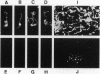
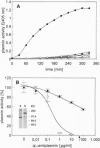
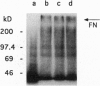
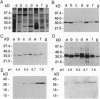
Abstract
The spirochete Borrelia burgdorferi is the causative agent of Lyme borreliosis (Lyme disease) and is transmitted to mammalian hosts by tick vectors. In humans, the bacteria induce a complex disease, which involves the skin, joints, heart, and nervous system. However, the pathogenic principles of this multisystem illness are far from being understood. To disseminate from the site of the tick bite and invade multiple organ sites, spirochetes have to penetrate normal tissue barriers, such as vascular basement membranes and other organized extracellular matrices. Substantial evidence from other invasive bacterial infections suggest that spirochetes may use endogenous or host-derived enzymes--in particular, proteinases--for this purpose. Here we show that B. burgdorferi binds human plasmin(ogen)--mainly via its outer cell surface lipoprotein A. Binding of plasminogen to spirochetal receptor leads to an accelerated formation of active plasmin in the presence of host-derived plasminogen activator. The cell-surface-associated plasmin cannot be regulated by the serum inhibitor alpha 2-antiplasmin and degrades high-molecular-weight glycoproteins, such as fibronectin. It is suggested that the acquisition of host-derived proteinase plasmin(ogen) contributes to the pathogenicity of B. burgdorferi.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ansorge W. Fast and sensitive detection of protein and DNA bands by treatment with potassium permanganate. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1985 May;11(1):13–20. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(85)90037-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comstock L. E., Thomas D. D. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi invasion of cultured endothelial cells. Microb Pathog. 1991 Feb;10(2):137–148. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(91)90074-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duray P. H., Steere A. C. Clinical pathologic correlations of Lyme disease by stage. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;539:65–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb31839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz H., Wunderer G. Biochemistry and applications of aprotinin, the kallikrein inhibitor from bovine organs. Arzneimittelforschung. 1983;33(4):479–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gassmann G. S., Kramer M., Göbel U. B., Wallich R. Nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding the Borrelia burgdorferi flagellin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3590–3590. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Justus C., Müller S., Kramer M. D. A monoclonal antibody recognizing plasminogen and plasmin--altered reactivity in psoriatic lesions. Br J Dermatol. 1987 Dec;117(6):687–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1987.tb07347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kramer M. D., Schaible U. E., Wallich R., Moter S. E., Petzoldt D., Simon M. M. Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi associated antigens by monoclonal antibodies. Immunobiology. 1990 Nov;181(4-5):357–366. doi: 10.1016/S0171-2985(11)80504-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause A., Burmester G. R., Rensing A., Schoerner C., Schaible U. E., Simon M. M., Herzer P., Kramer M. D., Wallich R. Cellular immune reactivity to recombinant OspA and flagellin from Borrelia burgdorferi in patients with Lyme borreliosis. Complexity of humoral and cellular immune responses. J Clin Invest. 1992 Sep;90(3):1077–1084. doi: 10.1172/JCI115923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuusela P., Ullberg M., Saksela O., Kronvall G. Tissue-type plasminogen activator-mediated activation of plasminogen on the surface of group A, C, and G streptococci. Infect Immun. 1992 Jan;60(1):196–201. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.1.196-201.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Goldfarb R. H., Brundage R., Siegal G. P., Terranova V., Garbisa S. Effect of plasminogen activator (urokinase), plasmin, and thrombin on glycoprotein and collagenous components of basement membrane. Cancer Res. 1981 Nov;41(11 Pt 1):4629–4636. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., DesJardin L. E., Wang H., Boyle M. D. Streptokinase-producing streptococci grown in human plasma acquire unregulated cell-associated plasmin activity. J Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;166(2):436–440. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lottenberg R., Minning-Wenz D., Boyle M. D. Capturing host plasmin(ogen): a common mechanism for invasive pathogens? Trends Microbiol. 1994 Jan;2(1):20–24. doi: 10.1016/0966-842x(94)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo O., Okada K., Fukao H., Tomioka Y., Ueshima S., Watanuki M., Sakai M. Thrombolytic properties of staphylokinase. Blood. 1990 Sep 1;76(5):925–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayer M. Biochemical and biological aspects of the plasminogen activation system. Clin Biochem. 1990 Jun;23(3):197–211. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(90)90601-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyashita C., Wenzel E., Heiden M. Plasminogen: a brief introduction into its biochemistry and function. Haemostasis. 1988;18 (Suppl 1):7–13. doi: 10.1159/000215824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkkinen J., Korhonen T. K. Binding of plasminogen to Escherichia coli adhesion proteins. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 3;250(2):437–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80772-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plow E. F., Freaney D. E., Plescia J., Miles L. A. The plasminogen system and cell surfaces: evidence for plasminogen and urokinase receptors on the same cell type. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2411–2420. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O. Plasminogen activation and regulation of pericellular proteolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Nov 12;823(1):35–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(85)90014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D., Museteanu C., Zimmer G., Mossmann H., Simon M. M. The severe combined immunodeficiency (scid) mouse. A laboratory model for the analysis of Lyme arthritis and carditis. J Exp Med. 1989 Oct 1;170(4):1427–1432. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.4.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodeinde O. A., Subrahmanyam Y. V., Stark K., Quan T., Bao Y., Goguen J. D. A surface protease and the invasive character of plague. Science. 1992 Nov 6;258(5084):1004–1007. doi: 10.1126/science.1439793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczepanski A., Furie M. B., Benach J. L., Lane B. P., Fleit H. B. Interaction between Borrelia burgdorferi and endothelium in vitro. J Clin Invest. 1990 May;85(5):1637–1647. doi: 10.1172/JCI114615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis J., Salvesen G. S. Human plasma proteinase inhibitors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:655–709. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.003255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullberg M., Kronvall G., Wiman B. New receptor for human plasminogen on gram positive cocci. APMIS. 1989 Nov;97(11):996–1002. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1989.tb00508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Sappino A. P., Belin D. The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest. 1991 Oct;88(4):1067–1072. doi: 10.1172/JCI115405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Helmes C., Schaible U. E., Lobet Y., Moter S. E., Kramer M. D., Simon M. M. Evaluation of genetic divergence among Borrelia burgdorferi isolates by use of OspA, fla, HSP60, and HSP70 gene probes. Infect Immun. 1992 Nov;60(11):4856–4866. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.11.4856-4866.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Schaible U. E., Simon M. M., Heiberger A., Kramer M. D. Cloning and sequencing of the gene encoding the outer surface protein A (OspA) of a European Borrelia burgdorferi isolate. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8864–8864. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Simon M. M., Hofmann H., Moter S. E., Schaible U. E., Kramer M. D. Molecular and immunological characterization of a novel polymorphic lipoprotein of Borrelia burgdorferi. Infect Immun. 1993 Oct;61(10):4158–4166. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.10.4158-4166.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]