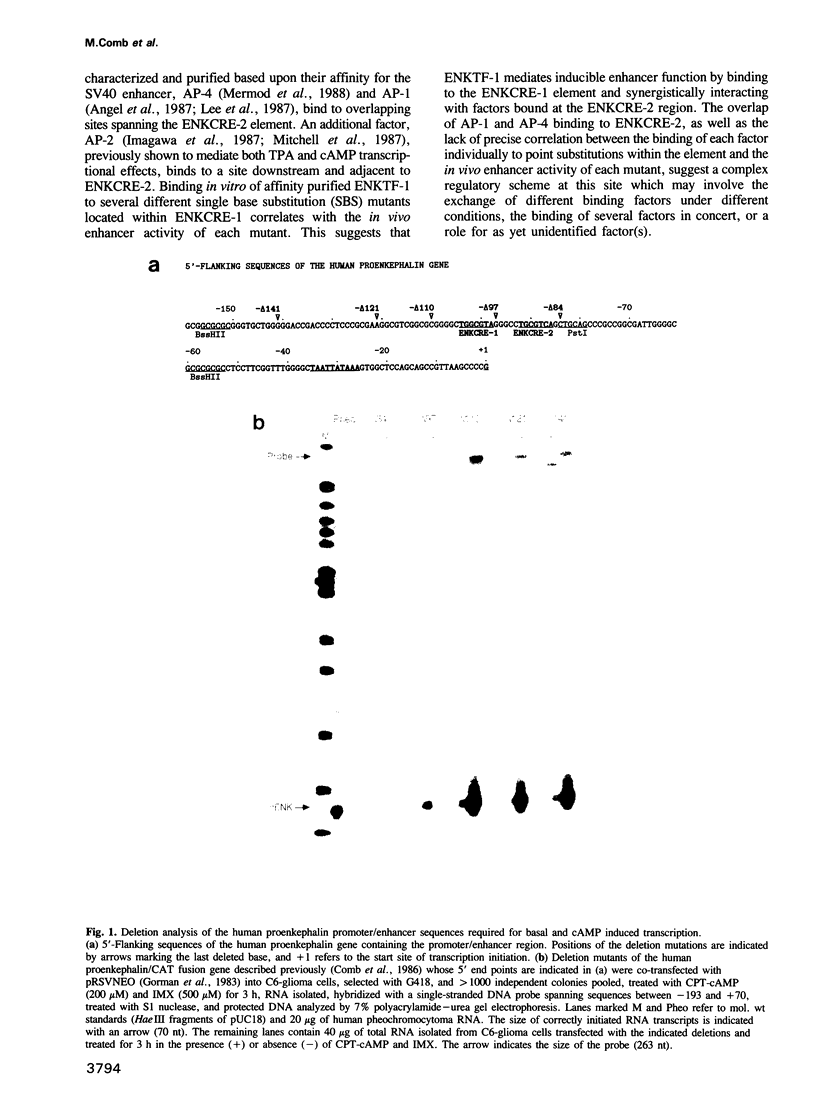
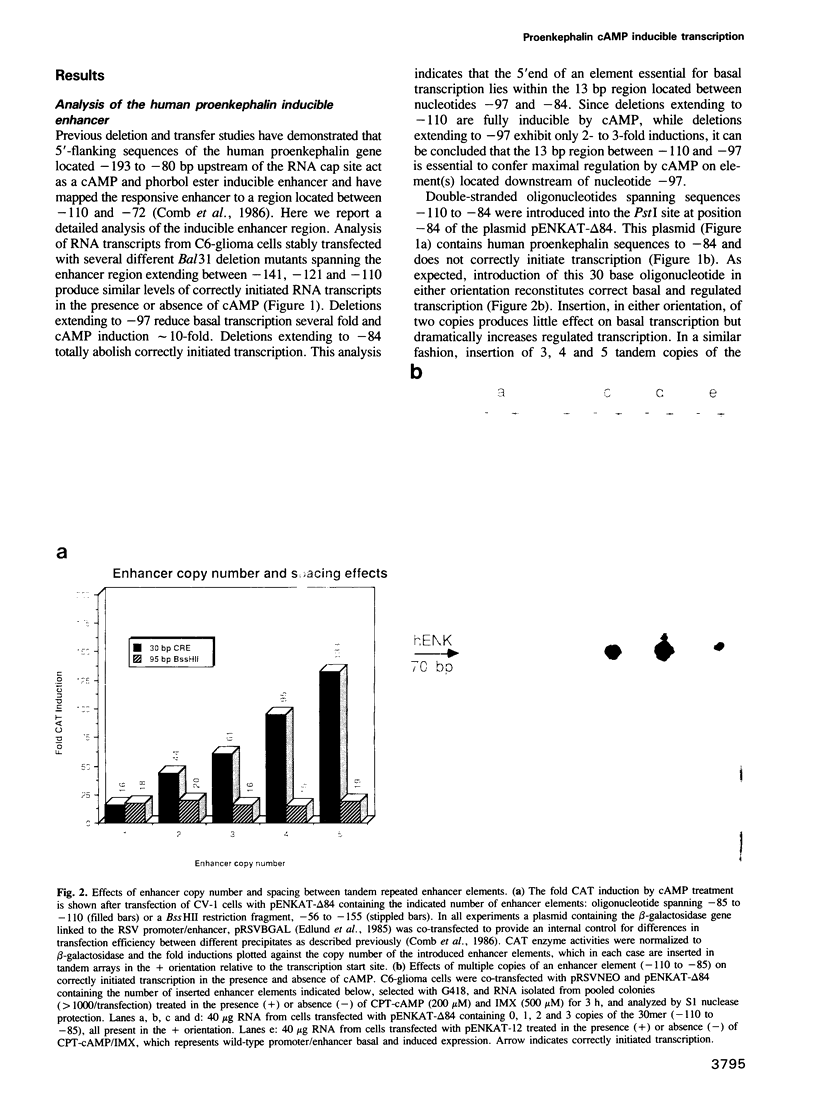
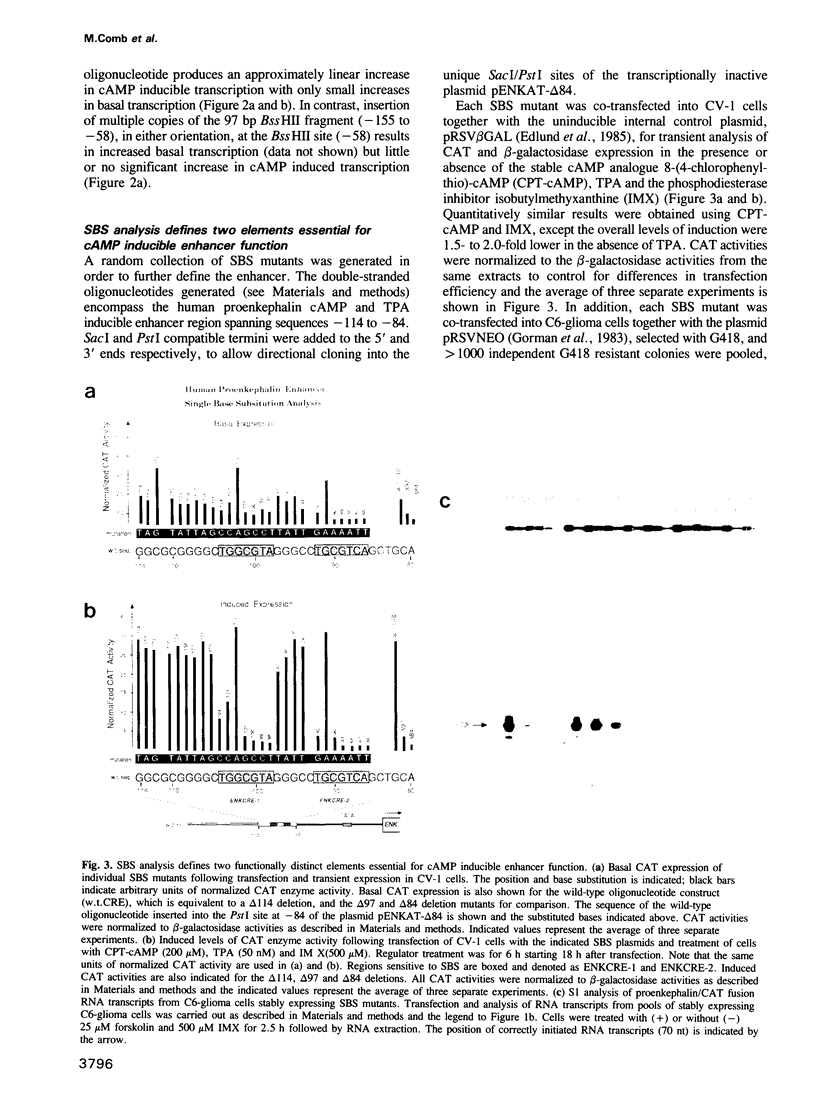
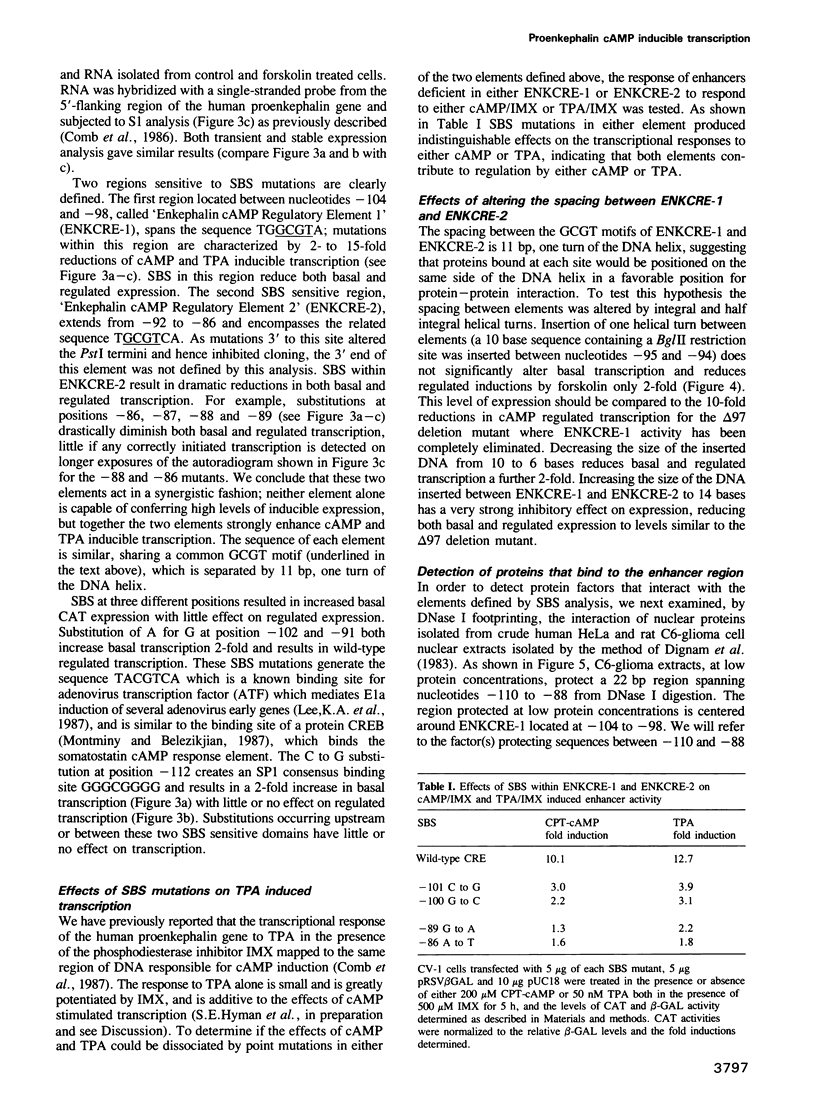
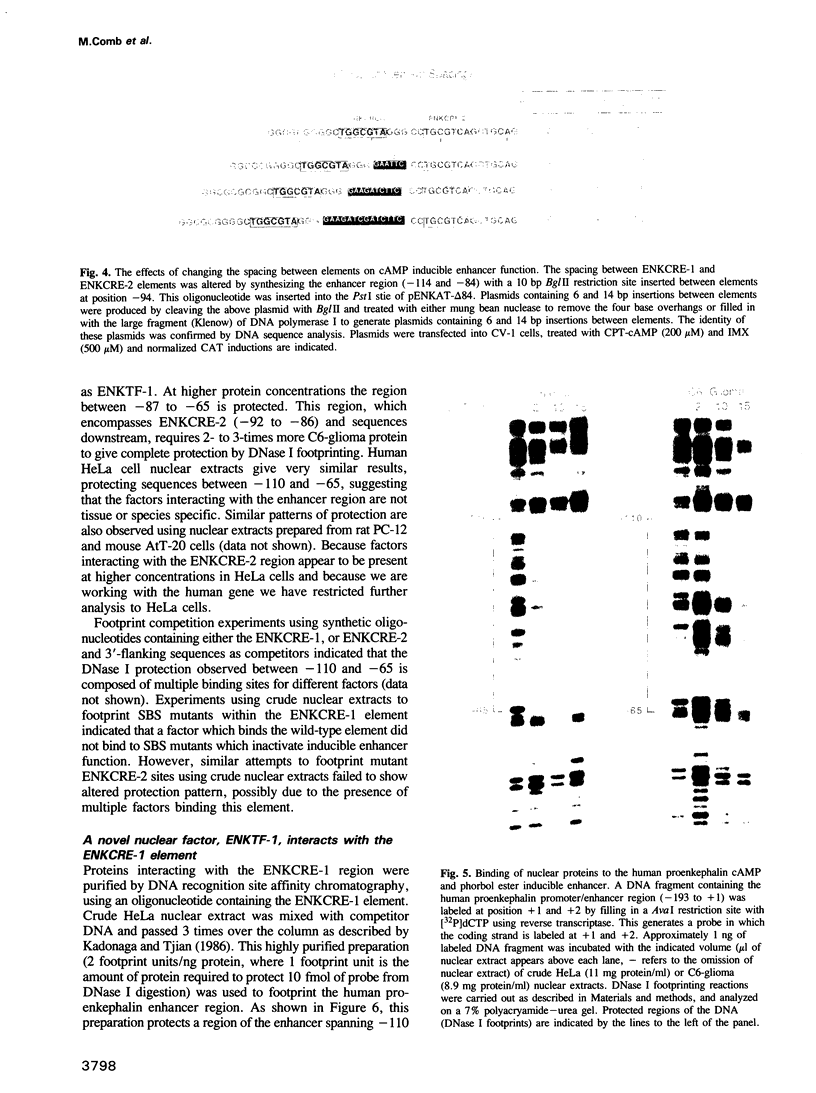
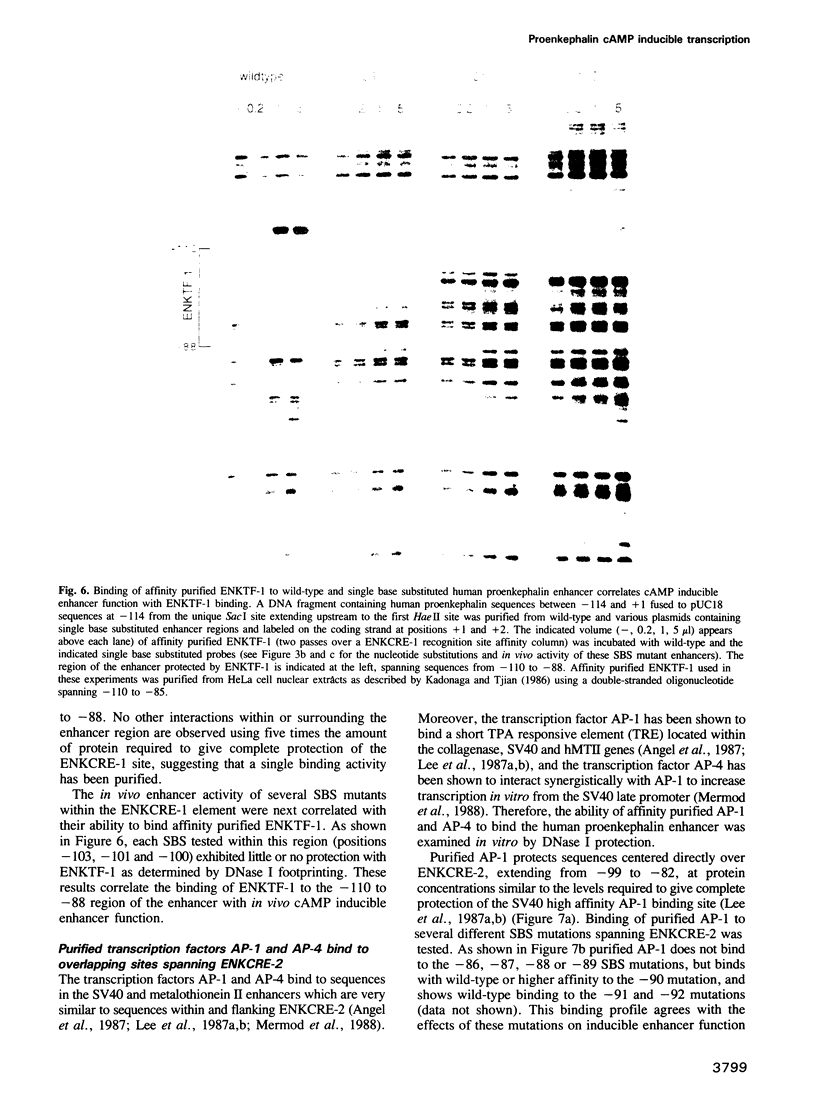
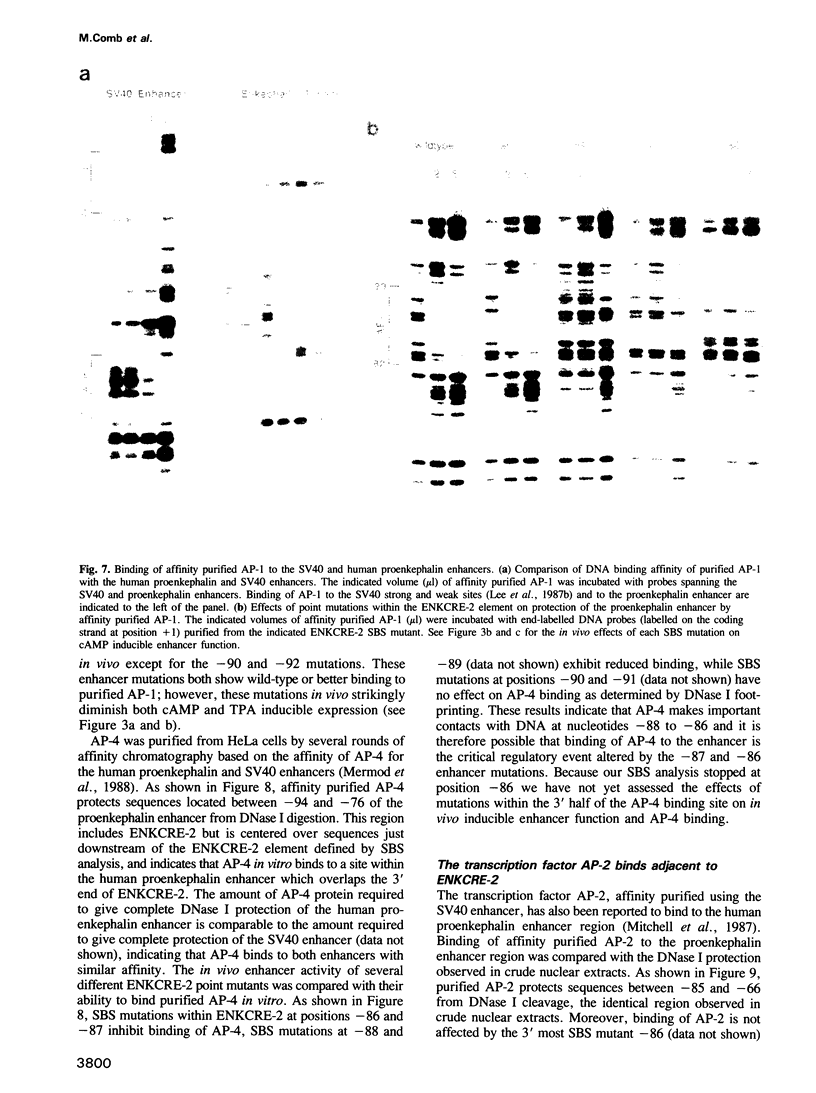
Abstract
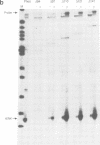
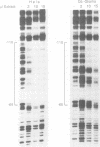
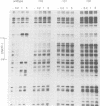
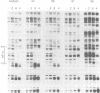
Synthesis of the endogenous opioid precursor, proenkephalin, is regulated by neurotransmitters and membrane depolarization. These events act through second messenger dependent signal transduction pathways via a short inducible DNA enhancer to regulate transcription of the proenkephalin gene. Two DNA elements located within this enhancer are essential for the transcriptional response to cAMP and phorbol ester. Inactivation of either element by mutation or by alteration of their stereospecific alignment eliminates inducible enhancer activity. The promoter distal element, ENKCRE-1, in the absence of a functional adjacent ENKCRE-2 element, has no inherent capacity to activate transcription. However, in the presence of a functional ENKCRE-2 element, this element synergistically augments cAMP and phorbol ester inducible transcription. The promoter proximal element, ENKCRE-2, is essential for both basal and regulated enhancer function. Four different protein factors found in HeLa cell nuclear extracts bind in vitro to the enhancer region. ENKTF-1, a novel enhancer binding protein, binds to the DNA region encompassing ENKCRE-1. The transcription factors AP-1 and AP-4 bind to overlapping sites spanning