Abstract
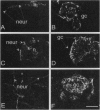
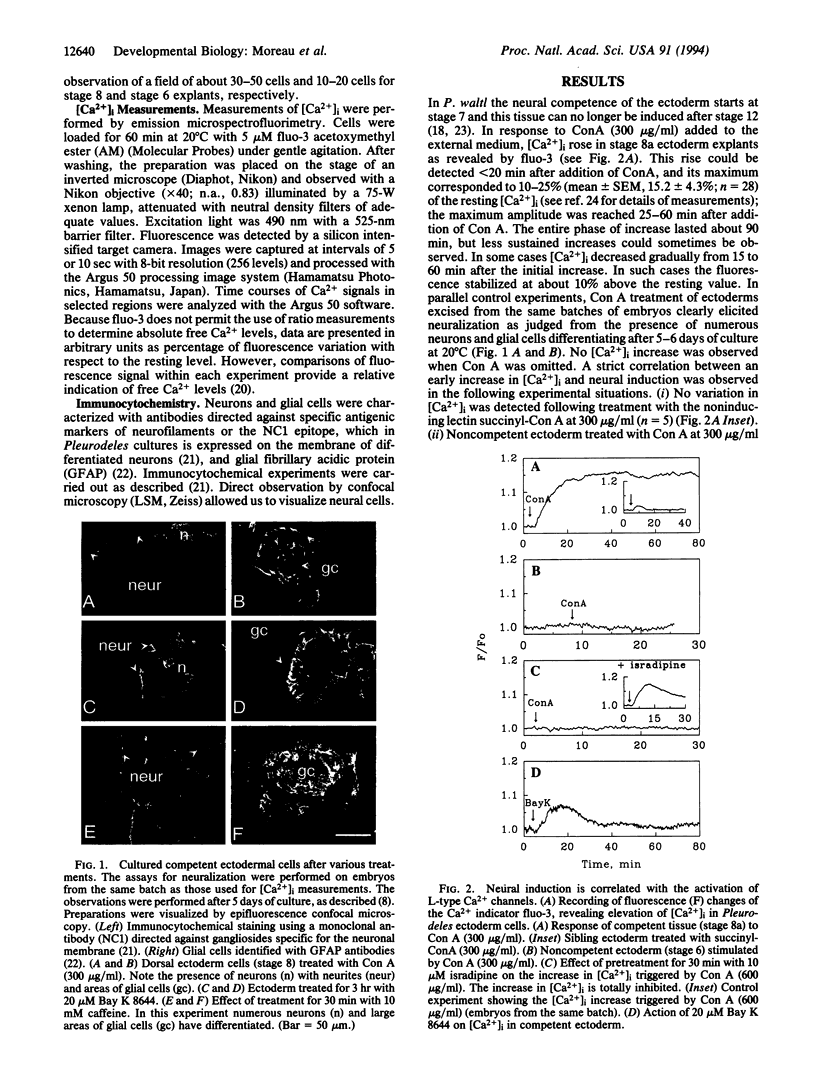
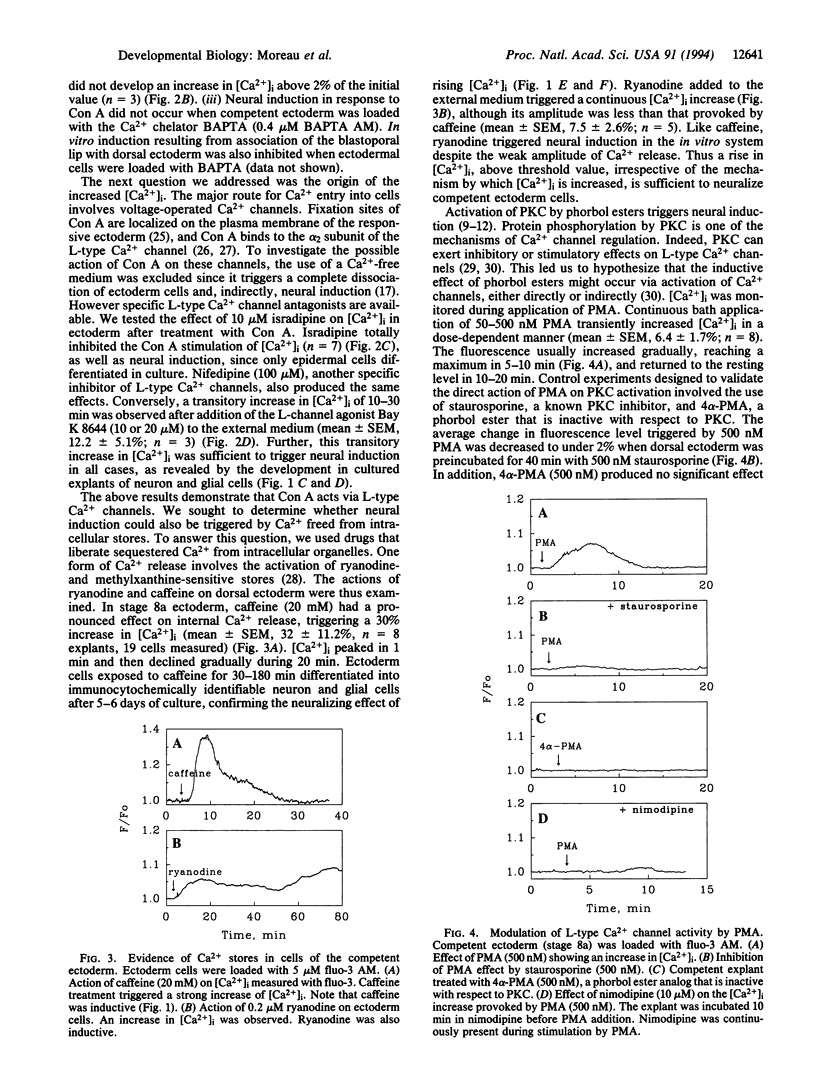
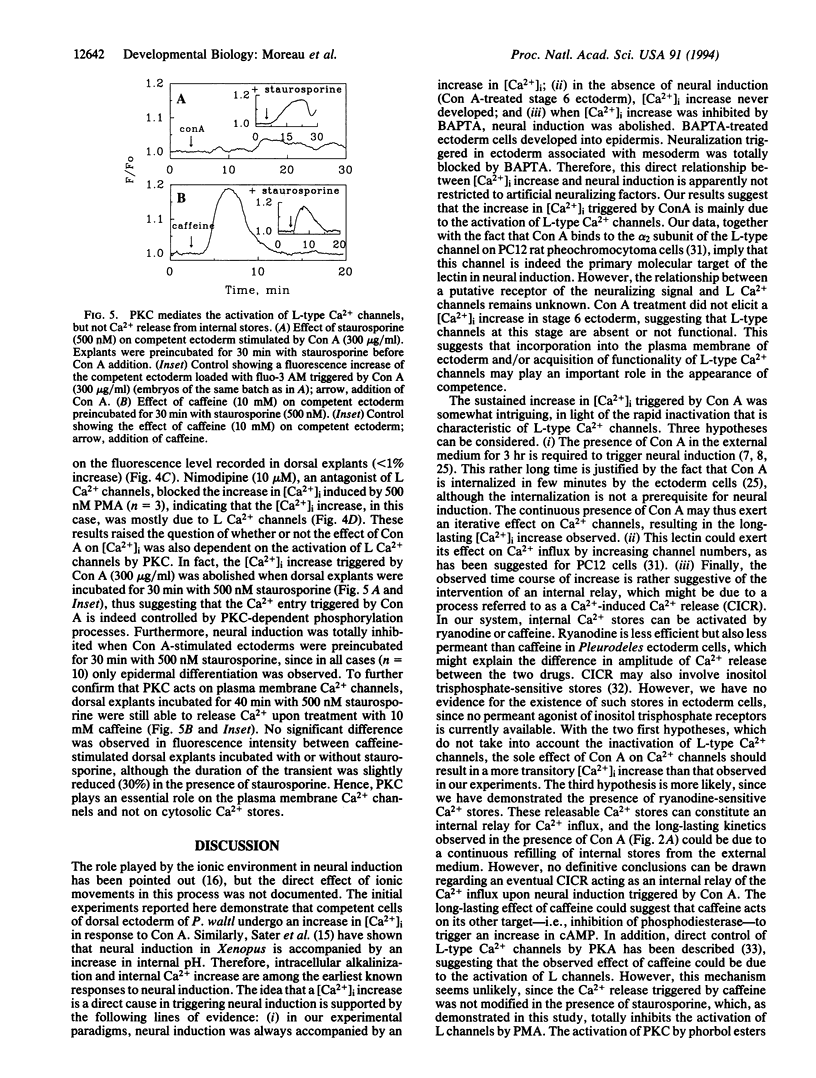
The molecular mechanism of neural induction is still unknown and the identity of the natural inducer remains elusive. It has been suggested that both the protein kinase C and cAMP signal transduction pathways may be involved in mediating its action. Here we provide evidence that Ca2+ is implicated in the process of transduction of the neuralizing signal. We find that an increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration [Ca2+]i occurs during neural induction provoked in vitro by the lectin Con A in Pleurodeles waltl embryo. We demonstrate that specific L-type Ca2+ channel agonists also trigger neural induction. Conversely, noninducing lectins do not raise [Ca2+]i. Ryanodine and caffeine trigger neural induction. An increase in [Ca2+]i was also observed after treatment with the phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate, which has been reported to be inductive. The [Ca2+]i increase triggered by phorbol ester and Con A was abolished by staurosporine and by L-type Ca2+ channel antagonists. Our findings demonstrate that the [Ca2+]i increase occurs via L-type Ca2+ channels. We suggest an amplification of this increase by a Ca(2+)-induced Ca2+ release mechanism which involves intracellular ryanodine-sensitive stores. We propose that Ca(2+)-dependent processes controlled by protein kinase C are implicated in the regulation of gene expression in response to neural induction.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlijanian M. K., Striessnig J., Catterall W. A. Phosphorylation of an alpha 1-like subunit of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive brain calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase and protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20192–20197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong D., Eckert R. Voltage-activated calcium channels that must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and calcium signalling. Nature. 1993 Jan 28;361(6410):315–325. doi: 10.1038/361315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borsotto M., Barhanin J., Norman R. I., Lazdunski M. Purification of the dihydropyridine receptor of the voltage-dependent Ca2+ channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules using (+) [3H]PN 200-110. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 16;122(3):1357–1366. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91241-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett J. W., Steele R. E. Alternative splicing of a neural-specific Src mRNA (Src+) is a rapid and protein synthesis-independent response to neural induction in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1993 Aug;158(2):487–495. doi: 10.1006/dbio.1993.1206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett J. W., Steele R. E. Identification and developmental expression of Src+ mRNAs in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1992 Jul;152(1):194–198. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(92)90170-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornell-Bell A. H., Finkbeiner S. M., Cooper M. S., Smith S. J. Glutamate induces calcium waves in cultured astrocytes: long-range glial signaling. Science. 1990 Jan 26;247(4941):470–473. doi: 10.1126/science.1967852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtis B. M., Catterall W. A. Purification of the calcium antagonist receptor of the voltage-sensitive calcium channel from skeletal muscle transverse tubules. Biochemistry. 1984 May 8;23(10):2113–2118. doi: 10.1021/bi00305a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duprat A. M., Saint-Jeannet J. P., Pituello F., Huang S., Boudannaoui S., Kan P., Gualandris L. From presumptive ectoderm to neural cells in an amphibian. Int J Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;34(1):149–156. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg D. A., Carpenter C. L., Messing R. O. Lectin-induced enhancement of voltage-dependent calcium flux and calcium channel antagonist binding. J Neurochem. 1987 Mar;48(3):888–894. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb05600.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunz H. Information transfer during embryonic induction in amphibians. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Nov;89 (Suppl):349–363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualandris L., Rouge P., Duprat A. M. Target cell surface glycoconjugates and neural induction in an amphibian. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1985 Apr;86:39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Kelly O. G., Melton D. A. Follistatin, an antagonist of activin, is expressed in the Spemann organizer and displays direct neuralizing activity. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati-Brivanlou A., Melton D. A. Inhibition of activin receptor signaling promotes neuralization in Xenopus. Cell. 1994 Apr 22;77(2):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90319-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. P., Harootunian A. T., Tsien R. Y. Photochemically generated cytosolic calcium pulses and their detection by fluo-3. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8179–8184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb T. M., Knecht A. K., Smith W. C., Stachel S. E., Economides A. N., Stahl N., Yancopolous G. D., Harland R. M. Neural induction by the secreted polypeptide noggin. Science. 1993 Oct 29;262(5134):713–718. doi: 10.1126/science.8235591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McPherson P. S., Campbell K. P. The ryanodine receptor/Ca2+ release channel. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jul 5;268(19):13765–13768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otte A. P., Koster C. H., Snoek G. T., Durston A. J. Protein kinase C mediates neural induction in Xenopus laevis. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):618–620. doi: 10.1038/334618a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otte A. P., Moon R. T. Protein kinase C isozymes have distinct roles in neural induction and competence in Xenopus. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90074-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Otte A. P., van Run P., Heideveld M., van Driel R., Durston A. J. Neural induction is mediated by cross-talk between the protein kinase C and cyclic AMP pathways. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):641–648. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90099-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saint-Jeannet J. P., Huang S., Duprat A. M. Modulation of neural commitment by changes in target cell contacts in Pleurodeles waltl. Dev Biol. 1990 Sep;141(1):93–103. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90104-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sater A. K., Alderton J. M., Steinhardt R. A. An increase in intracellular pH during neural induction in Xenopus. Development. 1994 Feb;120(2):433–442. doi: 10.1242/dev.120.2.433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxén L. Neural induction. Int J Dev Biol. 1989 Mar;33(1):21–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearman M. S., Sekiguchi K., Nishizuka Y. Modulation of ion channel activity: a key function of the protein kinase C enzyme family. Pharmacol Rev. 1989 Jun;41(2):211–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., Greenberg M. E. The regulation and function of c-fos and other immediate early genes in the nervous system. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):477–485. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90106-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheng M., McFadden G., Greenberg M. E. Membrane depolarization and calcium induce c-fos transcription via phosphorylation of transcription factor CREB. Neuron. 1990 Apr;4(4):571–582. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90115-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soula C., Sagot Y., Cochard P., Duprat A. M. Astroglial differentiation from neuroepithelial precursor cells of amphibian embryos: an in vivo and in vitro analysis. Int J Dev Biol. 1990 Sep;34(3):351–364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strong J. A., Fox A. P., Tsien R. W., Kaczmarek L. K. Stimulation of protein kinase C recruits covert calcium channels in Aplysia bag cell neurons. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):714–717. doi: 10.1038/325714a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J., Tsien R. W. Enhancement of N- and L-type calcium channel currents by protein kinase C in frog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1993 Feb;10(2):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90305-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]