovoytov V, Häggblom MM. Granulicella arctica sp. nov., Granulicella mallensis sp. nov., Granulicella tundricola sp. nov. and Granulicella sapmiensis sp. nov., novel acidobacteria from tundra soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2012;62(Pt 9):2097–2106. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.031864-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Constant P, Poissant L, Villemur R. Tropospheric H(2) budget and the response of its soil uptake under the changing environment. Sci Total Environ. 2009;407(6):1809–1823. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2008.10.064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Khdhiri M, et al. Soil carbon content and relative abundance of high affinity H2-oxidizing bacteria predict atmospheric H2 soil uptake activity better than soil microbial community composition. Soil Biol Biochem. 2015;85:1–9. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Conrad R. Soil microorganisms as controllers of atmospheric trace gases (H2, CO, CH4, OCS, N2O, and NO) Microbiol Rev. 1996;60(4):609–640. doi: 10.1128/mr.60.4.609-640.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Dunfield PF, Liesack W, Henckel T, Knowles R, Conrad R. High-affinity methane oxidation by a soil enrichment culture containing a type II methanotroph. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65(3):1009–1014. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.3.1009-1014.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bull ID, Parekh NR, Hall GH, Ineson P, Evershed RP. Detection and classification of atmospheric methane oxidizing bacteria in soil. Nature. 2000;405(6783):175–178. doi: 10.1038/35012061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.King GM, Weber CF. Distribution, diversity and ecology of aerobic CO-oxidizing bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5(2):107–118. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Snapper SB, Melton RE, Mustafa S, Kieser T, Jacobs WRJ., Jr Isolation and characterization of efficient plasmid transformation mutants of Mycobacterium smegmatis. Mol Microbiol. 1990;4(11):1911–1919. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02040.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Aung HL, et al. Novel regulatory roles of cAMP receptor proteins in fast-growing environmental mycobacteria. Microbiology. 2015;161(Pt 3):648–661. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.000015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bull TJ, Hermon-Taylor J, Pavlik I, El-Zaatari F, Tizard M. Characterization of IS900 loci in Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis and development of multiplex PCR typing. Microbiology. 2000;146(Pt 9):2185–2197. doi: 10.1099/00221287-146-9-2185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Walker JM. Nondenaturing Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis of Proteins. In: Walker JM, editor. The Protein Protocols Handbook. 2nd Ed. Springer; Berlin: 2002. pp. 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- 44.Conrad R, Goodwin S, Zeikus JG. Hydrogen metabolism in a mildly acidic lake sediment (Knaack Lake) FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1987;45(4):243–249. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(12):2725–2729. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]