Abstract
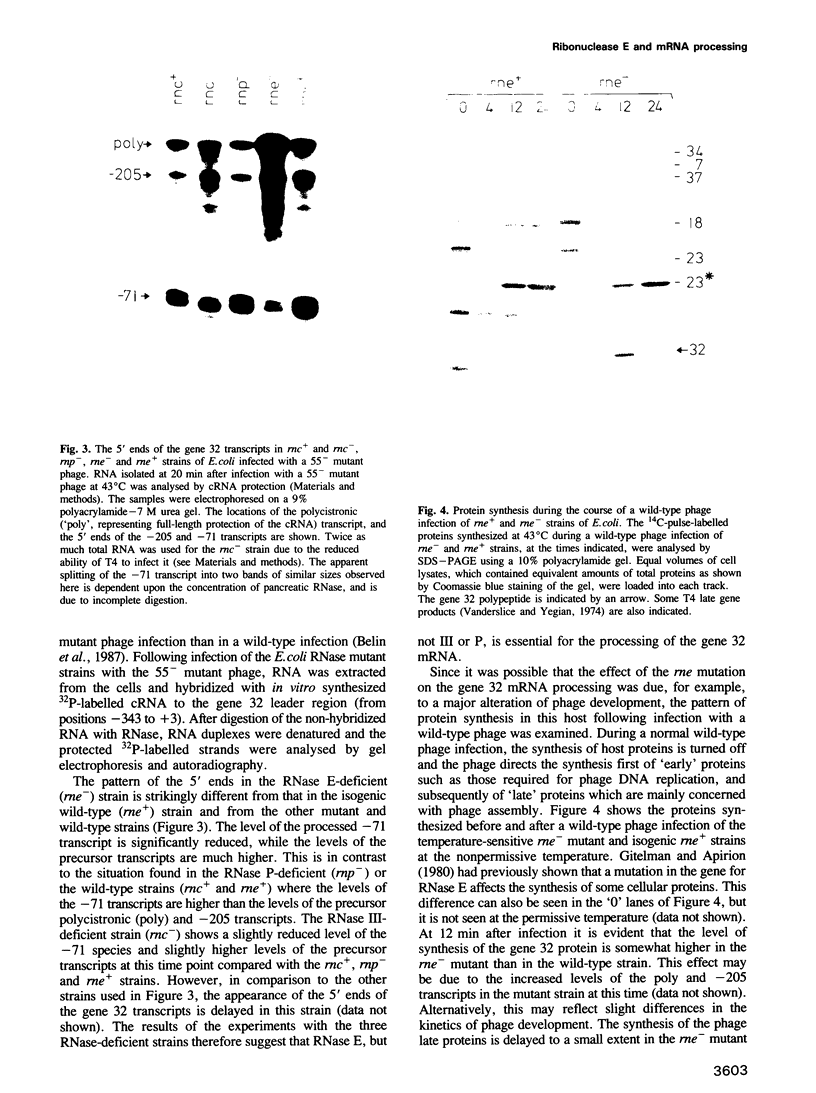
Gene 32 from bacteriophage T4 is transcribed as precursor transcripts which are processed to a stable product. This processing of the gene 32 mRNA was observed in RNase III or P-deficient strains of Escherichia coli. However, after infection of an RNase E-deficient strain, the amount of processed transcript was significantly reduced while the levels of the precursor transcripts remained high. RNase E therefore appears to have an essential role in the processing of the gene 32 mRNA. We have mapped the exact 5' end of the processed transcript by primer extension. The cleavage occurs near a stem-loop structure at a site which shows some similarity to other known RNase E cleavage sites. The effects of the processing on the differential stability of the upstream and downstream sequences, and on gene expression, are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adhya S., Gottesman M., De Crombrugghe B. Release of polarity in Escherichia coli by gene N of phage lambda: termination and antitermination of transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2534–2538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alberts B. M., Frey L. T4 bacteriophage gene 32: a structural protein in the replication and recombination of DNA. Nature. 1970 Sep 26;227(5265):1313–1318. doi: 10.1038/2271313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D. Isolation, genetic mapping and some characterization of a mutation in Escherichia coli that affects the processing of ribonuleic acid. Genetics. 1978 Dec;90(4):659–671. doi: 10.1093/genetics/90.4.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D., Lassar A. B. A conditional lethal mutant of Escherichia coli which affects the processing of ribosomal RNA. J Biol Chem. 1978 Mar 10;253(5):1738–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Apirion D., Watson N. Mapping and characterization of a mutation in Escherichia coli that reduces the level of ribonuclease III specific for double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):317–324. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.317-324.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry G., Squires C., Squires C. L. Attenuation and processing of RNA from the rplJL--rpoBC transcription unit of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3331–3335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belin D., Mudd E. A., Prentki P., Yi-Yi Y., Krisch H. M. Sense and antisense transcription of bacteriophage T4 gene 32. Processing and stability of the mRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1987 Mar 20;194(2):231–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolle A., Epstein R. H., Salser W., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription during bacteriophage T4 development: requirements for late messenger synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):339–362. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90193-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Båga M., Göransson M., Normark S., Uhlin B. E. Processed mRNA with differential stability in the regulation of E. coli pilin gene expression. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90508-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAMPE S. P., BENZER S. Reversal of mutant phenotypes by 5-fluorouracil: an approach to nucleotide sequences in messenger-RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1962 Apr 15;48:532–546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.48.4.532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannistraro V. J., Subbarao M. N., Kennell D. Specific endonucleolytic cleavage sites for decay of Escherichia coli mRNA. J Mol Biol. 1986 Nov 20;192(2):257–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90363-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Chou J., Cohen S. N. In vitro gene fusions that join an enzymatically active beta-galactosidase segment to amino-terminal fragments of exogenous proteins: Escherichia coli plasmid vectors for the detection and cloning of translational initiation signals. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):971–980. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.971-980.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Effect of RNAase III, cleavage on translation of bacteriophage T7 messenger RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 15;99(3):487–499. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duvoisin R. M., Belin D., Krisch H. M. A plasmid expression vector that permits stabilization of both mRNAs and proteins encoded by the cloned genes. Gene. 1986;45(2):193–201. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegenheimer P., Apirion D. Processing of procaryotic ribonucleic acid. Microbiol Rev. 1981 Dec;45(4):502–541. doi: 10.1128/mr.45.4.502-541.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghora B. K., Apirion D. Identification of a novel RNA molecule in a new RNA processing mutant of Escherichia coli which contains 5 S rRNA sequences. J Biol Chem. 1979 Mar 25;254(6):1951–1956. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghora B. K., Apirion D. Structural analysis and in vitro processing to p5 rRNA of a 9S RNA molecule isolated from an rne mutant of E. coli. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1055–1066. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90289-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitelman D. R., Apirion D. The synthesis of some proteins is affected in RNA processing mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Oct 16;96(3):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90060-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldblum K., Apririon D. Inactivation of the ribonucleic acid-processing enzyme ribonuclease E blocks cell division. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):128–132. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.128-132.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Roch J. M., Prentki P., Krisch H. M. The stability of bacteriophage T4 gene 32 mRNA: a 5' leader sequence that can stabilize mRNA transcripts. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):461–469. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90176-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guild N., Gayle M., Sweeney R., Hollingsworth T., Modeer T., Gold L. Transcriptional activation of bacteriophage T4 middle promoters by the motA protein. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 20;199(2):241–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90311-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurevitz M., Jain S. K., Apirion D. Identification of a precursor molecular for the RNA moiety of the processing enzyme RNase P. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4450–4454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen F. S., Young E. T. Effect of RNase III on efficiency of translation of bacteriophage T7 lysozyme mRNA. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):793–804. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.793-804.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. K., Gurevitz M., Apirion D. A small RNA that complements mutants in the RNA processing enzyme ribonuclease P. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):515–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90386-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisch H. M., Allet B. Nucleotide sequences involved in bacteriophage T4 gene 32 translational self-regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4937–4941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krisch H. M., Van Houwe G., Belin D., Gibbs W., Epstein R. H. Regulation of the expression of bacteriophage T4 genes 32 and 43. Virology. 1977 May 1;78(1):87–98. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90080-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaire G., Gold L., Yarus M. Autogenous translational repression of bacteriophage T4 gene 32 expression in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1978 Nov 25;126(1):73–90. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90280-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattson T., Van Houwe G., Epstein R. H. Isolation and characterization of conditional lethal mutations in the mot gene of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 15;126(3):551–570. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melefors O., von Gabain A. Site-specific endonucleolytic cleavages and the regulation of stability of E. coli ompA mRNA. Cell. 1988 Mar 25;52(6):893–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90431-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misra T. K., Apirion D. RNase E, an RNA processing enzyme from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 Nov 10;254(21):11154–11159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaev N., Silengo L., Schlessinger D. Synthesis of a large precursor to ribosomal RNA in a mutant of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3361–3365. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portier C., Dondon L., Grunberg-Manago M., Régnier P. The first step in the functional inactivation of the Escherichia coli polynucleotide phosphorylase messenger is a ribonuclease III processing at the 5' end. EMBO J. 1987 Jul;6(7):2165–2170. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02484.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragai B., Apirion D. Processing of bacteriophage T4 transfer RNAs. Structural analysis and in vitro processing of precursors that accumulate in RNase E-strains. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jan 25;154(3):465–484. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(82)80007-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Singh B., Roy M. K., Apirion D. Ribonuclease E is involved in the processing of 5-S rRNA from a number of rRNA transcription units. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jul;125(2):283–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06680.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy M. K., Singh B., Ray B. K., Apirion D. Maturation of 5-S rRNA: ribonuclease E cleavages and their dependence on precursor sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Régnier P., Portier C. Initiation, attenuation and RNase III processing of transcripts from the Escherichia coli operon encoding ribosomal protein S15 and polynucleotide phosphorylase. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jan 5;187(1):23–32. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90403-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Richardson C. C. Processing of mRNA by ribonuclease III regulates expression of gene 1.2 of bacteriophage T7. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90395-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl P., Primakoff P. Mutants of Escherichia coli thermosensitive for the synthesis of transfer RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2091–2095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmeissner U., McKenney K., Rosenberg M., Court D. Removal of a terminator structure by RNA processing regulates int gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 15;176(1):39–53. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90381-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. R., Hedgpeth J. Oligo(A) not coded by DNA generating 3'-terminal heterogeneity in a lambda phage RNA. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4818–4821. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W. Genetic mapping of a mutation that causes ribonucleases III deficiency in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):307–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.307-316.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm J., Polisky B. Structural analysis of RNA molecules involved in plasmid copy number control. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6381–6397. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomcsányi T., Apirion D. Processing enzyme ribonuclease E specifically cleaves RNA I. An inhibitor of primer formation in plasmid DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1985 Oct 20;185(4):713–720. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90056-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderslice R. W., Yegian C. D. The identification of late bacteriophage T4 proteins on sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gels. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90384-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Hippel P. H., Kowalczykowski S. C., Lonberg N., Newport J. W., Paul L. S., Stormo G. D., Gold L. Autoregulation of gene expression. Quantitative evaluation of the expression and function of the bacteriophage T4 gene 32 (single-stranded DNA binding) protein system. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 25;162(4):795–818. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90548-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