ENKCRE-2, and a fourth transcription factor, AP-2, binds to a site immediately downstream of ENKCRE-2. The binding of ENKTF-1 to mutant ENKCRE-1 sequences in vitro correlates with the in vivo inducibility of the mutant elements suggesting that ENKTF-1 acts in combination with factors that recognize the ENKCRE-2 domain to regulate cAMP inducible transcription. Together, the two DNA elements, ENKCRE-1 and ENKCRE-2 and the protein factors with which they interact, play a critical role in the transduction and reception of signals transmitted from cell surface receptors to the proenkephalin nuclear transcription complex.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becker P. B., Ruppert S., Schütz G. Genomic footprinting reveals cell type-specific DNA binding of ubiquitous factors. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90639-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Black I. B., Adler J. E., Dreyfus C. F., Friedman W. F., LaGamma E. F., Roach A. H. Biochemistry of information storage in the nervous system. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1263–1268. doi: 10.1126/science.2884727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Imagawa M., Imbra R. J., Bockoven J. R., Karin M. Multiple cis- and trans-acting elements mediate the transcriptional response to phorbol esters. Nature. 1987 Oct 15;329(6140):648–651. doi: 10.1038/329648a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Seeburg P. H., Adelman J., Eiden L., Herbert E. Primary structure of the human Met- and Leu-enkephalin precursor and its mRNA. Nature. 