Abstract
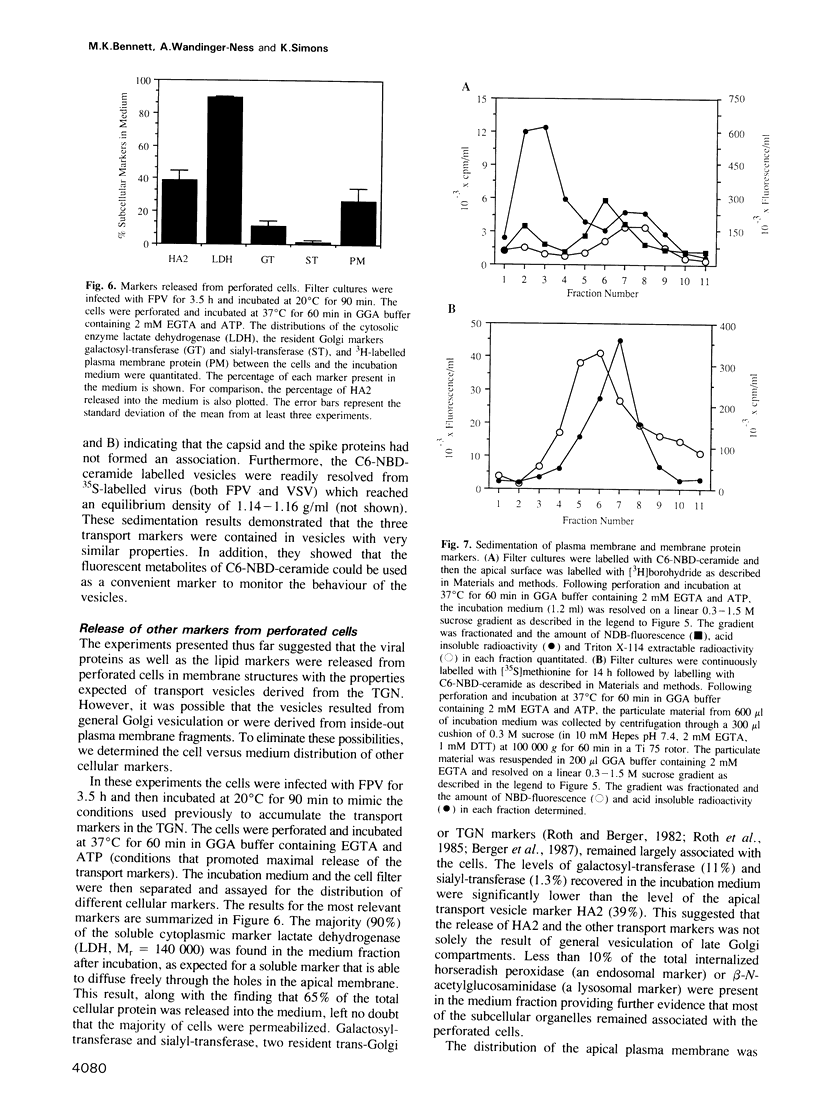
Mechanically perforated MDCK cells were used to study membrane transport between the trans-Golgi network and the apical and basolateral plasma membrane domains in vitro. Three membrane transport markers--an apical protein (fowl plague virus haemagglutinin), a basolateral protein (vesicular stomatitis virus G protein), and a lipid marker destined for both domains (C6-NBD-sphingomyelin)--were each accumulated in the trans-Golgi by a 20 degrees C block of transport and their behaviour monitored following cell perforation and incubation at 37 degrees C. In the presence of ATP and in the absence of calcium ions a considerable fraction of the transport markers were released from the perforated cells in sealed membrane vesicles. Control experiments showed that the vesicles were not generated by non-specific vesiculation of the Golgi complex or the plasma membrane. The vesicles had well defined sedimentation properties and the orientation expected of transport vesicles derived from the trans-Golgi network.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Dunphy W. G., Braell W. A., Rothman J. E. Reconstitution of the transport of protein between successive compartments of the Golgi measured by the coupled incorporation of N-acetylglucosamine. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):405–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Elliott M. M., Keller D. S. ATP-coupled transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein between the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14681–14689. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Glick B. S., Rothman J. E. Sequential intermediates in the pathway of intercompartmental transport in a cell-free system. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):525–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90459-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Keller D. S. ATP-coupled transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein. Functional boundaries of secretory compartments. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 5;261(31):14690–14696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E., Wagner K. R., Keller D. S. Reconstitution of transport of vesicular stomatitis virus G protein from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex using a cell-free system. J Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;104(3):749–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.3.749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckers C. J., Keller D. S., Balch W. E. Semi-intact cells permeable to macromolecules: use in reconstitution of protein transport from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. Cell. 1987 Aug 14;50(4):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90025-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. G., Thurnher M., Müller U. Galactosyltransferase and sialyltransferase are located in different subcellular compartments in HeLa cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Nov;173(1):267–273. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90352-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier C. Phase separation of integral membrane proteins in Triton X-114 solution. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1604–1607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braell W. A. Fusion between endocytic vesicles in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1137–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croze E. M., Morré D. J., Morré D. M., Kartenbeck J., Franke W. W. Distribution of clathrin and spiny-coated vesicles on membranes within mature Golgi apparatus elements of mouse liver. Eur J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;28(1):130–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey J., Hurtley S. M., Warren G. Reconstitution of an endocytic fusion event in a cell-free system. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):643–652. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90236-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Docherty K., Steiner D. F. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Annu Rev Physiol. 1982;44:625–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.44.030182.003205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Bosch F. X., Linder D., Rott R., Klenk H. D. Proteolytic activation of the influenza virus hemagglutinin: The structure of the cleavage site and the enzymes involved in cleavage. Virology. 1981 Dec;115(2):361–374. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90117-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garten W., Linder D., Rott R., Klenk H. D. The cleavage site of the hemagglutinin of fowl plague virus. Virology. 1982 Oct 15;122(1):186–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90387-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Pfeiffer S., Simons K., Matlin K. Exit of newly synthesized membrane proteins from the trans cisterna of the Golgi complex to the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):949–964. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffiths G., Simons K. The trans Golgi network: sorting at the exit site of the Golgi complex. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):438–443. doi: 10.1126/science.2945253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruenberg J. E., Howell K. E. Reconstitution of vesicle fusions occurring in endocytosis with a cell-free system. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 1;5(12):3091–3101. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04615.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harms E., Kern H., Schneider J. A. Human lysosomes can be purified from diploid skin fibroblasts by free-flow electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6139–6143. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holcomb C. L., Etcheverry T., Schekman R. Isolation of secretory vesicles from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):328–334. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90581-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. N., Lodish H. F. Transmembrane biogenesis of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1979 Feb;80(2):416–426. doi: 10.1083/jcb.80.2.416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. N., Rothman J. E., Knipe D. M., Lodish H. F. Membrane assembly: synthesis and intracellular processing of the vesicular stomatitis viral glycoprotein. J Supramol Struct. 1977;7(3-4):353–370. doi: 10.1002/jss.400070308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreis T. E. Microinjected antibodies against the cytoplasmic domain of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein block its transport to the cell surface. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):931–941. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04306.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsky N. G., Pagano R. E. Sphingolipid metabolism in cultured fibroblasts: microscopic and biochemical studies employing a fluorescent ceramide analogue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2608–2612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lodish H. F., Kong N., Hirani S., Rasmussen J. A vesicular intermediate in the transport of hepatoma secretory proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi complex. J Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;104(2):221–230. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louvard D. Apical membrane aminopeptidase appears at site of cell-cell contact in cultured kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4132–4136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Infectious entry pathway of influenza virus in a canine kidney cell line. J Cell Biol. 1981 Dec;91(3 Pt 1):601–613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.3.601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Reggio H., Helenius A., Simons K. Pathway of vesicular stomatitis virus entry leading to infection. J Mol Biol. 1982 Apr 15;156(3):609–631. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Reduced temperature prevents transfer of a membrane glycoprotein to the cell surface but does not prevent terminal glycosylation. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):233–243. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90154-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlin K. S., Simons K. Sorting of an apical plasma membrane glycoprotein occurs before it reaches the cell surface in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2131–2139. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T., Ward L. J., Semerjian A. Intracellular processing of the Newcastle disease virus fusion glycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):851–857. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.851-857.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Ravazzola M., Storch M. J., Anderson R. G., Vassalli J. D., Perrelet A. Proteolytic maturation of insulin is a post-Golgi event which occurs in acidifying clathrin-coated secretory vesicles. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):865–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90624-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pesonen M., Ansorge W., Simons K. Transcytosis of the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus after implantation into the apical plasma membrane of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. I. Involvement of endosomes and lysosomes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;99(3):796–782. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.3.796. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeiffer S., Fuller S. D., Simons K. Intracellular sorting and basolateral appearance of the G protein of vesicular stomatitis virus in Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):470–476. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. C., Simmons N. L. Demonstration of protein asymmetries in the plasma membrane of cultured renal (MDCK) epithelial cells by lactoperoxidase-mediated iodination. FEBS Lett. 1979 Sep 15;105(2):201–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80611-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rindler M. J., Ivanov I. E., Plesken H., Rodriguez-Boulan E., Sabatini D. D. Viral glycoproteins destined for apical or basolateral plasma membrane domains traverse the same Golgi apparatus during their intracellular transport in doubly infected Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;98(4):1304–1319. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.4.1304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodriguez Boulan E., Pendergast M. Polarized distribution of viral envelope proteins in the plasma membrane of infected epithelial cells. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90233-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Gallione C. J. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus G and M proteins determined from cDNA clones containing the complete coding regions. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):519–528. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.519-528.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Berger E. G. Immunocytochemical localization of galactosyltransferase in HeLa cells: codistribution with thiamine pyrophosphatase in trans-Golgi cisternae. J Cell Biol. 1982 Apr;93(1):223–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.1.223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Taatjes D. J., Lucocq J. M., Weinstein J., Paulson J. C. Demonstration of an extensive trans-tubular network continuous with the Golgi apparatus stack that may function in glycosylation. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):287–295. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90034-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth M. G., Compans R. W., Giusti L., Davis A. R., Nayak D. P., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. Influenza virus hemagglutinin expression is polarized in cells infected with recombinant SV40 viruses carrying cloned hemagglutinin DNA. Cell. 1983 Jun;33(2):435–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Transport of the vesicular stomatitis glycoprotein to trans Golgi membranes in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12502–12510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sambrook J., Rodgers L., White J., Gething M. J. Lines of BPV-transformed murine cells that constitutively express influenza virus hemagglutinin. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):91–103. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02322.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons K., Virta H. Perforated MDCK cells support intracellular transport. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2241–2247. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tooze J., Hollinshead M., Frank R., Burke B. An antibody specific for an endoproteolytic cleavage site provides evidence that pro-opiomelanocortin is packaged into secretory granules in AtT20 cells before its cleavage. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):155–162. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walworth N. C., Novick P. J. Purification and characterization of constitutive secretory vesicles from yeast. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;105(1):163–174. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.1.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward C. W. Structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;94-95:1–74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68120-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren T. G., Shields D. Expression of preprosomatostatin in heterologous cells: biosynthesis, posttranslational processing, and secretion of mature somatostatin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):547–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90461-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wattenberg B. W., Balch W. E., Rothman J. E. A novel prefusion complex formed during protein transport between Golgi cisternae in a cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 15;261(5):2202–2207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodman P. G., Edwardson J. M. A cell-free assay for the insertion of a viral glycoprotein into the plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1829–1835. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Curtis I., Howell K. E., Simons K. Isolation of a fraction enriched in the trans-Golgi network from baby hamster kidney cells. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Apr;175(2):248–265. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Simons K. Viruses budding from either the apical or the basolateral plasma membrane domain of MDCK cells have unique phospholipid compositions. EMBO J. 1982;1(7):847–852. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01258.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Meer G., Stelzer E. H., Wijnaendts-van-Resandt R. W., Simons K. Sorting of sphingolipids in epithelial (Madin-Darby canine kidney) cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;105(4):1623–1635. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.4.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







