Abstract
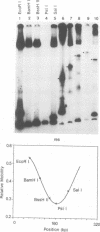
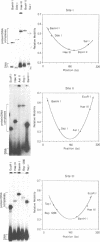
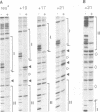
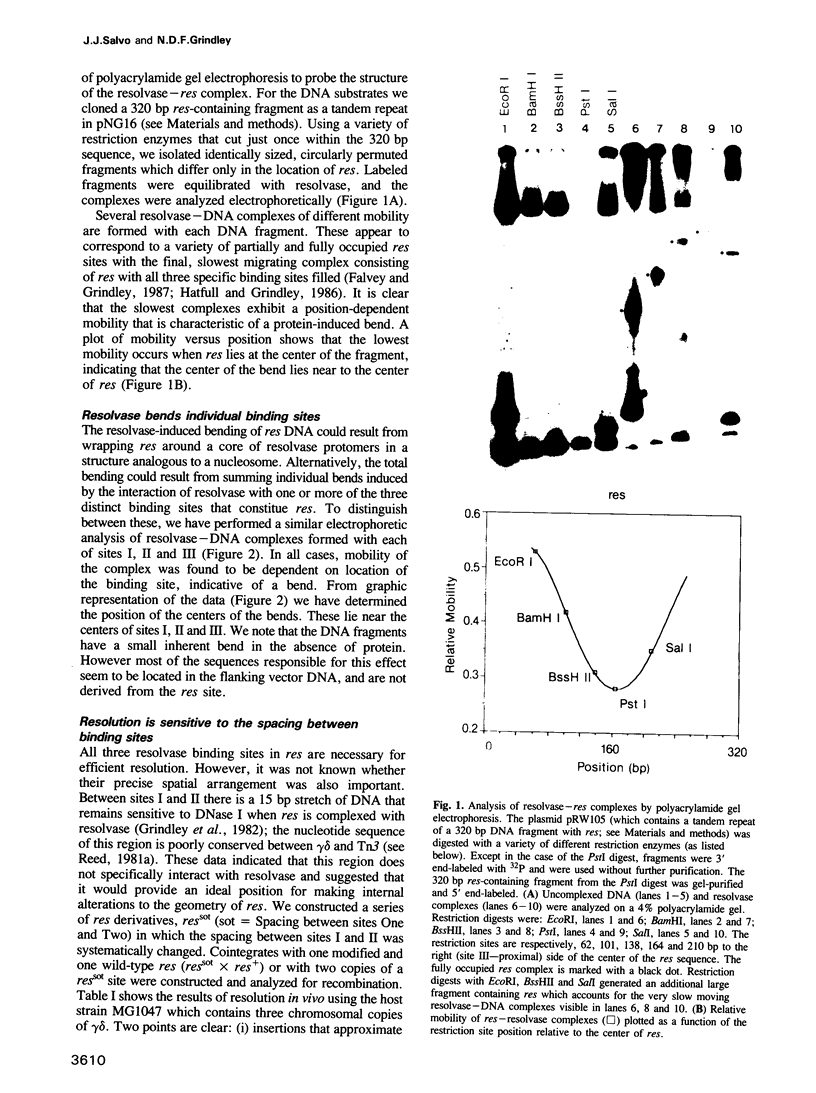
We have characterized complexes between the gamma delta resolvase and its recombination site, res, using both a gel retardation assay and DNase I cleavage. The mobility of resolvase-res complexes in polyacrylamide gels is sensitive to the location of res within the DNA fragment and is at a minimum when res is at its center. This behavior is characteristic of a protein-dependent bend. By the same assay we have found that bends are induced upon the binding of resolvase to each of the three individual binding sites that constitute res. In the wild-type res, the centers of binding sites I and II are 53 bp apart and the central section of the intersite DNA is sensitive to DNase I cleavage. We find that insertions of 10 or 21 bp (one or two turns of the DNA helix) have no discernible effect on the ability of res to recombine or to form complexes with resolvase. However, insertions of short segment (e.g. 6 or 17 bp) equivalent to nonintegral numbers of helical turns, inhibit recombination and prevent the formation of the normally compact resolvase-res complex. Complexes of resolvase with res containing 10 or 21 bp insertions exhibit a pattern of enhanced and suppressed DNase I cleavages that suggest that the intersite segment is curved. This curvature requires both that site I and II are appropriately spaced, and that site III is also present and occupied.