1982 Feb 25;295(5851):663–666. doi: 10.1038/295663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn A., Bollekens J., Staub A., Benoist C., Mathis D. A multiplicity of CCAAT box-binding proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):863–872. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90513-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edlund T., Walker M. D., Barr P. J., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression of the rat insulin gene: evidence for role of two distinct 5' flanking elements. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):912–916. doi: 10.1126/science.3904002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden L. E., Giraud P., Affolter H. U., Herbert E., Hotchkiss A. J. Alternative modes of enkephalin biosynthesis regulation by reserpine and cyclic AMP in cultured chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3949–3953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goelet P., Castellucci V. F., Schacher S., Kandel E. R. The long and the short of long-term memory--a molecular framework. 1986 Jul 31-Aug 6Nature. 322(6078):419–422. doi: 10.1038/322419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C., Padmanabhan R., Howard B. H. High efficiency DNA-mediated transformation of primate cells. Science. 1983 Aug 5;221(4610):551–553. doi: 10.1126/science.6306768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Seeburg P., Hoffman B. J., Gage L. P., Udenfriend S. Molecular cloning establishes proenkephalin as precursor of enkephalin-containing peptides. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):206–208. doi: 10.1038/295206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T. A thousand and one protein kinases. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90509-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Nordeen S. K., Vogt K., Edgell M. H. A complete library of point substitution mutations in the glucocorticoid response element of mouse mammary tumor virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):710–714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman S. E., Comb M., Lin Y. S., Pearlberg J., Green M. R., Goodman H. M. A common trans-acting factor is involved in transcriptional regulation of neurotransmitter genes by cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4225–4233. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa M., Chiu R., Karin M. Transcription factor AP-2 mediates induction by two different signal-transduction pathways: protein kinase C and cAMP. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90152-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbra R. J., Karin M. Phorbol ester induces the transcriptional stimulatory activity of the SV40 enhancer. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):555–558. doi: 10.1038/323555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jantzen H. M., Strähle U., Gloss B., Stewart F., Schmid W., Boshart M., Miksicek R., Schütz G. Cooperativity of glucocorticoid response elements located far upstream of the tyrosine aminotransferase gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90752-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanamatsu T., Unsworth C. D., Diliberto E. J., Jr, Viveros O. H., Hong J. S. Reflex splanchnic nerve stimulation increases levels of proenkephalin A mRNA and proenkephalin A-related peptides in the rat adrenal