Abstract
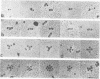
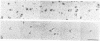
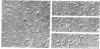
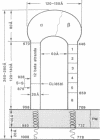
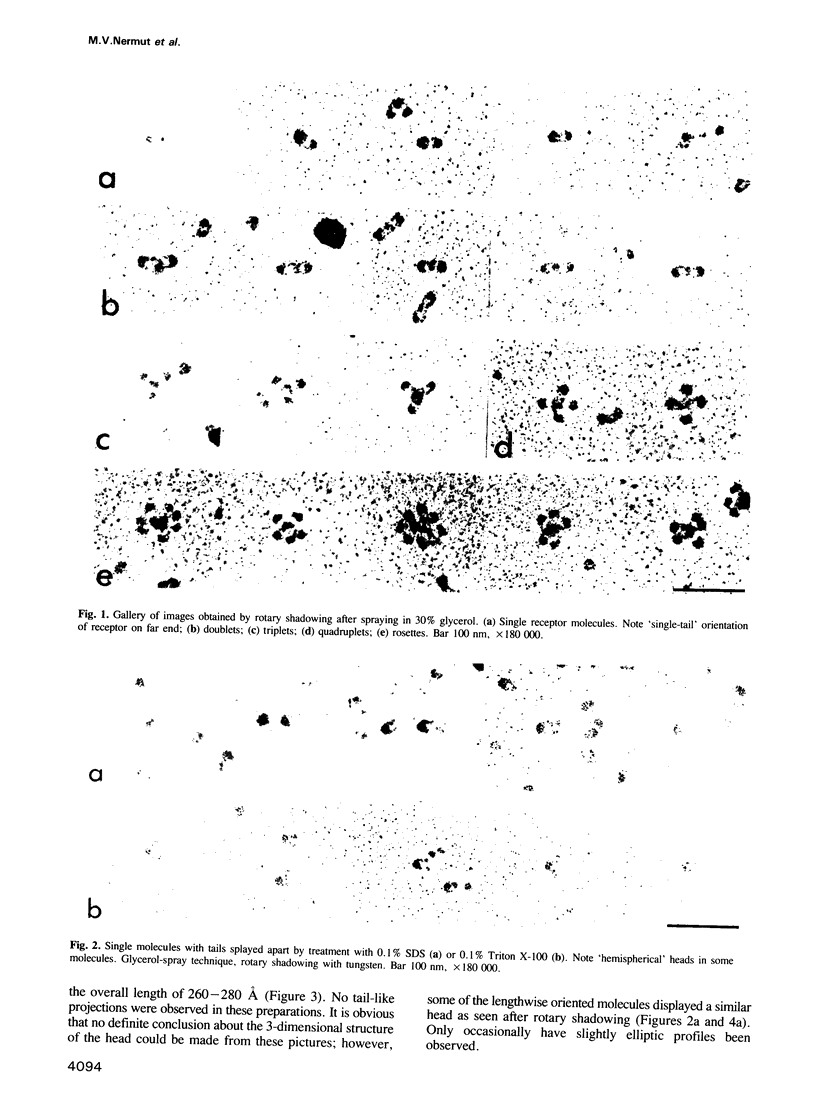
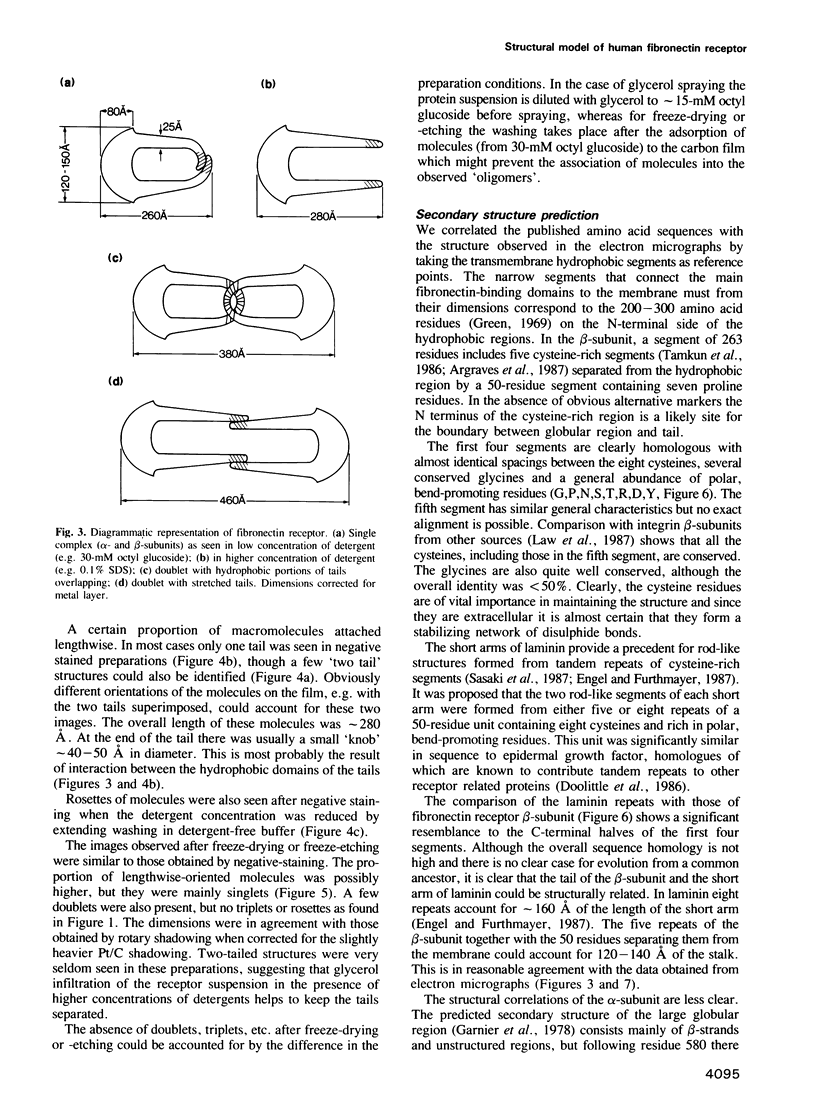
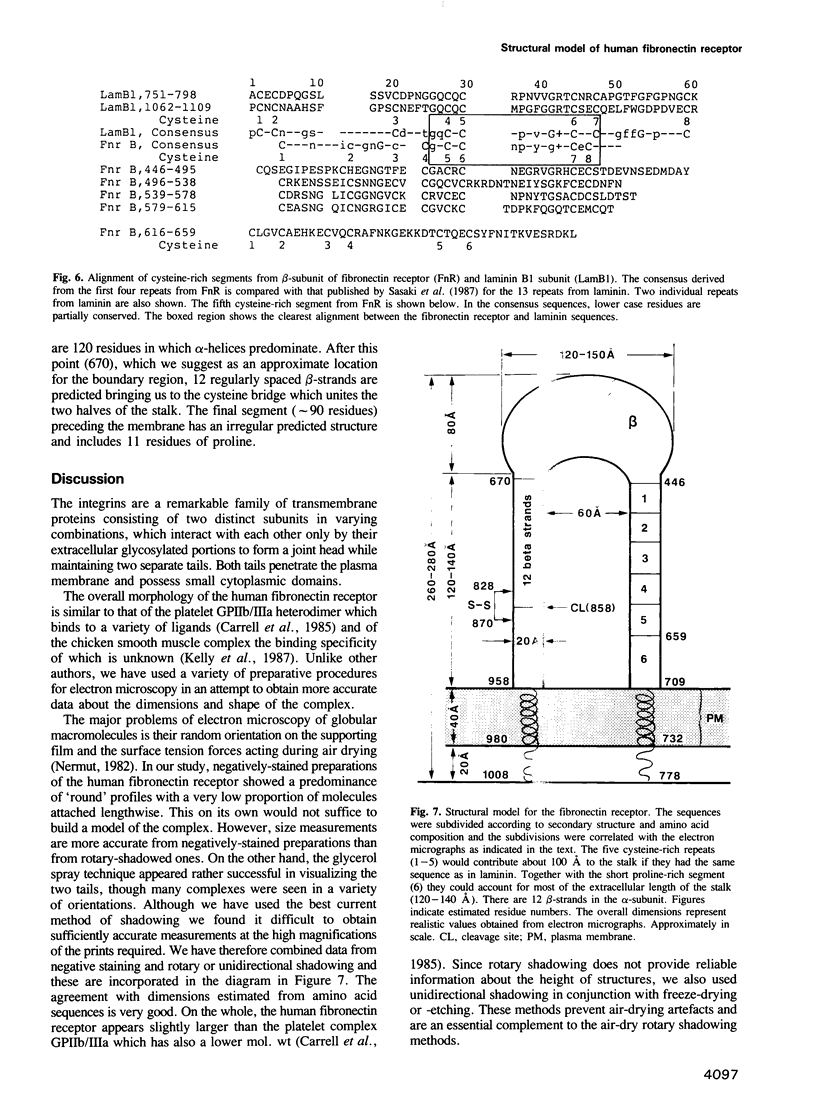
Highly-purified human fibronectin receptor (a heterodimer of two distinct subunits, alpha and beta) was studied using electron microscopy and a variety of preparative procedures. It was found that the receptor consists of a globular head approximately 80 by 120 A and two tails about 20 A thick and 180-200 A long. The whole complex is approximately 280 A long. At low concentrations of detergent the receptor forms doublets, triplets or rosettes associated with the tails which possess the transmembrane portion of the molecule. Computer-assisted structure prediction using the published amino acid sequence of both subunits showed differences in the secondary structure of the tails, the alpha-tail being rich in beta-strands, the beta-tail having five cysteine-rich repeats analogous to the EGF-like repeats of laminin. Estimates of the length of the tails from the predicted structure conformed well with the dimensions obtained from electron micrographs.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argraves W. S., Suzuki S., Arai H., Thompson K., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Amino acid sequence of the human fibronectin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buck C. A., Horwitz A. F. Cell surface receptors for extracellular matrix molecules. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:179–205. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.001143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrell N. A., Fitzgerald L. A., Steiner B., Erickson H. P., Phillips D. R. Structure of human platelet membrane glycoproteins IIb and IIIa as determined by electron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1743–1749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S., McClure M. A. Relationships of human protein sequences to those of other organisms. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):447–455. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel J., Furthmayr H. Electron microscopy and other physical methods for the characterization of extracellular matrix components: laminin, fibronectin, collagen IV, collagen VI, and proteoglycans. Methods Enzymol. 1987;145:3–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)45003-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Charo I. F., Phillips D. R. Human and bovine endothelial cells synthesize membrane proteins similar to human platelet glycoproteins IIb and IIIa. