Abstract
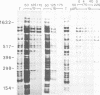
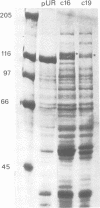
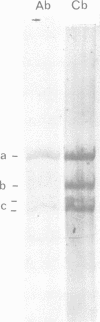
All known Balbiani ring (BR) genes in Chironomus tentans, coding for giant secretory proteins, the sp-I family, end with a short (110 codons) 3'-end exon which is highly conserved in evolution and is structurally unrelated to the sequences characterizing the core of these proteins. We find that the expressed product, the C-terminal domain, shows sequence-specific DNA binding and that it is likely to be absent in one of the sp-I components, sp-Ib, believed to be coded by the BR2.2 gene. Immunohistochemistry shows that material with reactivity towards antibody against the C-terminal domain is present in the nuclei, and specifically enriched in Balbiani ring 1 and 2. Western blotting of extracts from isolated nuclei demonstrates a component with the same antibody reactivity and of an apparent size somewhat larger than that of the domain. The possibility is discussed that the C-terminal part, which is part of the secretion when derived from some of the BR genes, might be cleaved off and function as a feedback signal to control BR gene activity when derived from the BR2.2 gene.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beermann W. Directed changes in the pattern of Balbiani ring puffing in Chironomus: effects of a sugar treatment. Chromosoma. 1973;41(3):297–326. doi: 10.1007/BF00344024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bäumlein H., Pustell J., Wobus U., Case S. T., Kafatos F. C. The 3' ends of two genes in the Balbiani ring c locus of Chironomus thummi. J Mol Evol. 1986;24(1-2):72–82. doi: 10.1007/BF02099953. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case S. T. Correlated changes in steady-state levels of Balbiani ring mRNAs and secretory polypeptides in salivary glands of Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma. 1986;94(6):483–491. doi: 10.1007/BF00292758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The Drosophila developmental gene, engrailed, encodes a sequence-specific DNA binding activity. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):630–635. doi: 10.1038/318630a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edström J. E., Rydlander L., Francke C. Concomitant induction of a Balbiani ring and a giant secretory protein in Chironomus salivary glands. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):115–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00292426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francke C., Edström J. E., McDowall A. W., Miller O. L. Electron microscopic visualization of a discrete class of giant translation units in salivary gland cells of Chironomus tentans. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):59–62. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01124.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galler R., Rydlander L., Riedel N., Kluding H., Edström J. E. Balbiani ring induction in phosphate metabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1448–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galler R., Saiga H., Widmer R. M., Lezzi M., Edström J. E. Two genes in Balbiani ring 2 with metabolically different 75S transcripts. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2977–2982. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04032.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring W. J. Homeo boxes in the study of development. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1245–1252. doi: 10.1126/science.2884726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grond C., Saiga H., Edström J. E. The sp-I genes in the Balbiani rings of Chironomus salivary glands. Results Probl Cell Differ. 1987;14:69–80. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-47783-9_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbach U. Chromosome puffs and gene expression in polytene cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1974;38:619–627. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.038.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hélène C., Lancelot G. Interactions between functional groups in protein-nucleic acid associations. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;39(1):1–68. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(83)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög C., Daneholt B., Wieslander L. Terminal repeats in long repeat arrays are likely to reflect the early evolution of Balbiani ring genes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Apr 20;200(4):655–664. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90478-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hög C., Engberg C., Wieslander L. A BR 1 gene in Chironomus tentans has a composite structure: a large repetitive core block is separated from a short unrelated 3'-terminal domain by a small intron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):703–719. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jäckle H., Almeida J. C., Galler R., Kluding H., Lehrach H., Edström J. E. Constant and variable parts in the Balbiani ring 2 repeat unit and the translation termination region. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):883–888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01264.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao W. Y., Case S. T. A novel giant secretion polypeptide in Chironomus salivary glands: implications for another Balbiani ring gene. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1044–1051. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pustell J., Kafatos F. C., Wobus U., Bäumlein H. Balbiani ring DNA: sequence comparisons and evolutionary history of a family of hierarchically repetitive protein-coding genes. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(3-4):281–295. doi: 10.1007/BF02104734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringborg U., Rydlander L. Nucleolar-derived ribonucleic acid in chromosomes, nuclear sap, and cytoplasm of Chironomus tentans salivary gland cells. J Cell Biol. 1971 Nov;51(21):355–368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.51.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydlander L., Edström J. E. Large sized nascent protein as dominating component during protein synthesis in Chironomus salivary glands. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):85–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00292424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydlander L., Pigon A., Edström J. E. Sequences translated by Balbiani ring 75S RNA in vitro are present in giant secretory protein from Chironomus tentans. Chromosoma. 1980;81(1):101–113. doi: 10.1007/BF00292425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiga H., Botella L., Edström J. E. Subrepeats within the BR1 beta repeat unit in Chironomus pallidivittatus can be classified into different types depending on codon usage. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(4):298–302. doi: 10.1007/BF02101191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sass H. Features of in vitro puffing and RNA synthesis in polytene chromosomes of Chironomus. Chromosoma. 1980;78(1):33–78. doi: 10.1007/BF00291908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley K. K., Luzio J. P. Construction of a new family of high efficiency bacterial expression vectors: identification of cDNA clones coding for human liver proteins. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1429–1434. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieslander L., Hög C., Hög J. O., Jörnvall H., Lendahl U., Daneholt B. Conserved and nonconserved structures in the secretory proteins encoded in the Balbiani ring genes of Chironomus tentans. J Mol Evol. 1984;20(3-4):304–312. doi: 10.1007/BF02104736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]