Full text
PDF
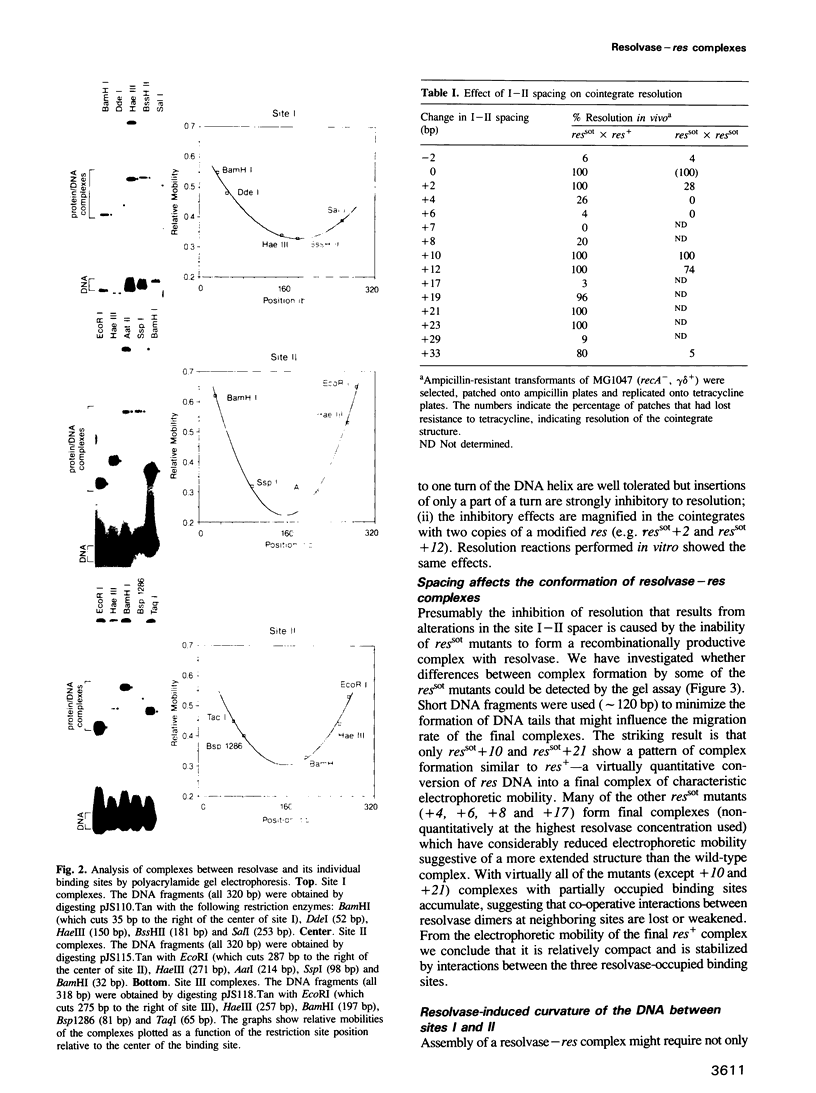
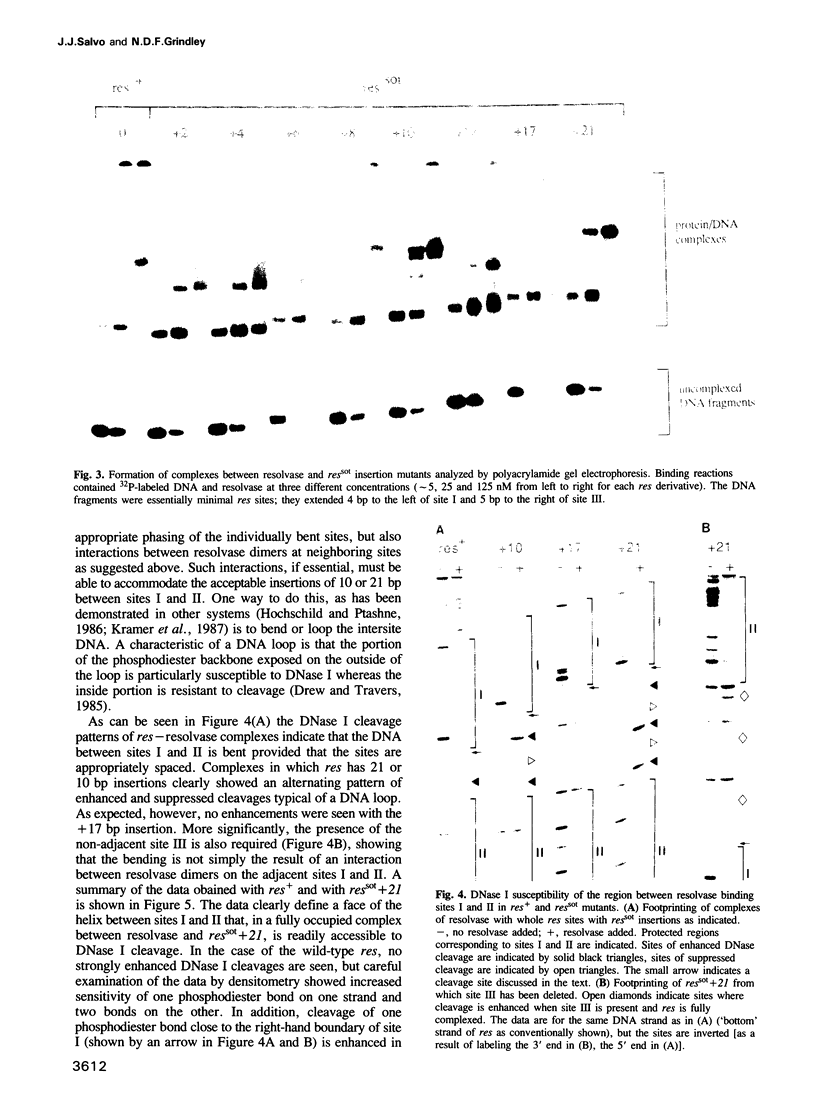
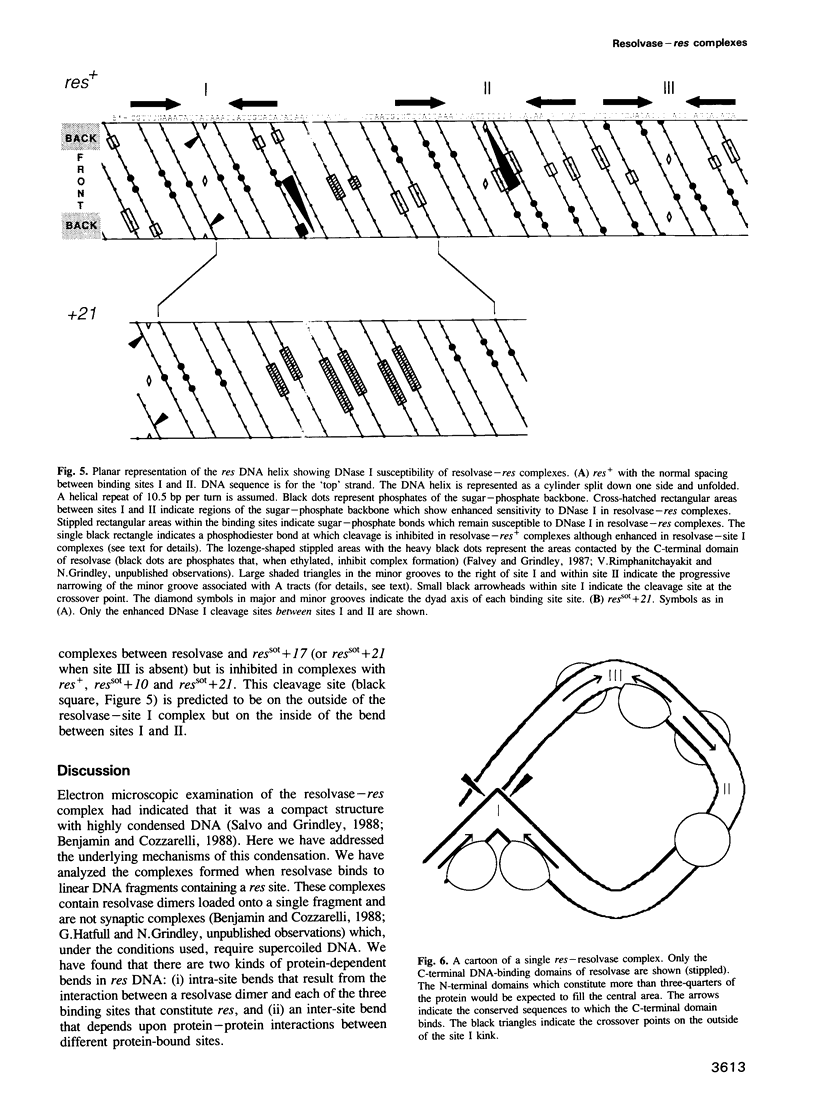

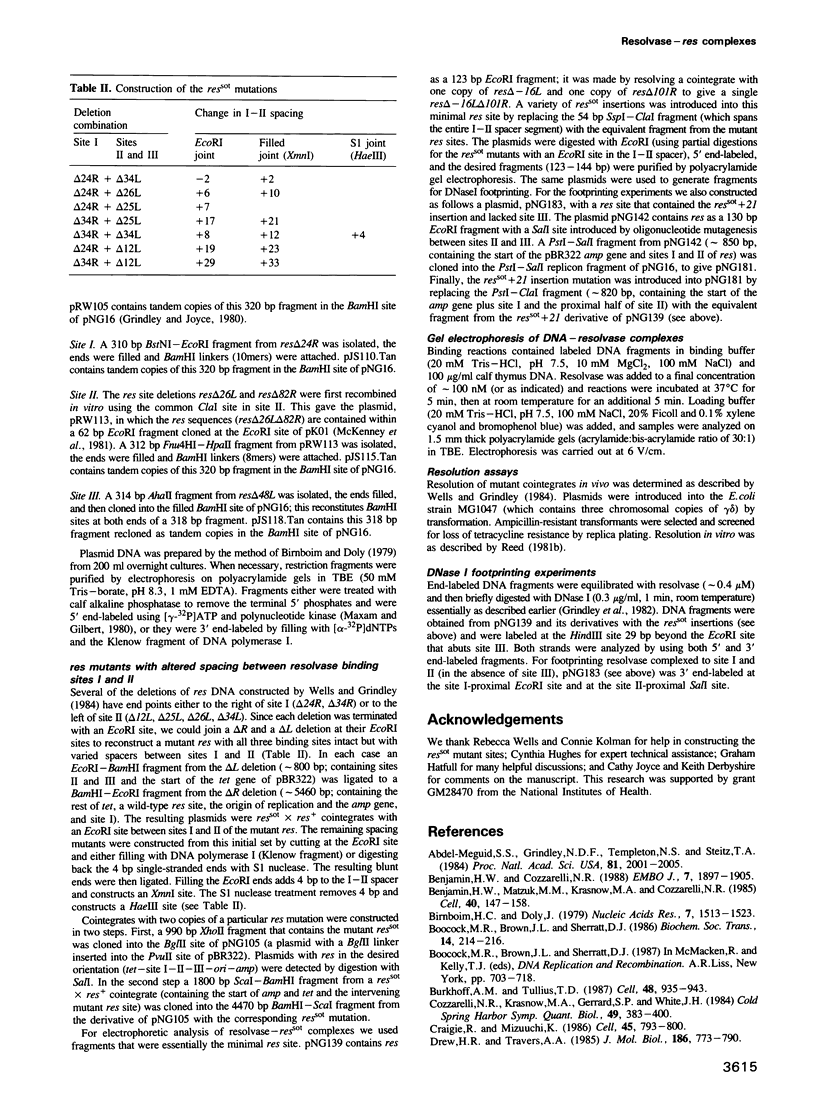

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdel-Meguid S. S., Grindley N. D., Templeton N. S., Steitz T. A. Cleavage of the site-specific recombination protein gamma delta resolvase: the smaller of two fragments binds DNA specifically. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2001–2005. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Cozzarelli N. R. Isolation and characterization of the Tn3 resolvase synaptic intermediate. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1897–1905. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03023.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin H. W., Matzuk M. M., Krasnow M. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Recombination site selection by Tn3 resolvase: topological tests of a tracking mechanism. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):147–158. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90318-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boocock M. R., Brown J. L., Sherratt D. J. Structural and catalytic properties of specific complexes between Tn3 resolvase and the recombination site res. Biochem Soc Trans. 1986 Apr;14(2):214–216. doi: 10.1042/bst0140214a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhoff A. M., Tullius T. D. The unusual conformation adopted by the adenine tracts in kinetoplast DNA. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):935–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90702-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozzarelli N. R., Krasnow M. A., Gerrard S. P., White J. H. A topological treatment of recombination and topoisomerases. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1984;49:383–400. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1984.049.01.045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craigie R., Mizuuchi K. Role of DNA topology in Mu transposition: mechanism of sensing the relative orientation of two DNA segments. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):793–800. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90554-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drew H. R., Travers A. A. DNA bending and its relation to nucleosome positioning. J Mol Biol. 1985 Dec 20;186(4):773–790. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90396-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunn T. M., Hahn S., Ogden S., Schleif R. F. An operator at -280 base pairs that is required for repression of araBAD operon promoter: addition of DNA helical turns between the operator and promoter cyclically hinders repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5017–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falvey E., Grindley N. D. Contacts between gamma delta resolvase and the gamma delta res site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):815–821. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Joyce C. M. Genetic and DNA sequence analysis of the kanamycin resistance transposon Tn903. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7176–7180. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Lauth M. R., Wells R. G., Wityk R. J., Salvo J. J., Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: identification of three binding sites for resolvase at the res sites of gamma delta and Tn3. Cell. 1982 Aug;30(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grindley N. D., Reed R. R. Transpositional recombination in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:863–896. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman P. J. Sequence dependence of the curvature of DNA: a test of the phasing hypothesis. Biochemistry. 1985 Dec 3;24(25):7033–7037. doi: 10.1021/bi00346a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Grindley N. D. Analysis of gamma delta resolvase mutants in vitro: evidence for an interaction between serine-10 of resolvase and site I of res. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5429–5433. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatfull G. F., Noble S. M., Grindley N. D. The gamma delta resolvase induces an unusual DNA structure at the recombinational crossover point. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90760-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochschild A., Ptashne M. Cooperative binding of lambda repressors to sites separated by integral turns of the DNA helix. Cell. 1986 Mar 14;44(5):681–687. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90833-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo H. S., Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. DNA bending at adenine . thymine tracts. Nature. 1986 Apr 10;320(6062):501–506. doi: 10.1038/320501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasnow M. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Site-specific relaxation and recombination by the Tn3 resolvase: recognition of the DNA path between oriented res sites. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1313–1324. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krämer H., Niemöller M., Amouyal M., Revet B., von Wilcken-Bergmann B., Müller-Hill B. lac repressor forms loops with linear DNA carrying two suitably spaced lac operators. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1481–1491. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02390.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKenney K., Shimatake H., Court D., Schmeissner U., Brady C., Rosenberg M. A system to study promoter and terminator signals recognized by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:383–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R., Grindley N. D. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination in vitro: DNA cleavage and protein-DNA linkage at the recombination site. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):721–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90179-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Resolution of cointegrates between transposons gamma delta and Tn3 defines the recombination site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3428–3432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed R. R. Transposon-mediated site-specific recombination: a defined in vitro system. Cell. 1981 Sep;25(3):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90178-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salvo J. J., Grindley N. D. Helical phasing between DNA bends and the determination of bend direction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9771–9779. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. A., Cozzarelli N. R. Determination of the stereostructure of the product of Tn3 resolvase by a general method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1079–1083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasserman S. A., Dungan J. M., Cozzarelli N. R. Discovery of a predicted DNA knot substantiates a model for site-specific recombination. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):171–174. doi: 10.1126/science.2990045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells R. G., Grindley N. D. Analysis of the gamma delta res site. Sites required for site-specific recombination and gene expression. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 15;179(4):667–687. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. M., Crothers D. M. The locus of sequence-directed and protein-induced DNA bending. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):509–513. doi: 10.1038/308509a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkel S. S., Crothers D. M. DNA bend direction by phase sensitive detection. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):178–181. doi: 10.1038/328178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]