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):10893–10896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Poncz M., Steiner B., Rall S. C., Jr, Bennett J. S., Phillips D. R. Comparison of cDNA-derived protein sequences of the human fibronectin and vitronectin receptor alpha-subunits and platelet glycoprotein IIb. Biochemistry. 1987 Dec 15;26(25):8158–8165. doi: 10.1021/bi00399a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald L. A., Steiner B., Rall S. C., Jr, Lo S. S., Phillips D. R. Protein sequence of endothelial glycoprotein IIIa derived from a cDNA clone. Identity with platelet glycoprotein IIIa and similarity to "integrin". J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 25;262(9):3936–3939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N. M. Electron microscopy of the immunoglobulins. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:1–30. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60476-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: a family of cell surface receptors. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90233-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juliano R. L. Membrane receptors for extracellular matrix macromolecules: relationship to cell adhesion and tumor metastasis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Nov 25;907(3):261–278. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(87)90009-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T., Molony L., Burridge K. Purification of two smooth muscle glycoproteins related to integrin. Distribution in cultured chicken embryo fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):17189–17199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. K., Gagnon J., Hildreth J. E., Wells C. E., Willis A. C., Wong A. J. The primary structure of the beta-subunit of the cell surface adhesion glycoproteins LFA-1, CR3 and p150,95 and its relationship to the fibronectin receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):915–919. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leeksma O. C., Zandbergen-Spaargaren J., Giltay J. C., van Mourik J. A. Cultured human endothelial cells synthesize a plasma membrane protein complex immunologically related to the platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa complex. Blood. 1986 Apr;67(4):1176–1180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nermut M. V., Williams L. D. Freeze-fracturing of monolayers (capillary layers) of cell, membranes and viruses: some technical considerations. J Microsc. 1977 Jul;110(2):121–132. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1977.tb00023.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niggli V., Burger M. M. Interaction of the cytoskeleton with the plasma membrane. J Membr Biol. 1987;100(2):97–121. doi: 10.1007/BF02209144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parise L. V., Phillips D. R. Platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb-IIIa complex incorporated into phospholipid vesicles. Preparation and morphology. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1750–1756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Eisman R., Heidenreich R., Silver S. M., Vilaire G., Surrey S., Schwartz E., Bennett J. S. Structure of the platelet membrane glycoprotein IIb. Homology to the alpha subunits of the vitronectin and fibronectin membrane receptors. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8476–8482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pytela R., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Identification and isolation of a 140 kd cell surface glycoprotein with properties expected of a fibronectin receptor. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90322-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E. Fibronectin and its receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:375–413. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki M., Kato S., Kohno K., Martin G. R., Yamada Y. Sequence of the cDNA encoding the laminin B1 chain reveals a multidomain protein containing cysteine-rich repeats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):935–939. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamkun J. W., DeSimone D. W., Fonda D., Patel R. S., Buck C., Horwitz A. F., Hynes R. O. Structure of integrin, a glycoprotein involved in the transmembrane linkage between fibronectin and actin. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):271–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90744-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler J. M., Branton D. Rotary shadowing of extended molecules dried from glycerol. J Ultrastruct Res. 1980 May;71(2):95–102. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(80)90098-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zardi L., Carnemolla B., Balza E., Borsi L., Castellani P., Rocco M., Siri A. Elution of fibronectin proteolytic fragments from a hydroxyapatite chromatography column. A simple procedure for the purification of fibronectin domains. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;146(3):571–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08690.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]