Fig. 7.
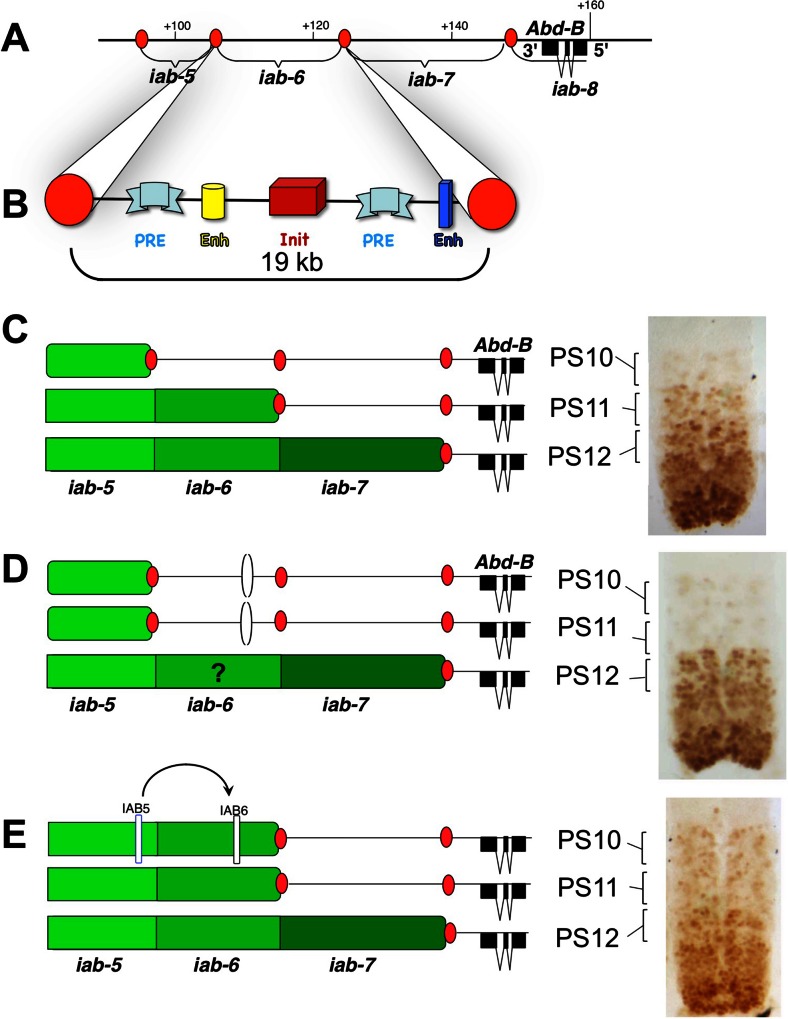
Initiators function as domain control regions. Figure reproduced from the review article of Maeda and Karch (2011); DOI: 10.1016/j.gde.2011.01.021, with the permission of Elsevier. This article was reviewing work published by our laboratory in 2010 (Iampietro et al. 2010). The Abd-B genes and associated regulatory regions iab-5, iab-6, iab-7, and iab-8 regulatory regions is drawn in panel a with a central nervous system (CNS) dissected out of an embryo stained with antibodies against Abd-B (see also legend of Fig. 4 for the parasegmental expression of Abd-B in the CNS.) In panel b, a magnification of the 19-kb-long iab-6 domain is drawn in the form of a cartoon. Ovals indicate boundaries. PREs, cell type-specific enhancer (Enh) and initiator elements (Init) are drawn. Panel c shows the sequential opening of the iab-5, iab-6, and iab-7 regulatory domains in PS10, PS11, and PS12, respectively. Panel d shows the consequence of deleting the iab-6 initator alone (a 927-bp-long deletion). Despite the fact that 18.1 kb of iab-6 remains intact, the whole domain seems inactive as revealed by the Abd-B expression pattern in PS11 which is a reiteration of the expression observed in PS10. In agreement with this embryonic phenotype, the adult flies emerge with a complete transformation of A6 into A5. The initiator swapping experiment is shown in panel e. In this strain, the iab-6 initiator was removed and replaced by the initiator of iab-5. Note the PS10 Abd-B expression pattern that is similar to the pattern normally present in PS11, indicating that the iab-6 domain is opened in PS10. In agreement with this effect in embryos, adult flies emerge with a transformation of A5 into A6. In these initiator swapping flies, the parasegmental address is provided by the iab-5 initiator and the segmental identity is provided by the cell-type-specific enhancers of iab-6