medulla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9245–9249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kley N., Loeffler J. P., Pittius C. W., Höllt V. Involvement of ion channels in the induction of proenkephalin A gene expression by nicotine and cAMP in bovine chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):4083–4089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Green M. R. A cellular transcription factor E4F1 interacts with an E1a-inducible enhancer and mediates constitutive enhancer function in vitro. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1345–1353. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02374.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee K. A., Hai T. Y., SivaRaman L., Thimmappaya B., Hurst H. C., Jones N. C., Green M. R. A cellular protein, activating transcription factor, activates transcription of multiple E1A-inducible adenovirus early promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8355–8359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Haslinger A., Karin M., Tjian R. Activation of transcription by two factors that bind promoter and enhancer sequences of the human metallothionein gene and SV40. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):368–372. doi: 10.1038/325368a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W., Mitchell P., Tjian R. Purified transcription factor AP-1 interacts with TPA-inducible enhancer elements. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):741–752. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90612-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Interaction of a common cellular transcription factor, ATF, with regulatory elements in both E1a- and cyclic AMP-inducible promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Williams T. J., Tjian R. Enhancer binding factors AP-4 and AP-1 act in concert to activate SV40 late transcription in vitro. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):557–561. doi: 10.1038/332557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Wang C., Tjian R. Positive and negative regulation of transcription in vitro: enhancer-binding protein AP-2 is inhibited by SV40 T antigen. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):847–861. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90512-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montarolo P. G., Goelet P., Castellucci V. F., Morgan J., Kandel E. R., Schacher S. A critical period for macromolecular synthesis in long-term heterosynaptic facilitation in Aplysia. Science. 1986 Dec 5;234(4781):1249–1254. doi: 10.1126/science.3775383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Bilezikjian L. M. Binding of a nuclear protein to the cyclic-AMP response element of the somatostatin gene. Nature. 1987 Jul 9;328(6126):175–178. doi: 10.1038/328175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montminy M. R., Sevarino K. A., Wagner J. A., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a cyclic-AMP-responsive element within the rat somatostatin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6682–6686. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6682. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nairn A. C., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P. Protein kinases in the brain. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:931–976. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noda M., Furutani Y., Takahashi H., Toyosato M., Hirose T., Inayama S., Nakanishi S., Numa S. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA for bovine adrenal preproenkephalin. Nature. 1982 Jan 21;295(5846):202–206. doi: 10.1038/295202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Muller M., Otsuka-Murakami H., Renkawitz R. Cooperativity of the glucocorticoid receptor and the CACCC-box binding factor. Nature. 1988 Mar 3;332(6159):87–90. doi: 10.1038/332087a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B., Sheen J. Y. A simple phase-extraction assay for chloramphenicol acyltransferase activity. Gene. 1988 Jul 30;67(2):271–277. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90403-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukada T., Fink J. S., Mandel G., Goodman R. H. Identification of a region in the human vasoactive intestinal polypeptide gene responsible for regulation by cyclic AMP. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8743–8747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshikawa K., Sabol S. L. Expression of the enkephalin precursor gene in C6 rat glioma cells: regulation by beta-adrenergic agonists and glucocorticoids. Brain Res. 1986 Jul;387(1):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0169-328x(86)90022-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Bonner T. I., Brann M. R. Mesencephalic dopamine neurons regulate the expression of neuropeptide mRNAs in the rat forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9827–9831. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]